Difference between revisions of "Rhynchospora plumosa"
(→Taxonomic notes) |
(→Taxonomic notes) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
Common name: Plumed beaksedge | Common name: Plumed beaksedge | ||
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| − | Synonym: '' | + | Synonym: ''Rynchospora pineticola'' C.B. Clarke<ref>Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref>; ''Rynchospora semiplumosa'' A. Gray |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
Revision as of 13:32, 8 June 2021
| Rhynchospora plumosa | |
|---|---|
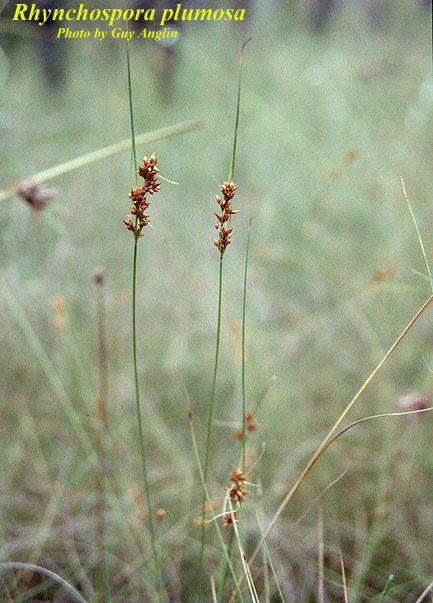

| |
| Photo by Guy Anglin, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Rhynchospora |
| Species: | R. plumosa |
| Binomial name | |
| Rhynchospora plumosa Elliott | |
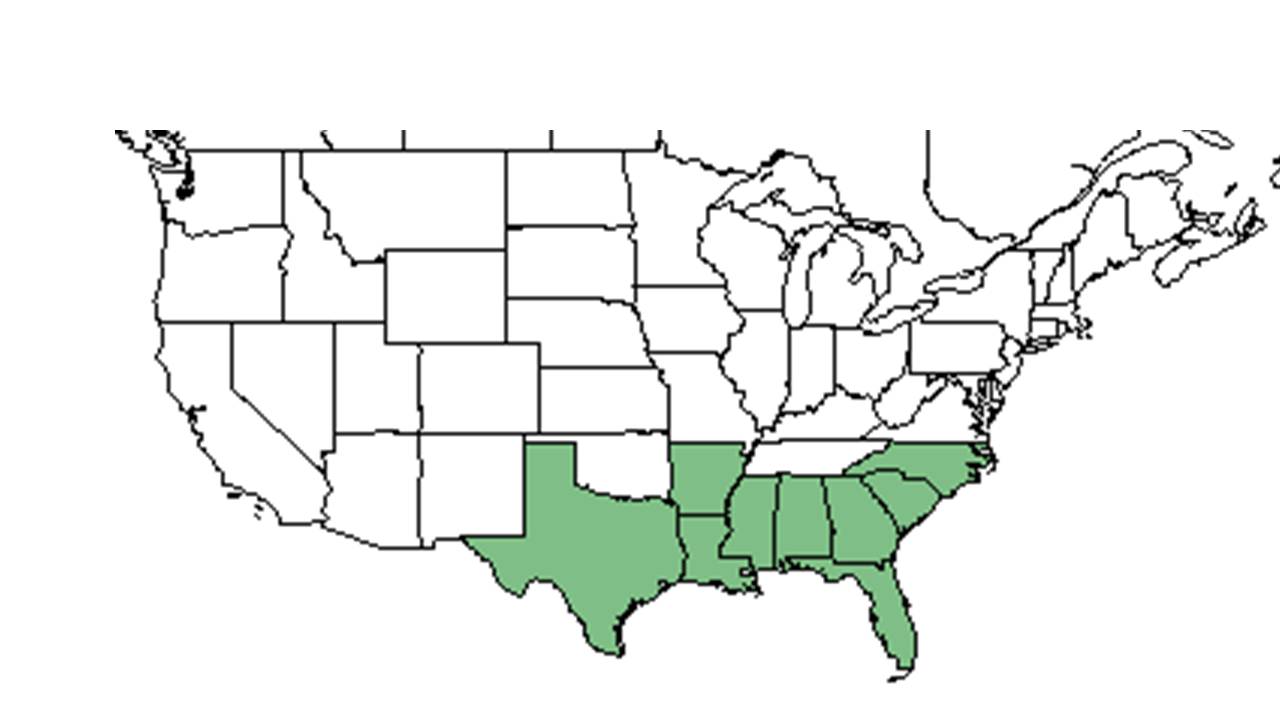
| |
| Natural range of Rhynchospora plumosa from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Plumed beaksedge
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Rynchospora pineticola C.B. Clarke[1]; Rynchospora semiplumosa A. Gray
Description
A description of Rhynchospora plumosa is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, R. plumosa can occur in savannas, open scrub oak savannas, wiregrass savannas, pine-palmetto scrub oaks, seasonally wet depressions in open pinewoods, pine flatwoods, regularly burned pine flatwoods, slash pine-wiregrass flatwoods, exposed sandy bottoms of lakes, seepages slopes, hillside bogs, grass-sedge bogs, shrubby borders of depression marshes, sand ridges, mangrove swamps, dry pine barrens, and drying ephemeral ponds.[2] It can also be found in power line corridors, sandy roadsides, wet borrow pits, shrub bog clearings, pine flatwood clearings, moist roadside depressions, cut-over pinewoods, cleared palmetto scrubs, bull-dozed scrublands, boat ramps, pine plantations, and clobbered pine-wiregrass flatwoods. Soils include dry sand, moist sandy peat, loamy sand, sandy loam, and white sand.[2]
R. plumosa was found in non-disturbed longleaf pine sites in the North Carolina; in contrast, the species was not found in highly disturbed sites.[3] It responds negatively to soil disturbance by heavy silvilculture in North Carolina.[4]
Associated species include Aristida stricta, Pinus palustris, Serenoa repens, Hypericum, Stillingia, Xyris, Rhexia mariana, Dichanthelium wrightianum, Scleria georgiana, Sarracenia flava, Drosera, Sarracenia, Rhynchospora elliottii, R. corniculata, R. chapmannii, R. pusilla, R. fascicularis, R. baldwinii, R. globularis, R. wrightiana, R. fernaldii, and R. ciliaris.[2]
Rhynchospora plumosa is frequent and abundant in the Lower Panhandle Savannas community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[5]
Phenology
Flowers and fruits April through December.[2]
Fire ecology
In longleaf pine forests of the southeastern United States, R. plumosa benefits from higher fire fequencies and is common in the second winter after after a fire.[6][7]
Use by animals
The Henslow’s Sparrow (Ammodramus henslowii) does not prefer to eat the seeds.[7]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, S. F. Blake, Robert Kral, Mabel Kral, A. F. Clewell, Robert Blaisdell, Ann F. Johnson, Sidney McDaniel, Kurt E. Blum, S.L. Orzell, Edwin L. Bridges, H. E. Grelen, P. L. Redfearn, Edward Wheeler, S. M. Tracy, N. C. Henderson, Cecil R. Slaughter, M. Minno, Austin R. Mast, O. Lakela, A. H. Curtiss, Chris Buddenhagen, Becky Bee, Annie Schmidt. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Bay, Bradford, Calhoun, Citrus, Collier, Dixie, Duval, Flagler, Franklin, Gulf, Hernando, Lee, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Martin, Nassau, Okaloosa, Orange, Osceola, Pasco, Pinellas, Polk, Santa Rosa, St. Johns, Sumter, Taylor, Volusia, Wakulla, Walton, Washington. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Cohen, S., R. Braham and F. Sanchez. 2004. Seed bank viability in disturbed longleaf pine sites. Restoration Ecology 12:503-515.
- ↑ Cohen, S., R. Braham, and F. Sanchez. (2004). Seed Bank Viability in Disturbed Longleaf Pine Sites. Restoration Ecology 12(4):503-515.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng and D. D. Wade. 2003. Fire frequency effects on longleaf pine (Pinus palustris, P.Miller) vegetation in South Carolina and northeast Florida, USA. Natural Areas Journal 23:22-37.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 DiMiceli, J. K., P. C. Stouffer, E. I. Johnson, C. Leonardi and E. B. Moser. 2007. Seed preferences of wintering Henslow's sparrows. Condor 109:595-604.