Difference between revisions of "Tragia urens"
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation, cultivation, and restoration== |
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==Cultural use== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Revision as of 13:08, 8 June 2021
| Tragia urens | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Tragia |
| Species: | T. urens |
| Binomial name | |
| Tragia urens L. | |
| |
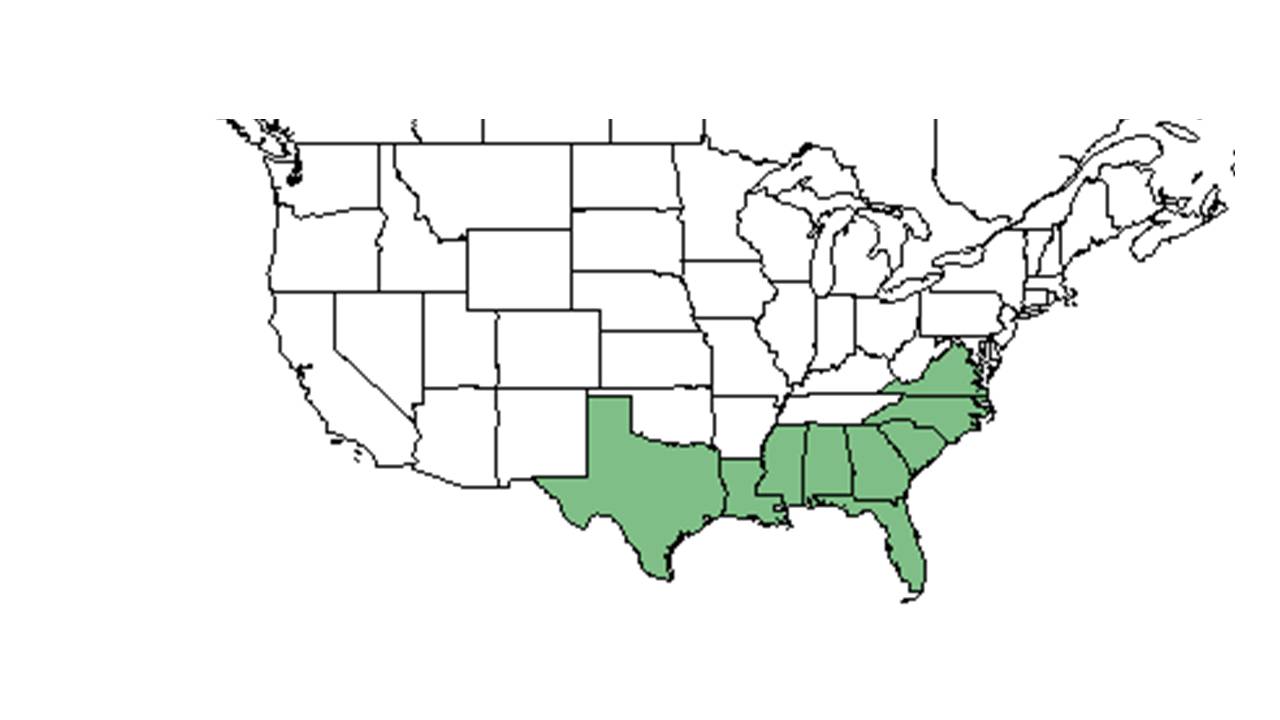
| Natural range of Tragia urens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Wavyleaf noseburn, Southeastern noseburn
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Tragia linearifolia Elliott.[1]
Description
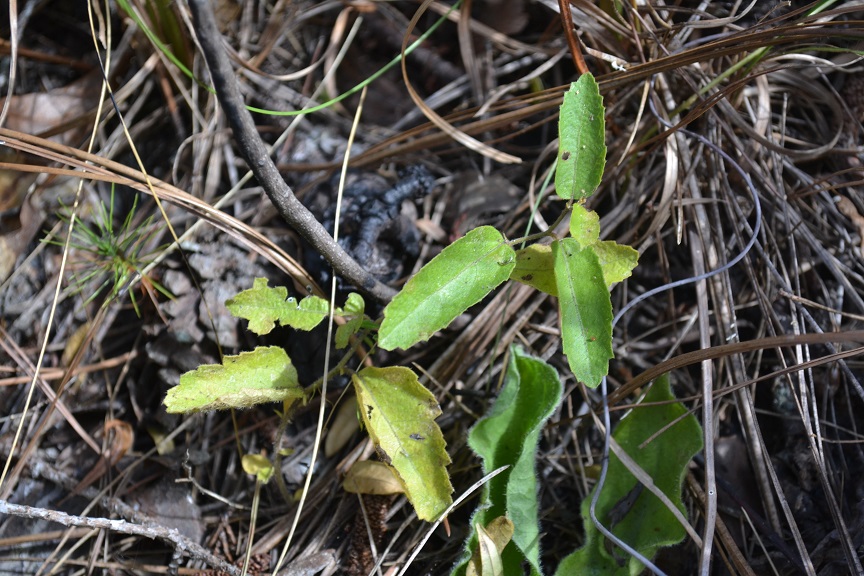
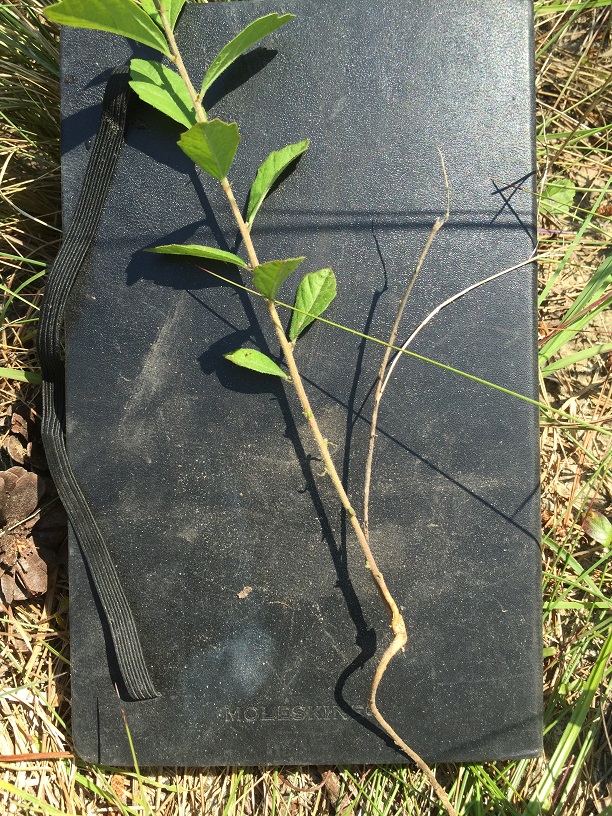
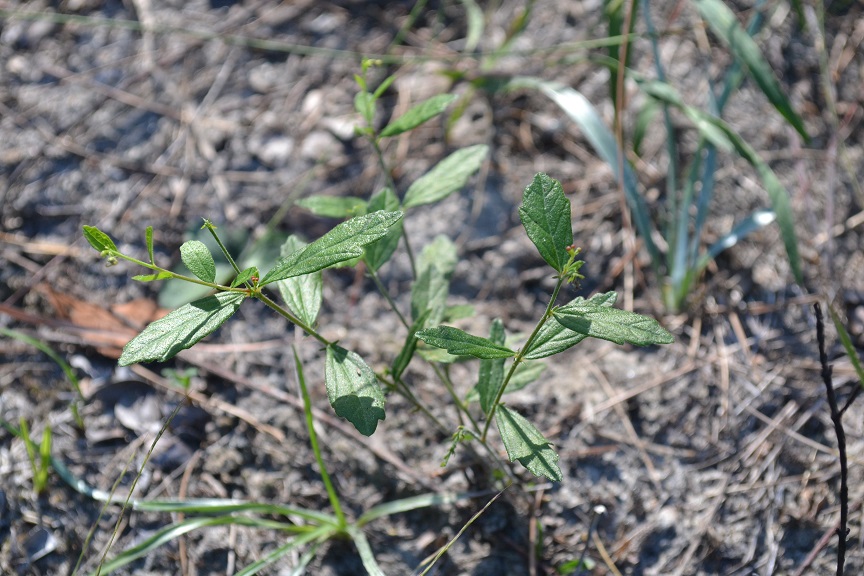
"Monoecious, perennial, rhizomatous herbs, armed with stinging trichomes. Leaves alternate, stipulate. Racemes axillary or terminal, or both, lowest 1 or 2 flowers pistillate, the upper staminate. Flowers greenish or purplish; petals absent; staminate flowers with 3-5 sepals and 2 or 3 stamens; pistillate with 3-8 sepals and 3 stigmas. Capsule 3-locular, 4-5 mm long, 7-8 mm in diam., each locule 1-seeded. Seeds light brown with darker mottling, or entirely dark brown, ovoid, 3-3.5 mm long; caruncle obsolete."[2]
"Plant 2-5 dm tall, freely branched. Leaves narrowly elliptic to oblanceolate or linear, 2-10 cm long, 0.2-2 cm wide, irregularly serrate, undulate or entire, base cuneate to attenuate; petioles 1-3 mm long. Racemes short or elongate, 0.3-12 cm long."[2]
The root system of Tragia urens includes stem tubers which store non-structural carbohydrates (NSC) important for both resprouting following fire and persisting during long periods of fire exclusion.[3] Diaz-Toribio and Putz (2021) recorded this species to have an NSC concentration of 137 mg/g (ranking 41 out of 100 species studied) and water content of 52.2% (ranking 20 out of 100 species studied).[3]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, T. urens has been found in sand of open woodlands, pine uplands, fallow fields, annually burned pineland, sandhills, sand pine scrub, longleaf pine/wiregrass communities, and open pine savannas.[4] Associated species include longleaf pine, sand pine, and wiregrass.[4] T. urens responds positively to agricultural-based soil disturbance in South Carolina coastal plain communities. This marks it as a possible indicator species for post-agricultural woodland.[5][6]
Tragia urens is frequent and abundant in the Peninsula Xeric Sandhills and Panhandle Xeric Sandhills community types and is an indicator species for the North Florida Subxeric Sandhills community type as described in Carr et al. (2010).[7]
Phenology
T. urens has been observed flowering in April, May, and July and fruiting May through September.[8]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by ants and/or explosive dehiscence.[9]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draf of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 665. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Diaz-Toribio, M.H. and F. E. Putz 2021. Underground carbohydrate stores and storage organs in fire-maintained longleaf pine savannas in Florida, USA. American Journal of Botany 108: 432-442.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R. A. Norris, Robert K. Godfrey, Andre F. Clewell, Chris Cooksey, M. Davis, J. M. Kane, R. Komarek, Lisa Keppner, Cecil R Slaughter, Annie Schmidt. States and Counties: Florida: Duval, Franklin, Gadsden, Jackson, Leon, Osceola, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Thomas. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., E Grman, C.W. Habeck, and J.A. Ledvina. (2013). Strong legacy of agricultural land use on soils and understory plant communities in longleaf pine woodlands. Forest Ecology and Management 310: 944-955.
- ↑ Brudvig, L.A., J.L. Orrock, E.I. Damschen, C.D. Collins, P.G. Hahn, W.B. Mattingly, J.W. Veldman, and J.L. Walker. (2014). Land-Use History and Contemporary Management Inform an Ecological Reference Model for Longleaf Pine Woodland Understory Plant Communities. PLoS ONE 9(1): e86604.
- ↑ Carr, S.C., K.M. Robertson, and R.K. Peet. 2010. A vegetation classification of fire-dependent pinelands of Florida. Castanea 75:153-189.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 14 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.

