Difference between revisions of "Penstemon multiflorus"
Emmazeitler (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | Common name: Manyflower beardtongue | + | Common name: Manyflower beardtongue<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> |
==Taxonomic notes== | ==Taxonomic notes== | ||
| + | Synonyms: none.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Varieties: none.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| + | ''P. multiflorus'' has cauline leaves with basal leaves that are petioled. The inflorescence of many nodes with anther cells dehiscing by short proximal slits.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Distribution== | ||
| + | This plant ranges from south-central Florida and southern Alabama, south to southern Florida.<ref name="weakley">Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.</ref> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''P. multiflorus'' occurs in sandy or loamy soil, preferring areas with high light levels. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Rodie White, R. A. Norris, Robert K. Godfrey, M. Davis, and Cecil R Slaughter. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Columbia, Gadsden, Leon, Osceola, and Wakulla. Georgia: Grady.</ref> It can be found in oak-pine-palmetto flatwoods, cabbage palm hammocks, and open stands of longleaf pine and scrub oak. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> It can also occur in disturbed areas, including slash pine plantations, firebreaks, and roadsides. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> Associated species include sand oak, live oak, saw palmetto, longleaf pine, scrub oak, and slash pine. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | + | ''P. multiflorus'' occurs in sandy or loamy soil, preferring areas with high light levels.<ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Rodie White, R. A. Norris, Robert K. Godfrey, M. Davis, and Cecil R Slaughter. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Columbia, Gadsden, Leon, Osceola, and Wakulla. Georgia: Grady.</ref> It can be found in oak-pine-palmetto flatwoods, cabbage palm hammocks, and open stands of longleaf pine and scrub oak.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> It can also occur in disturbed areas, including slash pine plantations, firebreaks, and roadsides.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> Associated species include sand oak, live oak, saw palmetto, longleaf pine, scrub oak, and slash pine.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| Line 35: | Line 41: | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | This species has been found in habitat that is maintained by fire. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> | + | This species has been found in habitat that is maintained by fire.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
<!--===Pollination--> | <!--===Pollination--> | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 15:59, 16 November 2020
| Penstemon multiflorus | |
|---|---|
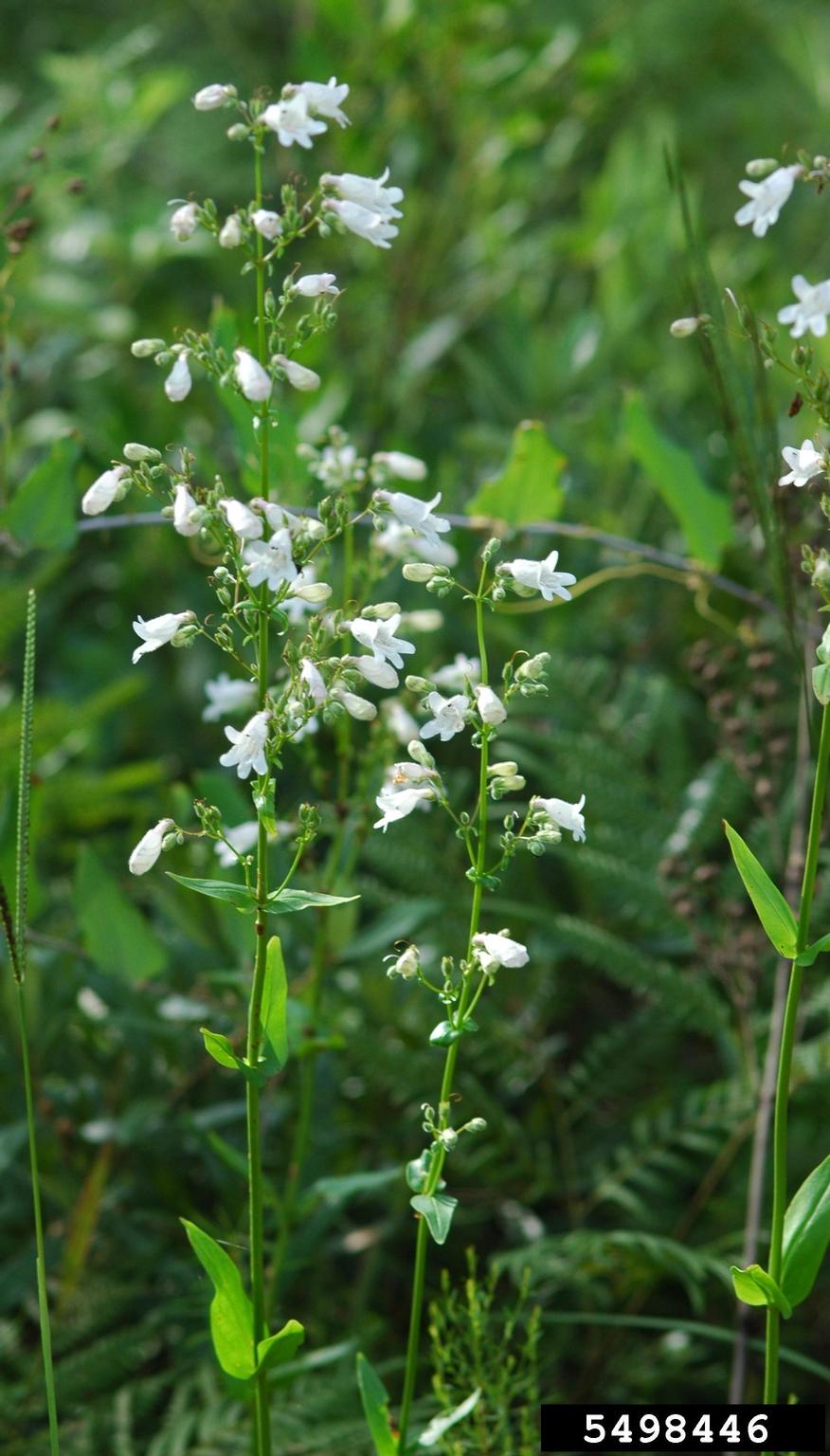

| |
| Photo by Karan A. Rawlins, University of Georgia, Bugwood.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Scrophulariaceae |
| Genus: | Penstemon |
| Species: | P. multiflorus |
| Binomial name | |
| Penstemon multiflorus Chapm. ex Benth. | |
| |
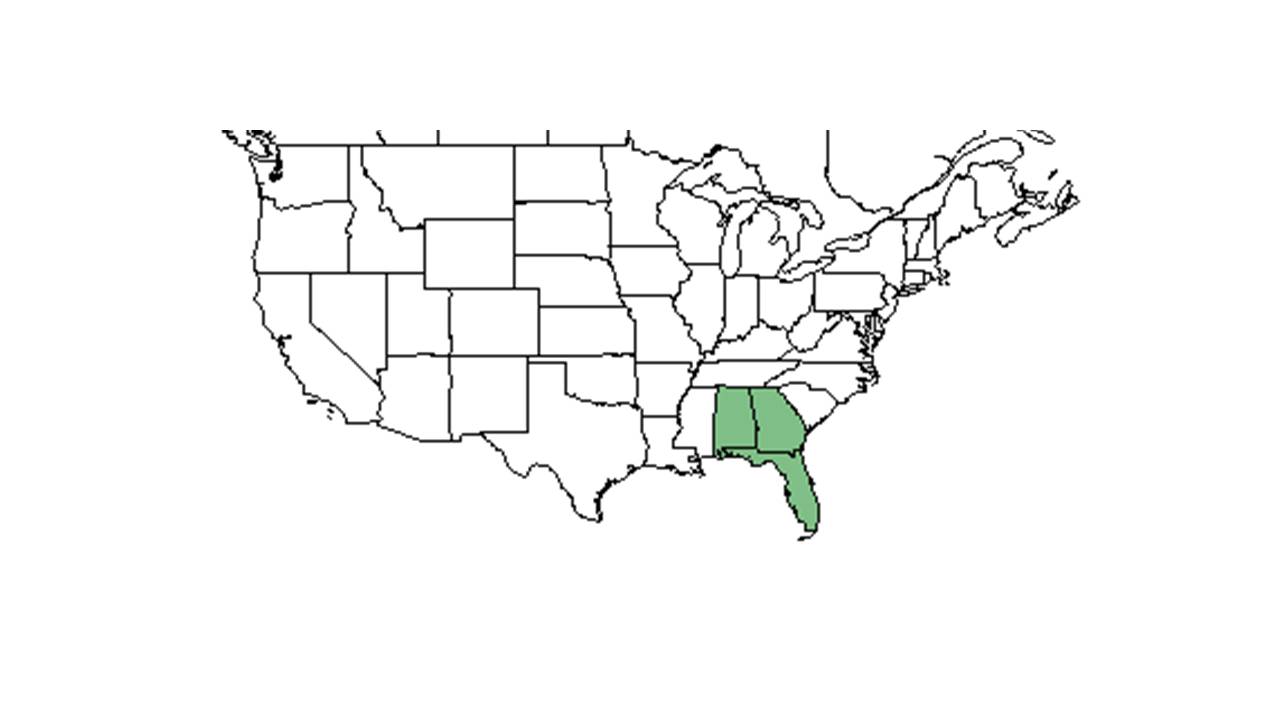
| Natural range of Penstemon multiflorus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Manyflower beardtongue[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none.[1]
Varieties: none.[1]
Description
P. multiflorus has cauline leaves with basal leaves that are petioled. The inflorescence of many nodes with anther cells dehiscing by short proximal slits.[1]
Distribution
This plant ranges from south-central Florida and southern Alabama, south to southern Florida.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
P. multiflorus occurs in sandy or loamy soil, preferring areas with high light levels.[2] It can be found in oak-pine-palmetto flatwoods, cabbage palm hammocks, and open stands of longleaf pine and scrub oak.[2] It can also occur in disturbed areas, including slash pine plantations, firebreaks, and roadsides.[2] Associated species include sand oak, live oak, saw palmetto, longleaf pine, scrub oak, and slash pine.[2]
Phenology
P. multiflorus has been observed flowering from May to August and fruiting have been observed in July and August.[2][3]
Fire ecology
This species has been found in habitat that is maintained by fire.[2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley, A.S. 2015. Flora of the southern and mid-atlantic states. Working Draft of 21 May 2015. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Rodie White, R. A. Norris, Robert K. Godfrey, M. Davis, and Cecil R Slaughter. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Columbia, Gadsden, Leon, Osceola, and Wakulla. Georgia: Grady.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 12 DEC 2016