Difference between revisions of "Hyptis alata"
(→Habitat) |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== | ===Habitat=== | ||
| − | ''H. alata'' is commonly found in wet pine savannas, edges of swamp forests, and moist ditches.<ref name= "Weakley"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> | + | ''H. alata'' is commonly found in wet pine savannas, edges of swamp forests, and moist ditches.<ref name= "Weakley"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> Additionally, habitats that specimens of ''H. alata'' have been recovered from include pine flatwoods, in sandy peat of swampland, burned pineland, cypress dome, wet sandy loam, and coastal hammock. <ref name = "FSU herbarium"> URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, R. Kral, Samuel B. Jones, Jr., Karen MacClendon, Gary R. Knight, Loran C. Anderson. States and counties: Florida (Charlotte, Brevard, Calhoun, Jackson, Franklin), Mississippi (Lamar) </ref> It is listed by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service as an obligate wetland species that is almost exclusively found in wetland habitats.<ref name= "USDA"/> |
| − | + | <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | |
| − | |||
===Phenology=== | ===Phenology=== | ||
Generally, ''H. alata'' flowers from late June until September.<ref name= "Weakley"/> It has been observed to flower in June, July, September, and October. <ref name= "Pan Flora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 22 MAY 2018</ref> | Generally, ''H. alata'' flowers from late June until September.<ref name= "Weakley"/> It has been observed to flower in June, July, September, and October. <ref name= "Pan Flora"> Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 22 MAY 2018</ref> | ||
Revision as of 18:32, 30 May 2019
Common names: clustered bushmint [1] , musky mint [2]
| Hyptis alata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by the Southeastern Flora Plant Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae |
| Genus: | Hyptis |
| Species: | H. alata |
| Binomial name | |
| Hyptis alata Raf. | |
| |
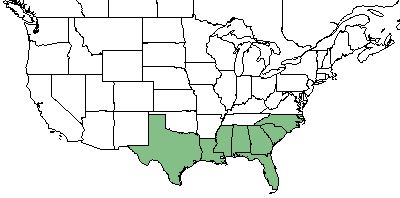
| Natural range of Hyptis alata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: H. radiata Willdenow
Description
H. alata is a perennial forb/herb of the Lamiaceae family that is native to North America. [1]
Distribution
H. alata is specifically found in Florida, Georgia, South Carolina, North Carolina, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, and Texas in the southeastern United States. [1] It is also native to the West Indies.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
H. alata is commonly found in wet pine savannas, edges of swamp forests, and moist ditches.[3] Additionally, habitats that specimens of H. alata have been recovered from include pine flatwoods, in sandy peat of swampland, burned pineland, cypress dome, wet sandy loam, and coastal hammock. [4] It is listed by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service as an obligate wetland species that is almost exclusively found in wetland habitats.[1]
Phenology
Generally, H. alata flowers from late June until September.[3] It has been observed to flower in June, July, September, and October. [5]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Kalmbacher, R. S., et al. (1994). "South Florida flatwoods range vegetation responses to season of deferment from grazing." Journal of Range Management 47(1): 43-47.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: R.K. Godfrey, R. Kral, Samuel B. Jones, Jr., Karen MacClendon, Gary R. Knight, Loran C. Anderson. States and counties: Florida (Charlotte, Brevard, Calhoun, Jackson, Franklin), Mississippi (Lamar)
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 22 MAY 2018