Difference between revisions of "Hymenachne hemitomon"
(→Ecology) |
(→Conservation and Management) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
| − | It is considered a species of special concern by the Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation, Natural Heritage Program.<ref name= "USDA"/> ''H. hemitomon'' is also considered to have growth characteristics that can make it become weedy or invasive in some habitats or regions.<ref name= "fact"/> | + | It is considered a species of special concern by the Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation, Natural Heritage Program.<ref name= "USDA"/> For management, fertilization can help establish new plantings or when it is used as ofrage since it responds favorably to fertilization. To maintain healthy stands for grazing, no more than half of its biomass should be removed by either cutting or grazing. On the other hand, ''H. hemitomon'' is also considered to have growth characteristics that can make it become weedy or invasive in some habitats or regions since it has growth characteristics that can help it grow into monotypic stands. This species can be controlled through mowing, with fire, or with hydroperiod management, and herbicides can also be used to create wetland openings.<ref name= "fact"/> |
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
Revision as of 19:44, 22 May 2019
| Hymenachne hemitomon | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Hymenachne |
| Species: | H. hemitomon |
| Binomial name | |
| Hymenachne hemitomon J.A. Schultes | |
| |
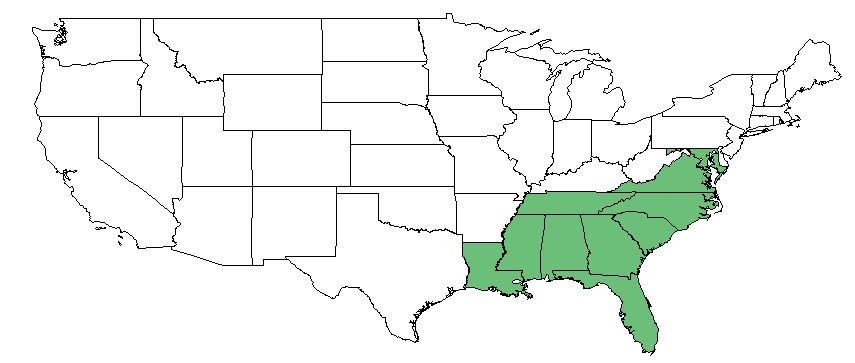
| Natural range of Hymenachne hemitomon from Weakley [1] | |
Common name(s): Maidencane
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Panicum hemitomon J.A. Schultes
Description
This species is a perennial graminoid in the Poaceae family.[2] It is a rhizomatous grass that reaches heights between 2 to 5 feet with alternate leaves and overlapping sheaths grasping the stem. Plant is glabrous containing a membranous ligule, and seed heads look very delicate. Often, reproductive stems will be much outnumbered by vegetative stems.[3]
Distribution
H. hemitomon can be found from Texas to southern New Jersey, but it is most common in Florida.[2] More specifically, it is distributed from the southeastern coastal plain from southern New Jersey south to Florida, west to Texas, and also in Tennessee, and ranges farther south to South America.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
Generally, Hymenachne hemitomon can be found in river, lake and pond shores, marshes, ditches, swamp borders, and most often in shallow water. It also commonly forms dense colonies located in shallow waters and low margins of limesink ponds.[1] This species is frequently found at swamp margins and marshy drainage canals in wet soil or shallow, standing water [4]. Sandhills and wetlands are possible habitats for Hymenachne hemitomon.[5] Within the Atlantic and Gulf Coastal Plain, H. hemitomon is considered an obligate wetland species that can only be found in wetland habitats.[2] It is tolerant of a large range of soil textures and anaerobic conditions, but is not tolerant of salt, and mostly prefers an almost neutral pH.[3]
Phenology
H. hemitomon has been observed to flower from the beginning of may to mid August [4], but flowering is most common from June to July [1].
Seed bank and germination
Since this species is not a dependable seed producer, it typically established itself by vegetative propagules instead.[3]
Fire ecology
This species is fire tolerant if roots and rhizomes are moist.[3]
Use by animals
This species is very palatable to livestock, and is an important forage grass. With other wildlife, it is considered to have a fair forage value. It provides cover and habitat for many mammals, amphibians, reptiles, fish, and birds. It also is frequently used by the Florida Panther and white-tailed deer.[3]
Conservation and Management
It is considered a species of special concern by the Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation, Natural Heritage Program.[2] For management, fertilization can help establish new plantings or when it is used as ofrage since it responds favorably to fertilization. To maintain healthy stands for grazing, no more than half of its biomass should be removed by either cutting or grazing. On the other hand, H. hemitomon is also considered to have growth characteristics that can make it become weedy or invasive in some habitats or regions since it has growth characteristics that can help it grow into monotypic stands. This species can be controlled through mowing, with fire, or with hydroperiod management, and herbicides can also be used to create wetland openings.[3]
Cultivation and restoration
For restoration, H. hemitomon can be used for shoreline stabilization in locations with fresh water. This is because it has a rapid growth rate, and grows into dense stands that can extend from shallow water up along the bank as far as moisture will permit it. As well, it is capable of lessening wave energies and trapping sediment that is suspended; its roots and rhizomes form a network that anchors the soil and traps these sediments in place.[3]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 USDA Plants Database: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=PAHE2
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Shadow, R. A. (2012). Plant Fact Sheet: Maidencane Panicum hemitomon. N.R.C.S. United States Department of Agriculture. East Texas Plant Materials Center, Nacogdoches, Texas.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2018. Collectors: George R. Cooley, R. J. Eaton, Carroll E. Wood, Jr., C. Earle Smith, Jr., Robert K. Godfrey, Loran C. Anderson, M. Darst, R. Mattson, L. Peed, Grady W. Reinert, K. Craddock Burks, P.L. Redfearn, Jr., R. Kral, Jackson, Kurz, R. J. Vogl, R. F. Doren, William Lindsey, and Julie Neel. States and Counties: Florida: Citrus, Columbia, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Gulf, Hamilton, Hernando, Leon, Levy, Madison, Marion, Nassau, Okaloosa, Osceola, St. Johns, Union, Volusia, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Thomas.
- ↑ Comment by Edwin Bridges, on post by Adam Julius Arendell, July 18, 2016, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group July 2016.