Difference between revisions of "Hymenachne hemitomon"
(→Distribution) |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| binomial_authority = J.A. Schultes | | binomial_authority = J.A. Schultes | ||
| range_map = HYME_HEMI_DIST.JPG | | range_map = HYME_HEMI_DIST.JPG | ||
| − | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Hymenachne hemitomon'' from Weakley <ref | + | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Hymenachne hemitomon'' from Weakley <ref name= "Weakley"/> |
}} | }} | ||
Common name(s): Maidencane | Common name(s): Maidencane | ||
Revision as of 18:31, 22 May 2019
| Hymenachne hemitomon | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Hymenachne |
| Species: | H. hemitomon |
| Binomial name | |
| Hymenachne hemitomon J.A. Schultes | |
| |
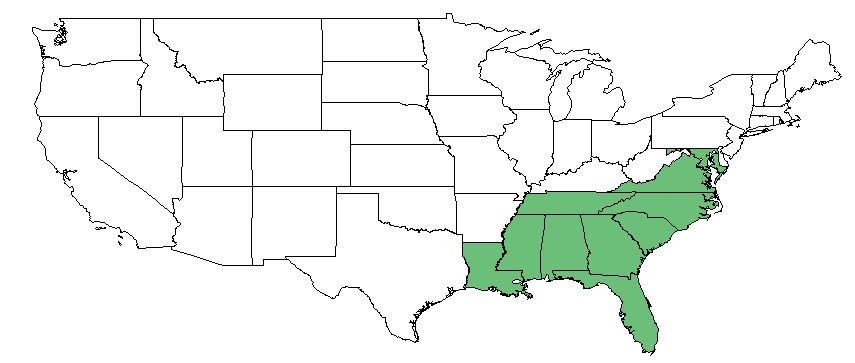
| Natural range of Hymenachne hemitomon from Weakley [1] | |
Common name(s): Maidencane
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Panicum hemitomon J.A. Schultes.
Varieties: none.
Description
This species is a perennial graminoid in the Poaceae family. Within the Atlantica and Gulf Coastal Plain, H. hemitomon is wetland obligate [2].
Distribution
H. hemitomon can be found from Texas to southern New Jersey, but it is most common in Florida.[2] More specifically, it is distributed from the southeastern coastal plain from southern New Jersey south to Florida, west to Texas, and also in Tennessee, and ranges farther south to South America.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
This species is frequently found at swamp margins and marshy drainage canals in wet soil or shallow, standing water [3]. Sandhills and wetlands are possible habitats for Hymenachne hemitomon.[4]
Phenology
H. hemitomon has been observed to flower from the beginning of may to mid August [3], but flowering is most common from June to July [1].
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 USDA Plants Database: https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=PAHE2
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: May 2018. Collectors: George R. Cooley, R. J. Eaton, Carroll E. Wood, Jr., C. Earle Smith, Jr., Robert K. Godfrey, Loran C. Anderson, M. Darst, R. Mattson, L. Peed, Grady W. Reinert, K. Craddock Burks, P.L. Redfearn, Jr., R. Kral, Jackson, Kurz, R. J. Vogl, R. F. Doren, William Lindsey, and Julie Neel. States and Counties: Florida: Citrus, Columbia, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Gulf, Hamilton, Hernando, Leon, Levy, Madison, Marion, Nassau, Okaloosa, Osceola, St. Johns, Union, Volusia, Wakulla, and Washington. Georgia: Thomas.
- ↑ Comment by Edwin Bridges, on post by Adam Julius Arendell, July 18, 2016, posted to Florida Flora and Ecosystematics Facebook Group July 2016.