Difference between revisions of "Gymnopogon brevifolius"
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | It has been observed to flower and fruit in January, April, September through October, and December.<ref name=fsu/> It also flowers in August.<ref name="Flint 1887">Flint, C. L. (1887). Grasses and forage plants: a practical treatise comprising their natural history; comparative nutritive value; methods of cultivating, cutting, and curing. Boston, MA, Lee and Shepard Publishers.</ref> | + | Generally, this species flowers from August until October.<ref name= "Weakley"/> It has been observed to flower and fruit in January, April, September through October, and December.<ref name=fsu/> It also flowers in August.<ref name="Flint 1887">Flint, C. L. (1887). Grasses and forage plants: a practical treatise comprising their natural history; comparative nutritive value; methods of cultivating, cutting, and curing. Boston, MA, Lee and Shepard Publishers.</ref> |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
Revision as of 19:41, 17 May 2019
| Gymnopogon brevifolius | |
|---|---|

| |
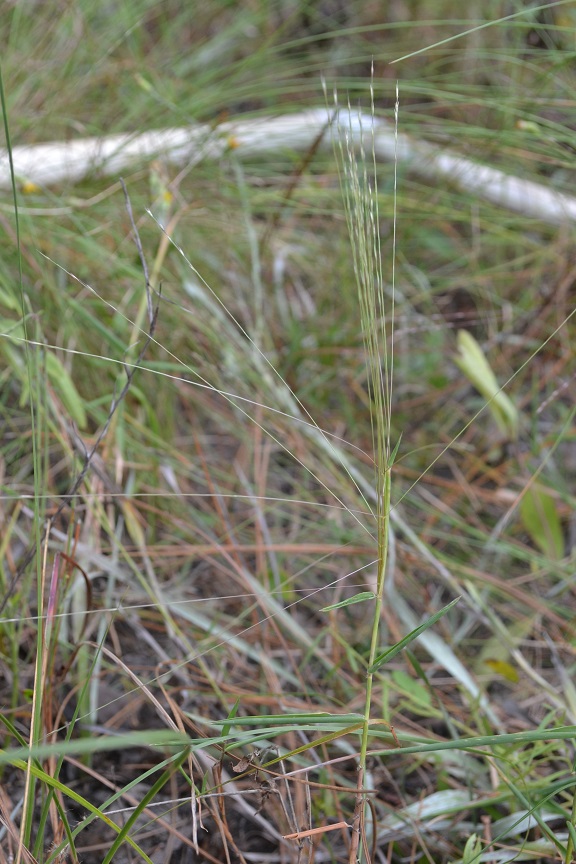
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Gymnopogon |
| Species: | G. brevifolius |
| Binomial name | |
| Gymnopogon brevifolius Trin. | |
| |
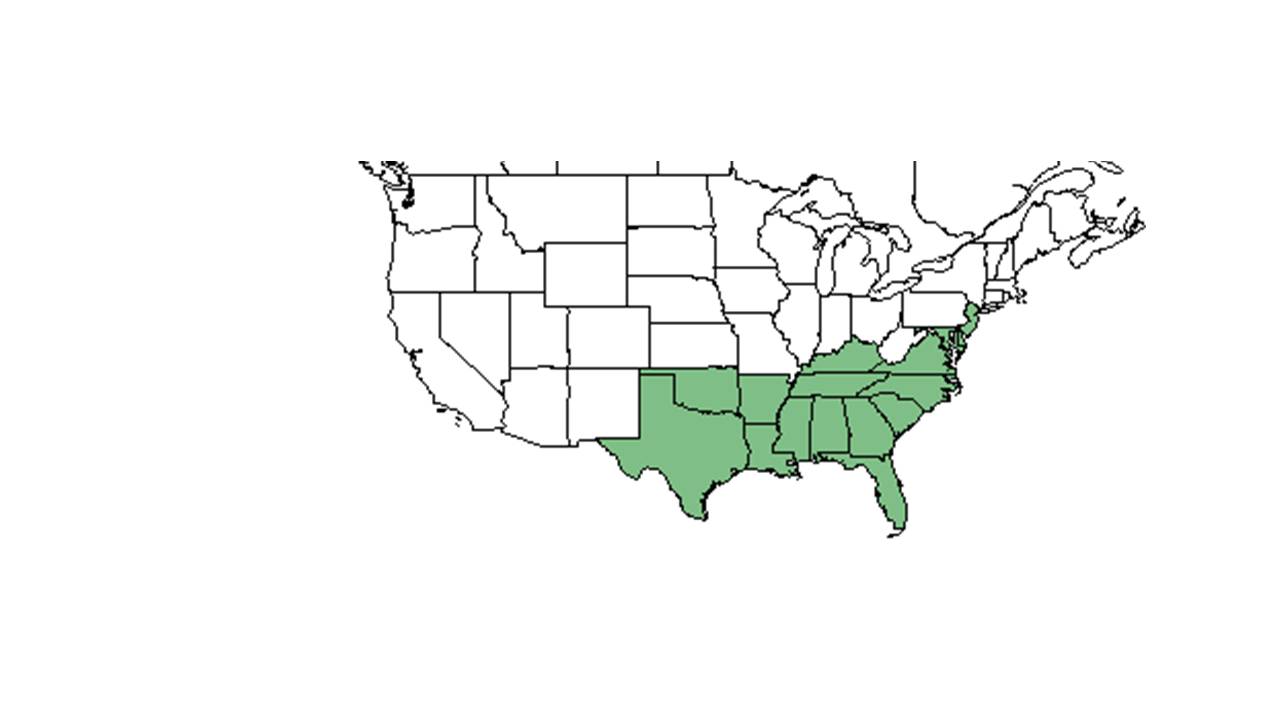
| Natural range of Gymnopogon brevifolius from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Shortleaf skeletongrass
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
"Tufted, rhizomatous, perennial; culms branching, nodes and internodes glabrous. Leaves cauline; blades glabrous on both surfaces, margins scaberulous, bases cordate; sheaths conspicuously overlapping, glabrous, usually pilose apically; ligules membranous, ciliolate, less than 0.4 mm long; collars usually pilose. Spikes racemose; branches spreading, flexuous, angled, scaberulous. Spikelets in two rows on one side of rachis, 1-flwoered, occasionally a rudiment present in G. amibguus, appressed; pedicels angled, scaberulous, absent or to 1.5 mm long. Glumes 1-nerved, margins usually scarious; paleas 2-nerved, margins usually scarious, acute; callus usually bearded; rachilla prolonged or capped by sterile floret. Grain reddish, linear-ellipsoid."[1]
"Culms 3-6 dm tall. Blades frequently cuspidate, to 9 cm long. Spikelets usually length of spike, 4.5-6.5 cmm long. Glumes 3.5-6.5 mm long; fertile lemma usually glabrous, body 3.5-4 mm long, awn usually 5-10 mm long, occasionally a long, awned sterile lemmas present; paleas 3.5-4 mm long. Grain 2.5-2.6 mm long."[1]
Distribution
It is generally found in the southeast and eastern United States.[2] More specifically, G. brevifolius can be found from southern New Jersey south to southern Florida, west to Louisiana and Arkansas, and disjunct in Kentucky in the Highland Rim and Texas.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
Gymnopogon brevifolius can generally be found in sandhills, pine savannas, prairies, dry woodlands, and calcareous glades.[3] This species is found on longleaf pine sandhills, open wiregrass-pinewoods savannas, mesic pine flatwoods, palmetto-wiregrass-longleaf pine woodlands, pine barrens, and mixed woodlands. Grows in dry and moist sandy loam in these environments as well as human disturbed habitats such as along back roads.[4]
Associated species includes Aristida stricta, Muhlenbergia, Schizachyrium, Panicum anceps, Paspalum bifidum, Pinus palutris, Andropogon, Pinus elliottii, Lilium, Verbesina chapmanii, Platanthera integra, Carphephorus paniculatus, Sabal palmetto, Quercus falcata.[4]
Phenology
Generally, this species flowers from August until October.[3] It has been observed to flower and fruit in January, April, September through October, and December.[4] It also flowers in August.[5]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [6]
Use by animals
Comprised deer diets more in the summer than in the winter.[7]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 118. Print.
- ↑ USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 17 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Trina Mitchell, James R. Burkhalter, A. H. Curtiss, R. Kral, R.K. Godfrey, W. A. Silveus, and Carolyn Kindell. States and Counties: Florida: Calhoun, Duval, Franklin, Gulf, Jackson, Liberty, Santa Rosa, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington. Georgia: Grady.
- ↑ Flint, C. L. (1887). Grasses and forage plants: a practical treatise comprising their natural history; comparative nutritive value; methods of cultivating, cutting, and curing. Boston, MA, Lee and Shepard Publishers.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Thill, R. E. (1983). Deer and cattle forage selection on Louisiana pine-hardwood sites. New Orleans, LA, USDA Forest Service.