Difference between revisions of "Elephantopus nudatus"
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | It is found in edges of swamps, creek bottomlands, hammocks, Longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, edges of deciduous forests, open pine flatwoods, boggy bottomlands, in wooded area above floodplains and in floodplains, in mesic flatwoods, and edges of ponds. Is also found in human disturbed areas such as along the roadside, flatwoods that have been clear cut, and in lawn adjacent to parking lot area. Can thrive in areas of low light or high light levels. Is associated with moist, loamy sand; fine, sandy soils; alluvial sands; and loamy humus soil types.<ref name=fsu>Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, D. B. Ward, Robert K. Godfrey, R. D. Houk, D. B. Ward, S. S. Ward, Jean W. Wooten, R. Kral, Almut G. Jones, R. A. Norris, R. Komarek, and Cecil R Slaughter. States and Counties: Florida: Baker, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hamilton, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Marion, Nassau, Putnam, Santa Rosa, St Johns, Union, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.</ref> | + | Generally, ''E. nudatus'' can be found in usually fairly dry woodlands and woodland borders.<ref name= "Weakley">Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> It is found in edges of swamps, creek bottomlands, hammocks, Longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, edges of deciduous forests, open pine flatwoods, boggy bottomlands, in wooded area above floodplains and in floodplains, in mesic flatwoods, and edges of ponds. Is also found in human disturbed areas such as along the roadside, flatwoods that have been clear cut, and in lawn adjacent to parking lot area. Can thrive in areas of low light or high light levels. Is associated with moist, loamy sand; fine, sandy soils; alluvial sands; and loamy humus soil types.<ref name=fsu>Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, D. B. Ward, Robert K. Godfrey, R. D. Houk, D. B. Ward, S. S. Ward, Jean W. Wooten, R. Kral, Almut G. Jones, R. A. Norris, R. Komarek, and Cecil R Slaughter. States and Counties: Florida: Baker, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hamilton, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Marion, Nassau, Putnam, Santa Rosa, St Johns, Union, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.</ref> |
Associated species include ''Chasmanthium sessiliflorum, Cyperus tetragonus, Panicum hamitomon, Bacopa.'' <ref name=fsu/> | Associated species include ''Chasmanthium sessiliflorum, Cyperus tetragonus, Panicum hamitomon, Bacopa.'' <ref name=fsu/> | ||
Revision as of 16:53, 6 May 2019
| Elephantopus nudatus | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Chris Evans, University of Illinois, Bugwood.org | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Elephantopus |
| Species: | E. nudatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Elephantopus nudatus A. Gray | |
| |
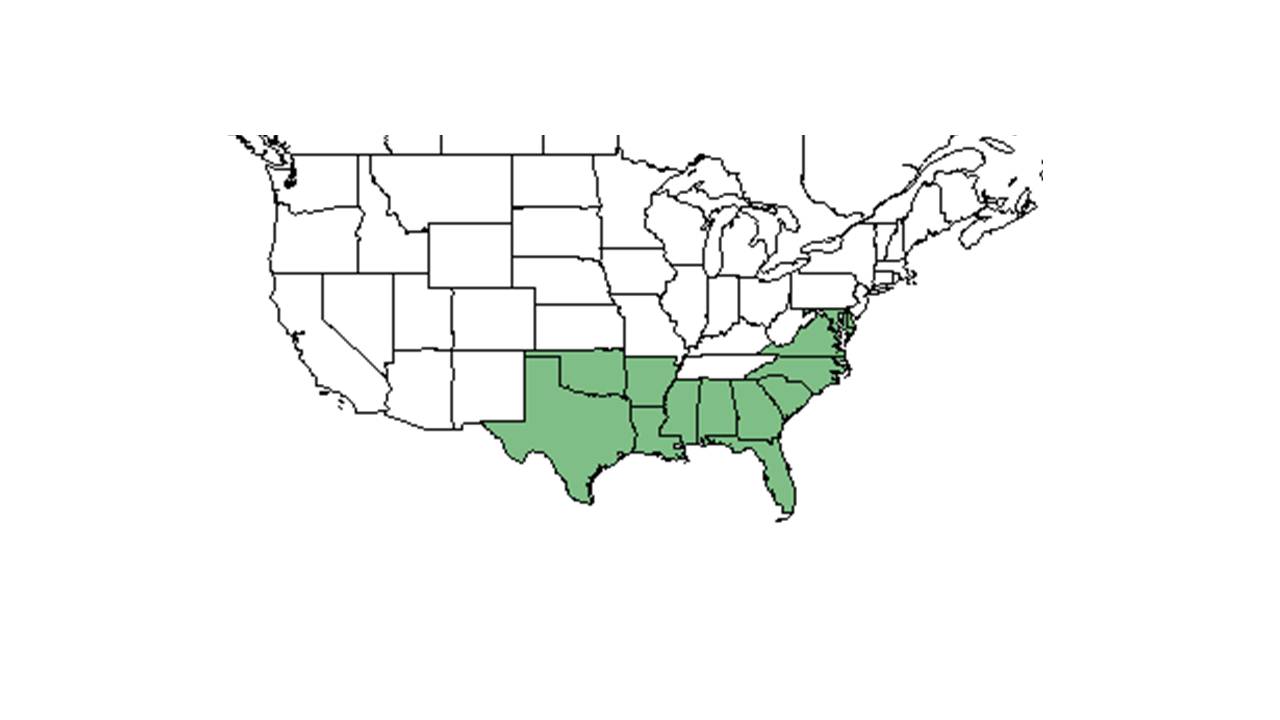
| Natural range of Elephantopus nudatus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name(s): smooth elephantsfoot; Coastal Plain elephant's-foot
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Elephantopus nudatus is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Generally, E. nudatus can be found in usually fairly dry woodlands and woodland borders.[1] It is found in edges of swamps, creek bottomlands, hammocks, Longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, edges of deciduous forests, open pine flatwoods, boggy bottomlands, in wooded area above floodplains and in floodplains, in mesic flatwoods, and edges of ponds. Is also found in human disturbed areas such as along the roadside, flatwoods that have been clear cut, and in lawn adjacent to parking lot area. Can thrive in areas of low light or high light levels. Is associated with moist, loamy sand; fine, sandy soils; alluvial sands; and loamy humus soil types.[2]
Associated species include Chasmanthium sessiliflorum, Cyperus tetragonus, Panicum hamitomon, Bacopa. [2]
Phenology
E. nudatus has been observed flowering in September[3] and October.[2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, D. B. Ward, Robert K. Godfrey, R. D. Houk, D. B. Ward, S. S. Ward, Jean W. Wooten, R. Kral, Almut G. Jones, R. A. Norris, R. Komarek, and Cecil R Slaughter. States and Counties: Florida: Baker, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hamilton, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Marion, Nassau, Putnam, Santa Rosa, St Johns, Union, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: JULY 2015