Difference between revisions of "Diodia virginiana"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| − | This species consists of approximately 5-10% of the diet for large mammals and various terrestrial birds.<ref>Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> | + | This species consists of approximately 5-10% of the diet for large mammals and various terrestrial birds.<ref>Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> However, it is considered to have a poor ofrage value.<ref>Hilman, J. B. (1964). "Plants of the Caloosa Experimental Range " U.S. Forest Service Research Paper SE-12 </ref> |
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
Revision as of 20:04, 2 May 2019
| Diodia virginiana | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Photo taken by Gil | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Rubiales |
| Family: | Rubiaceae |
| Genus: | Diodia |
| Species: | D. virginiana |
| Binomial name | |
| Diodia virginiana L. | |
| |
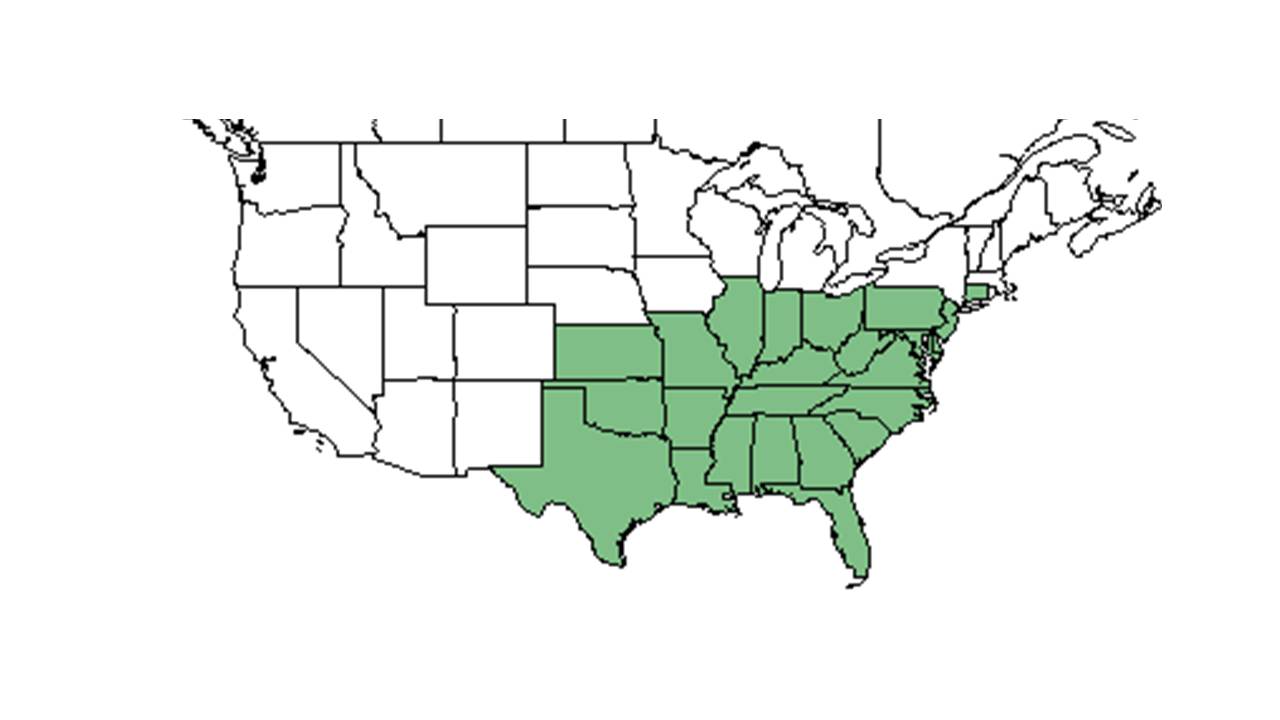
| Natural range of Diodia virginiana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Virginia buttonweed
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Diodia virginiana var. attenuata Fernald; D. virginiana var. latifolia Torrey & A. Gray; D. virginiana var. virginiana; D. tetragona Walter; D. hirsuta Pursh
Description
Diodia virginiana tends to grow in spreading mats, sometimes floating in shallow water.[1]
Generally, for Diodia genus, they are "annual or perennial herbs. Leaves sessile, opposite pubescent or glabrate, margins hyaline, setose-serrate; stipules linear or fimbriate, ½ as long, or longer than, the fruit. Flowers 4-merous, axillary, usually solitary, sessile; calyx lobes equal or unequal; corolla salverform. Fruit leathery, surmounted by the persistent calyx lobes, splitting into 2, indehiscent, 1-seeded segments." [2]
Specifically, for D. virginiana species, they are "erect or spreading, usually pubescent perennial from a woody root crown, the stems branched, 1-6 dm or more long. Leaves elliptic-lanceolate to oblanecolate, mostly 2-7 cm long, 4-12 mm wide. Calyx lobes 2, linear-lanceolate, 2-4 mm long, pubescent; corolla white, tube filiform, 7-9 mm long, lobes 3-4 mm long, the inner surface pubescent; stigmas filiform or the style appearing cleft. Fruit pubescent, oblong-ellipsoid, 5-9 mm long, 3-5 mm in diam., prominently ridged. Fruit splitting into 2, indehiscent, 1-seeded segments." [2]
Distribution
D. virginiana is native to eastern and central United States, from Connecticut, Pennsylvania, Illinois, and Kansas south to Florida and Texas.[3]
Ecology
Habitat
Typical habitats of this species include wet fields, ditches, and other wet to moist habitats.[3] D. virginiana occurs in moist to wet areas, and areas subject to periodic inundation like ephemeral ponds. It occurs in a wide range of light levels, from deep shade to full sun, but tends to prefer sandy soil types such as loamy sand, sand, sandy loam and sandy peat. It can be found in natural communities including pine savannas, grassy areas near lakes and ponds, prairies, floodplain forests, sand bars, cypress-hardwood swamps, swampy woodlands, wetland areas, and calcareous hammocks. However, it can also appear in disturbed habitat, like cutover pine woods, roadsides, old fields, and mowed areas.[1]
Associated species include Diodia teres, Aristida stricta, Polygonum, Sabatia dodecandra, Hypericum galioides, Eupatorium semiserratum.[1]
Phenology
Generally, this species flowers from June until December.[3] D. virginiana has been observed flowering and fruiting from May through November with peak inflorescence in May.[4][1]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by gravity. [5]
Seed bank and germination
Tilling and burning cause increase in cover percentage. [6]
Fire ecology
It is favored by frequent fire,[7] and grows in habitats maintained by fire.[1]
Use by animals
This species consists of approximately 5-10% of the diet for large mammals and various terrestrial birds.[8] However, it is considered to have a poor ofrage value.[9]
Conservation and management
D. virginiana is listed as threatened by the Indiana Department of Natural Resources, Division of Nature Preserves, and listed as endangered by the New Jersey Department of Environmental Protection, Office of Natural Lands Management. It is also considered to be weedy or invasive in some areas of the northeast and the southeast.[10]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R. K. Godfrey, R. Komarek, R. Kral, Sidney McDaniel, R. A. Norris, A.E. Radford, Cecil R. Slaughter, B. K. Holst, Valerie Renard, Lovette E. Williams, Rev. Robert Brinker, Robert L. Lazor, Grady W. Reinert, Suellen Folensbee, Paul L. Redfearn, Jr., S. W. Leonard, Gary R. Knight, Jame Amoroso, W. G. D'Arcy, Gywnn W. Ramsey, H. Larry Stripling, W. P. Adams, K. Craddock Burks, William Lindsey, D. W. Mather, Jean W. Wooten, Robert J. Lemaire, O. Lakela, Robert J. Lemaire, Leon Neel, R. F. Doren, A. Gholson Jr., K. Willis, R. Cherry, and Annie Schmidt. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Bay, Calhoun, Charlotte, Citrus, Collier, Columbia, Dade, Dixie, Duval, Escambia, Flagler, Franklin, Hamilton, Highland, Holmes, Indian River, Jackson, Jefferson, Lake, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Marion, Okaloosa, Orange, Osceola, Palm Beach, Polk, Osceola, Sarasota, Santa Rosa, St. Johns, Sumter, Taylor, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 979. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 8 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. K. and R. R. Sharitz (1994). "Vegetation disturbance and maintenance of diversity in intermittently flooded Carolina bays in South Carolina." Ecological Applications 4: 177-188.
- ↑ Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, et al. (2003). "Fire frequency effects on longleaf pine (Pinus palustris, P.Miller) vegetation in South Carolina and northeast Florida, USA." Natural Areas Journal 23: 22-37.
- ↑ Miller, J.H., and K.V. Miller. 1999. Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.
- ↑ Hilman, J. B. (1964). "Plants of the Caloosa Experimental Range " U.S. Forest Service Research Paper SE-12
- ↑ USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 2 May 2019). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.