Difference between revisions of "Desmodium paniculatum"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
''Desmodium paniculatum'' has lower nitrogen concentrations in its tissues 1 year after burning than 3 years after.<ref name="Lajeunesse 2006">Lajeunesse S. D., Dilustro J. J., Sharitz R. R., and Collins B. S. (2006). Ground layer carbon and nitrogen cycling and legume nitrogen inputs following fire in mixed pine forests. American Journal of Botany 93(1):84-93.</ref> | ''Desmodium paniculatum'' has lower nitrogen concentrations in its tissues 1 year after burning than 3 years after.<ref name="Lajeunesse 2006">Lajeunesse S. D., Dilustro J. J., Sharitz R. R., and Collins B. S. (2006). Ground layer carbon and nitrogen cycling and legume nitrogen inputs following fire in mixed pine forests. American Journal of Botany 93(1):84-93.</ref> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Pollination=== | ||
| + | The following bees in the Hymenoptera family are known to pollinate this species: ''Bombus impatiens'', ''Bombus pensylvanica'', ''Megachile brevis brevis'', ''Megachile mendica'', ''Megachile petulans'', ''Melissodes bimaculata bimaculata'', ''Nomia nortoni nortoni'', and ''Calliopsis andreniformis''.<ref name= "fact"/> | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''D. paniculatum'' produces seeds which attract birds and small rodents, including upland game birds such as bobwhite quail and wild turkey and rodents such as the white-footed mouse and deer mouse. It also serves as a source of food for cottontail rabbits, livestock, and other hoofed mammalian herbivores including white tailed deer.<ref name="Leif & Belt 2013">Leif J. and Belt S. (2013). Plant Guide for Panicledleaf ticktrefoil (Desmodium paniculatum), USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, Rose Lake Plant Materials Center, East Lansing, Michigan, 48823 and USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service Norman Berg National Plant Materials Center, Beltsville, Maryland, 20705.</ref> Caterpillars of the following butterflies are known to feed on the plant: Hoary Edge (''Achalarus lyciades''), Silver-Spotted Skipper (''Epargyreus clarus''), Southern Cloudywing (''Thorybes bathyllus''), Northern Cloudywing (''Thorybes pylades''), Eastern Tailed Blue (''Everes comyntas''), and Gray Hairstreak (''Strymon melinus''). Historically, ''D. paniculatum'' was used by the Houma Indians in Louisiana for an infusion of the roots with whiskey to treat cramps and weakness.<ref name= "fact">Kirk, S. and Belt, S. 2009. Plant fact sheet for Panicledleaf Ticktrefoil (''Desmodium paniculatum''), USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, Norman A. Berg National Plant Materials Center, Beltsville, 20705.</ref> | + | ''D. paniculatum'' produces seeds which attract birds and small rodents, including upland game birds such as bobwhite quail and wild turkey and rodents such as the white-footed mouse and deer mouse. It also serves as a source of food for cottontail rabbits, livestock, and other hoofed mammalian herbivores including white tailed deer.<ref name="Leif & Belt 2013">Leif J. and Belt S. (2013). Plant Guide for Panicledleaf ticktrefoil (Desmodium paniculatum), USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, Rose Lake Plant Materials Center, East Lansing, Michigan, 48823 and USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service Norman Berg National Plant Materials Center, Beltsville, Maryland, 20705.</ref> Caterpillars of the following butterflies are known to feed on the plant: Hoary Edge (''Achalarus lyciades''), Silver-Spotted Skipper (''Epargyreus clarus''), Southern Cloudywing (''Thorybes bathyllus''), Northern Cloudywing (''Thorybes pylades''), Eastern Tailed Blue (''Everes comyntas''), and Gray Hairstreak (''Strymon melinus''). Other insects that feed on this plant include beetles, some thirps, aphids, stinkbugs, and moth caterpillars. Historically, ''D. paniculatum'' was used by the Houma Indians in Louisiana for an infusion of the roots with whiskey to treat cramps and weakness.<ref name= "fact">Kirk, S. and Belt, S. 2009. Plant fact sheet for Panicledleaf Ticktrefoil (''Desmodium paniculatum''), USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, Norman A. Berg National Plant Materials Center, Beltsville, 20705.</ref> |
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Revision as of 15:15, 26 April 2019
| Desmodium paniculatum | |
|---|---|
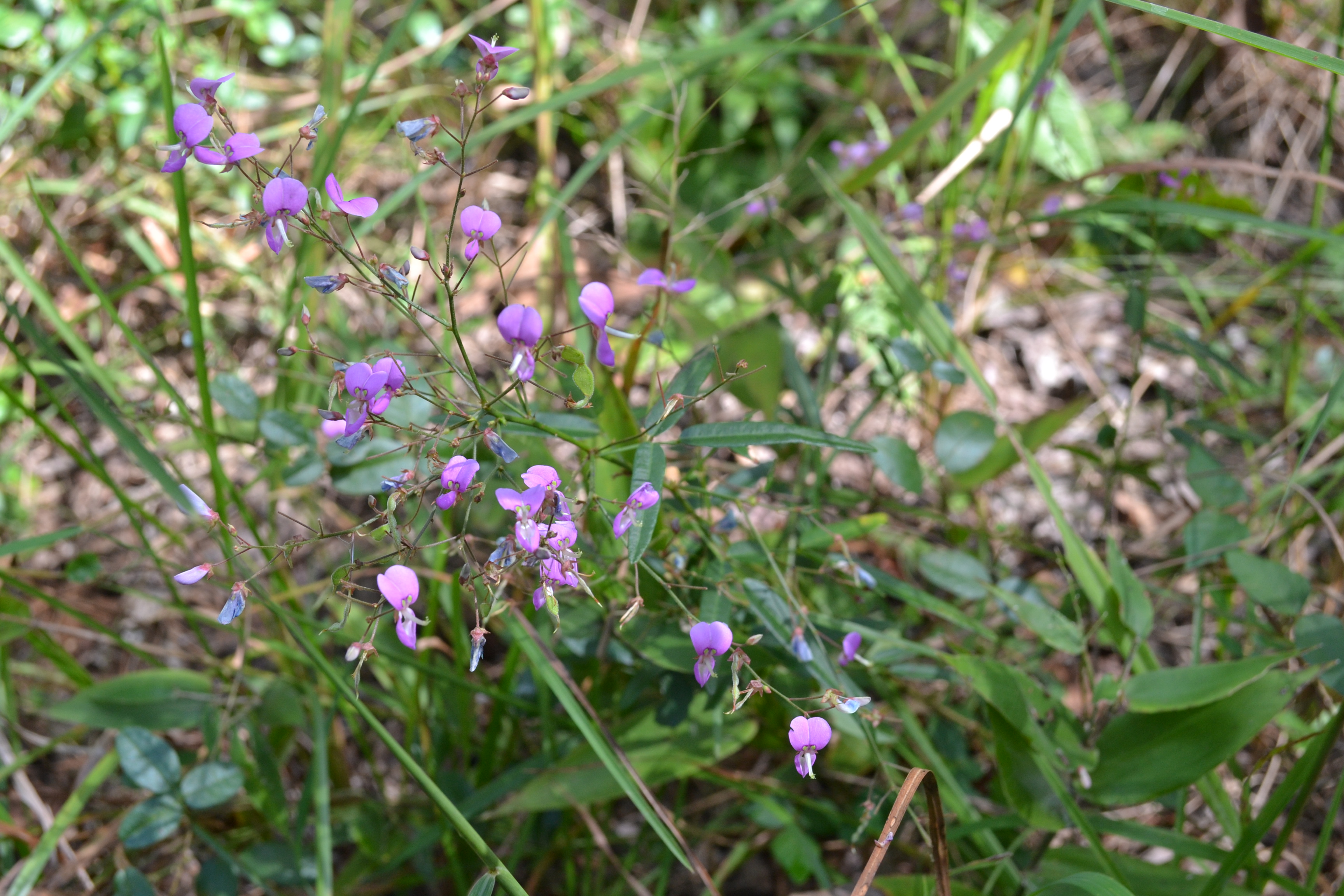

| |
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Desmodium |
| Species: | D. paniculatum |
| Binomial name | |
| Desmodium paniculatum L. | |
| |
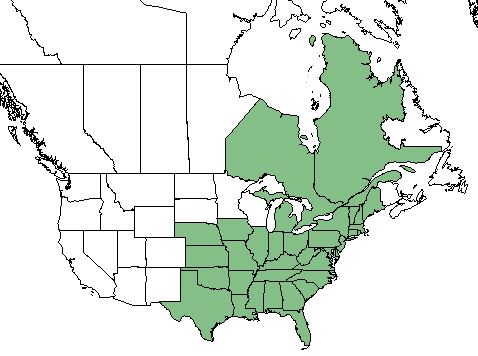
| Natural range of Desmodium paniculatum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): Panicledleaf Ticktrefoil[1]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: Meibomia chapmanii (Britton) Small; D. paniculatum (Linnaeus) A.P. de Candolle var. pubens Torrey & A. Gray; Meibomia paniculata (Linnaeus) Kuntze; Meibomia pubens (Torrey & A. Gray) Rydberg
Varieties: D. paniculatum (Linnaeus) A.P. de Candolle var. paniculatum; D. paniculatum (Linnaeus) A.P. de Candolle var. epetiolatum Schubert
Description
Desmodium paniculatum is a facultative upland dioecious perennial forb/herb.[1] It uses low amounts of water, inhabits dry clay or loamy soils, and prefers intermediate levels of shade.[2] A study showed D. paniculatum to contain 24% and 9% more dry weight in 50% and 80% shade, respectively, than in full sun.[3]
Distribution
Desmodium paniculatum can be found from Texas to Nebraska, eastward to Florida, the Carolina's, and Pennsylvania, and northward into Michigan, New York, Maine and parts of eastern Canada.[1] In Alabama, D. paniculatum is the most common species of Desmodium found.[4] D. paniculatum var. epetiolatum is distributed from southeast Virginia to either southeast North Carolina or east South Carolina while the distribution of D. paniculatum var. paniculatum is more widespread from south Maine west to south Ontatio, Michigan, and Nebraska south to south Florida and Texas.[5]
Ecology
Habitat
D. paniculatum var. epetiolatum is found in bogs and pine savannas and flatwoods while D. paniculatum var. paniculatum can be found in woodland borders, fields, and disturbed areas.[5] It is also considered a characteristic species for pine-oak-hickory woodlands.[6] It is listed as a facultative upland species, where it is commonly found in non-wetland habitats, but can occasionally be found in wetlands.[1]
Phenology
D. paniculatum has been observed to flower between July and November, with peak inflorescence in September[5][7] with conspicuous purple colored flowers.[2] Flowering can be delayed and seed production reduced when grown in high densities where competition is prevalent.[8] Seed weights vary by a factor of about 4 due to difference in several interacting variables including nutrient intake, water availability, photoperiod, temperature, and grazing impact.[9]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by translocation on animal fur or feathers. [10] Fruit coats are covered with sticky trichomes that allow the seeds to stick to passing organisms and be carried off until they eventually fall off.[9][11]
Seed bank and germination
Seeds of D. paniculatum germinate above the ground (epigeal germination).[12] Germination rates averaged around 25%.[13] However, larger seeds have higher rates of germination than smaller seeds.[13][14] Rates of germination can also be increased to around 50% and 68% by article clipping or scarification/surface sterilization, respectively.[13]
Fire ecology
Desmodium paniculatum has lower nitrogen concentrations in its tissues 1 year after burning than 3 years after.[15]
Pollination
The following bees in the Hymenoptera family are known to pollinate this species: Bombus impatiens, Bombus pensylvanica, Megachile brevis brevis, Megachile mendica, Megachile petulans, Melissodes bimaculata bimaculata, Nomia nortoni nortoni, and Calliopsis andreniformis.[16]
Use by animals
D. paniculatum produces seeds which attract birds and small rodents, including upland game birds such as bobwhite quail and wild turkey and rodents such as the white-footed mouse and deer mouse. It also serves as a source of food for cottontail rabbits, livestock, and other hoofed mammalian herbivores including white tailed deer.[17] Caterpillars of the following butterflies are known to feed on the plant: Hoary Edge (Achalarus lyciades), Silver-Spotted Skipper (Epargyreus clarus), Southern Cloudywing (Thorybes bathyllus), Northern Cloudywing (Thorybes pylades), Eastern Tailed Blue (Everes comyntas), and Gray Hairstreak (Strymon melinus). Other insects that feed on this plant include beetles, some thirps, aphids, stinkbugs, and moth caterpillars. Historically, D. paniculatum was used by the Houma Indians in Louisiana for an infusion of the roots with whiskey to treat cramps and weakness.[16]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 30 November 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Plant database: Desmodium paniculatum. (12 December 2017).Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=DEPA6
- ↑ Lin C. H., McGraw R. L., George M. F., and Garrett H. E. (1999). Shade effects on forage crops with potential in temperate agroforestry practices.
- ↑ Woods M. (2008). Then genera Desmodium and Hylodesmum (Fabaceae) in Alabama. Castanea 73(1):46-69.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Clewell A. F. (2013). Prior prevalence of shortleaf pine-oak-hickory woodlands in the Tallahassee red hills. Castanea 78(4):266-276.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 11 DEC 2017
- ↑ Wulff R. D. (1986). Seed size variation in Desmodium paniculatum: III. Effects on reproductive yield and competitive ability. Journal of Ecology 74(1):115-121.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Wulff R. D. (1986). Seed size variation in Desmodium paniculatum: I. Factors affecting seed size. Journal of Ecology 74(1):87-97.
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Isely D. (1953). Desmodium paniculatum (L.) DC. and D. viridiflorum (L.) DC. The American Midland Naturalist. 49(3):920-933.
- ↑ Wulff R. D. (1985). Effect of seed size on heteroblastic development in seedlings of Desmodium paniculatum.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Dormancy, small seed size and low germination rates contribute to low recruitment in Desmodium cuspidatum (Fabaceae). The Journal of the Torrey Botanical Society 137(4):355-365.
- ↑ Wulff R. D. (1986). Seed size variation in Desmodium paniculatum: II. Effects on seedling growth and physiological performance. Journal of Ecology 74(1):99-114.
- ↑ Lajeunesse S. D., Dilustro J. J., Sharitz R. R., and Collins B. S. (2006). Ground layer carbon and nitrogen cycling and legume nitrogen inputs following fire in mixed pine forests. American Journal of Botany 93(1):84-93.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Kirk, S. and Belt, S. 2009. Plant fact sheet for Panicledleaf Ticktrefoil (Desmodium paniculatum), USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, Norman A. Berg National Plant Materials Center, Beltsville, 20705.
- ↑ Leif J. and Belt S. (2013). Plant Guide for Panicledleaf ticktrefoil (Desmodium paniculatum), USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service, Rose Lake Plant Materials Center, East Lansing, Michigan, 48823 and USDA-Natural Resources Conservation Service Norman Berg National Plant Materials Center, Beltsville, Maryland, 20705.