Difference between revisions of "Ceanothus microphyllus"
(→Distribution) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat===<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat===<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | This species has been found in open longleaf pine-wiregrass savannahs, sandhills, ridges, slopes, and wetlands. It has been observed to grow in well-drained dry loamy sands in the uplands as well as mesic environments. Associated species include ''Pinus palustris'' and ''Aristida stricta.''<ref name="fsu"/><ref name= "Weakley>Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> | + | This species has been found in open longleaf pine-wiregrass savannahs, sandhills, ridges, slopes, and wetlands. It has been observed to grow in well-drained dry loamy sands in the uplands as well as mesic environments. Associated species include ''Pinus palustris'' and ''Aristida stricta.''<ref name="fsu"/><ref name= "Weakley">Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Revision as of 13:26, 3 April 2019
| Ceanothus microphyllus | |
|---|---|
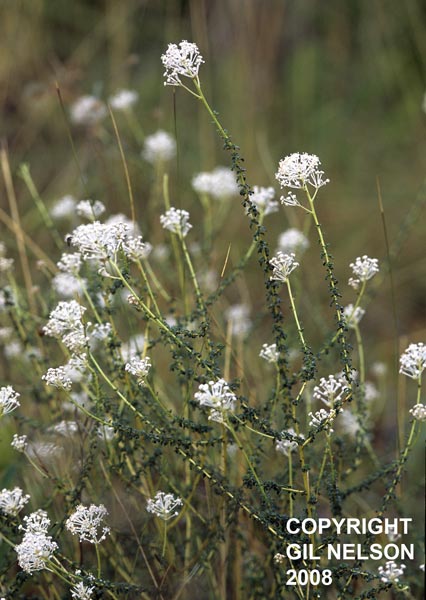

| |
| Photo by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Rhamnales |
| Family: | Rhamnaceae |
| Genus: | Ceanothus |
| Species: | C. microphyllus |
| Binomial name | |
| Ceanothus microphyllus Michx. | |
| |
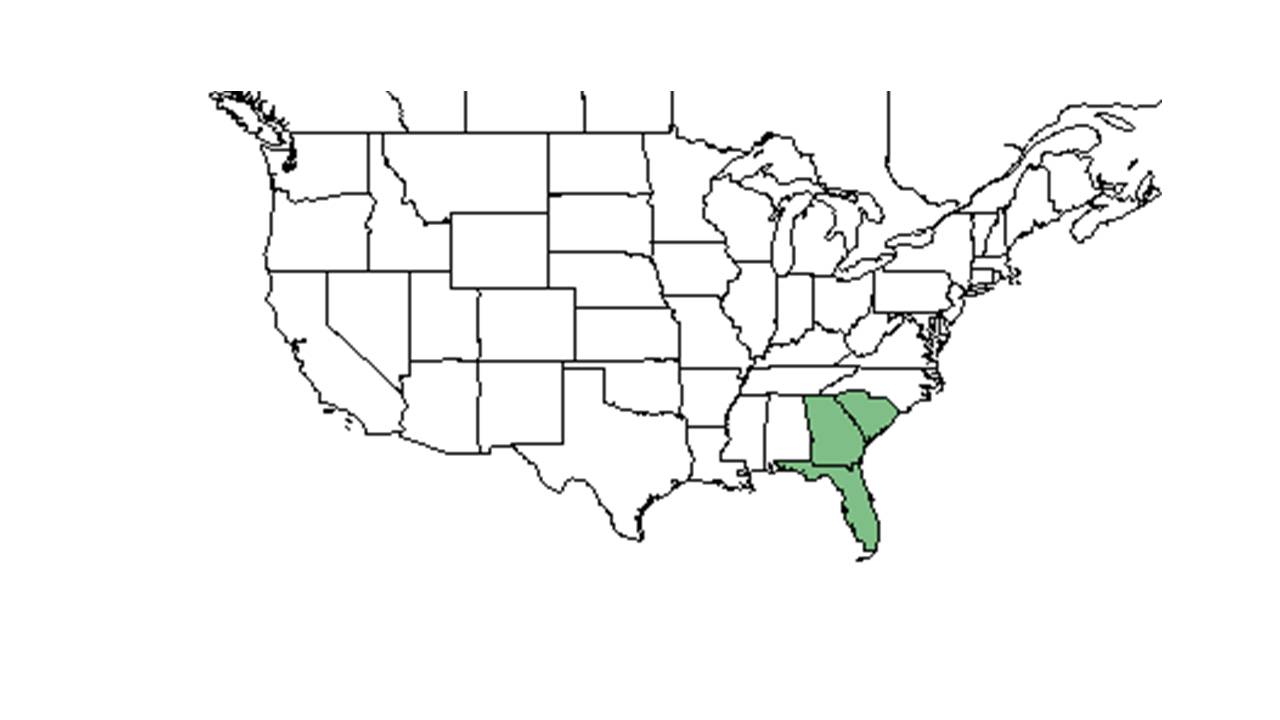
| Natural range of Ceanothus microphyllus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Littleleaf Buckbrush
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none
Varieties: none
The specific epithet refers to the reduced leaves that are tiny rounded nubs.[1]
Description
This species has been observed to have several main branches near the base.[2]
Distribution
It is found in Alabama, Georgia, and Florida. It is listed as vulnerable in Alabama and Georgia.[3] Weakley notes that C. microphyllus is found a few kilometers away from the South Carolina border, and may spread to that state.[4]
Ecology
Habitat
This species has been found in open longleaf pine-wiregrass savannahs, sandhills, ridges, slopes, and wetlands. It has been observed to grow in well-drained dry loamy sands in the uplands as well as mesic environments. Associated species include Pinus palustris and Aristida stricta.[2][4]
Phenology
C. microphyllus has been observed flowering from March to May and also in July with peak inflorescence in April.[5]
Seed dispersal
This species is thought to be dispersed by ants and/or explosive dehiscence. [6]
Fire ecology
This species occurs in mature longleaf pine communities that are frequently burned.[2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ [[1]]. Native Florida Wildflowers. Accessed: April 12, 2016
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, R. A. Norris, Andre F. Clewell, Robert K. Godfrey, Steve L. Orzell, R. Komarek and Helen Roth. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Liberty, and Wakulla. Georgia: Decatur, Grady, and Thomas.
- ↑ [[2]]NatureServe. Accessed: April 12, 2016
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 7 DEC 2016
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.