Difference between revisions of "Carex glaucescens"
(→Description) |
(→Conservation and Management) |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
| + | It is listed as endangered by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources.<ref name ="USDA"/> | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
Revision as of 13:13, 1 April 2019
Common Names: Southern Waxy Sedge; Blue Sedge[1]
| Carex glaucescens | |
|---|---|
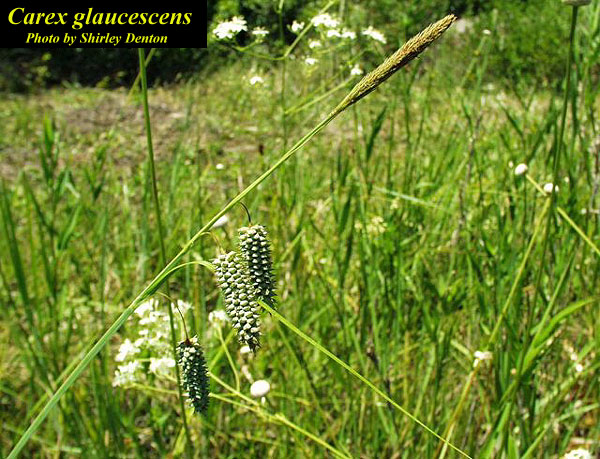

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Carex |
| Species: | C. glaucescens |
| Binomial name | |
| Carex glaucescens Elliot | |
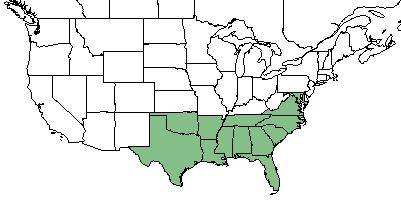
| |
| Natural range of Carex glaucescens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms:none
Varieties:none
Description
C. glaucescens is a perennial graminoid in the Cyperaceae family that is native to North America. [1]
Distribution
C. glaucescens is found in the southeastern United States. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
Common habitats for C. glaucescens is wetlands such as cypress and pine swamps, burned wetland pine savannas, and other swampy wetlands. [2]
C. glaucescens is considered an indicator species of common wetland habitats. [3]
Specimens of C. glaucescens have been collected from habitats such as wet pine flatwoods, wet sands of sypress pond swamps, burned over cypress gum swamps, pine wetlands, wet roadside ditch, edge of creek on pine savanna, and marshy shore of lakes. [4]
Phenology
C. glaucescens has been observed to flower in July, with some instances of earlier and later flowering during the rest of the summer months. [5]
Conservation and Management
It is listed as endangered by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources.[1]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 USDA Plant Database Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "USDA" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ FSU Herbarium
- ↑ Carr, S. C., et al. (2010). "A Vegetation Classification of Fire-Dependent Pinelands of Florida." Castanea 75(2): 153-189.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Cecil Slaughter, R. Kral, R.K. Godfrey, L.P. Gilespie, P.L. Redfearn, Robert L. Lazor, Steve L. Orzell. Edwin L. Bridges, R.R. Smith, Sidney McDaniel, Jean W. Wooten, A. F. Clewell, E.A. Hebb, Gil Nelson, A. Gholson Jr., Loran Anderson, R.A. Norris, Rodie White, Marc Minno, Albert B. Pittman, Kathy A. Boyle, Sudie Thomas, Herrick H. K. Brown, Richard Carter. States and counties: Florida (Flager, Madison, Jefferson, Liberty, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, Gulf, Leon, Wakulla, Holmes, Washington, Calhoun, Franklin, Jackson, Walton, Gadsden, Escambia, Osceola, Baker, Hamilton) Georgia (Clinch, Grady, Thomas, Lowndes), South Carolina (Richland) North Carolina (Dare, Tyrrell)
- ↑ Nelson, G. PanFlora: Plant data for the eastern United States with emphasis on the Southeastern Coastal Plains, Florida, and the Florida Panhandle. www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ Accessed: 16 MAY 2018