Difference between revisions of "Axonopus fissifolius"
(→Conservation and Management) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
| − | ''A. fissifolius'' is designated as a weedy or invasive plant by the Hawaiian Ecosystems at Risk Project, Biological Resources Division. <ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> | + | ''A. fissifolius'' is designated as a weedy or invasive plant by the Hawaiian Ecosystems at Risk Project, Biological Resources Division.<ref name= "USDA Plant Database"/> For the most production and efficient harvest by livestock, grazing should be rotated each 30 to 40 days with no more than 50% of the current year's growth grazed.<ref name= "Magee"/> |
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
Revision as of 19:43, 25 March 2019
Common name: Common Carpetgrass
| Axonopus fissifolius | |
|---|---|

| |
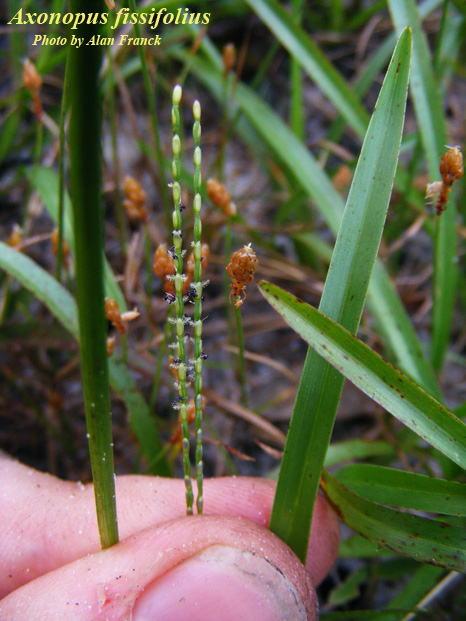
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Axonopus |
| Species: | A. fissifolius |
| Binomial name | |
| Axonopus fissifolius (Raddi) Kuhlmann | |
| |
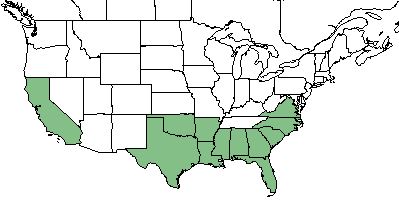
| Natural range of Axonopus fissifolius from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: Paspalum fissifolium Raddi; Axonopus affinis Chase
Varieties: none
Description
A. fissifolius is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family, is native to North America and Puerto Rico, and has been introduced to Hawaii. [1] Leaf blade can be flat or folded, fine hairs along margin near the base, slightly pointed or rounded, and purplish or reddish when mature. Seedhead has 3 slender racemes, 2 at summit and 1 (rarely 2) below.[2]
Distribution
A. fissifolius can be found in the southeastern United States from Texas to Virginia, California, Hawaii, and Puerto Rico. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
A. fissifolius is found in pine flatwoods, sandy forests, fields, roadsides, and lawns. [3] It has also been found in grassland areas with poor drainage, among other bunchgrasses. [4]
Phenology
A. fissifolius occurs more in spots where grazing and trampling were particularly heavy. [5]
Use by animals
A. fissifolius is rated as good forage. [6] It is grazed all year by various livestock.[2]
Conservation and Management
A. fissifolius is designated as a weedy or invasive plant by the Hawaiian Ecosystems at Risk Project, Biological Resources Division.[1] For the most production and efficient harvest by livestock, grazing should be rotated each 30 to 40 days with no more than 50% of the current year's growth grazed.[2]
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=AXFI
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Magee, P. (2005). Plant Fact Sheet: Common Carpetgrass Axonopus fissifolius. N.R.C.S. United States Department of Agriculture. Baton Rouge, LA.
- ↑ . Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Boughton, E., et al. (2013). "Season of fire and nutrient enrichment affect plant community dynamics in subtropical semi-natural grasslands released from agriculture." Biological Conservation 158: 239-247.
- ↑ Lewis, C. E. (1970). "Responses to chopping and rock phosphate on south Florida ranges " Journal of Range Management 23: 276-282.
- ↑ Hilmon, J. B. (1964). "Plants of the Caloosa Experimental Range " U.S. Forest Service Research Paper SE-12