Difference between revisions of "Paspalum laeve"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
| − | Common Names: field paspalum <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> | + | Common Names: field paspalum <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref>, field crowngrass <ref name="orzell">Orzell, S. L. and E. L. Bridges (2006). "Floristic composition of the south-central Florida dry prairie landscape." Florida Ecosystem 1(3): 123-133.</ref> |
<!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
Revision as of 18:55, 18 June 2018
Common Names: field paspalum [1], field crowngrass [2]
| Paspalum laeve | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Keith Bradley hosted at Atlas of Florida Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Paspalum |
| Species: | P. laeve |
| Binomial name | |
| Paspalum laeve Michx. | |
| |
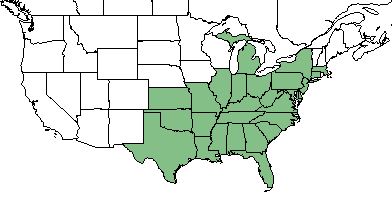
| Natural range of Paspalum laeve from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: P. longipilum(Nash)
Variety: Paspalum laeve var. circulare (Nash) Stone
Description
P. laeve is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family that is native to North America. [1]
Distribution
P. laeve is found throughout the southeastern United States, reaching as far north as New York and Michigan, and as far west as Texas and Kansas. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
This perennial grass is commonly found on forest edges, and disturbed areas. [3] Specimens have been colelcted from habitats that include moist loamy sands at the edges of a pond, grassy slopes of a roadside ditch, open pine/oak flatwoods, coastal hammocks, open margin of a swamp, dried up pond bottoms, wet sands od a marsh, small swale, wiregrass palmetto flatwoods, cypress pond, low field, and old pasture. [4]
The grass has a intermediate level of shade and drought tolerance. [1]
Phenology
P. laeve flowers infrequently during June and September.[5]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Orzell, S. L. and E. L. Bridges (2006). "Floristic composition of the south-central Florida dry prairie landscape." Florida Ecosystem 1(3): 123-133.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Wilson Baker, R.K. Godfrey, R. Kral, P.L. Redfearn, Sidney McDaniel, William Adams, C.V. Piper, R.A. Pursell, D.L. Martin, S. T. Cooper, A.H. Curtis, Allen Shuey, R. Norris, Cecil Slaughter, John B.. Nelson, Steve Bennett, P. Ferral, A. Williams, Danielle Dodier. States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Jackson, Bay, Liberty, Nassau, Taylor, Okaloosa, Brevard, Escambia, Madison, Leon, Charlotte, Jefferson, Marion, Manatee, Duval, Calhoun, Washington) Georgia (Clinch, Charlton, Thomas) South Carolina (Berkeley) Texas (Madison)
- ↑ Pan Flora