Difference between revisions of "Cyperus haspan"
(→Phenology) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{italic title}} | {{italic title}} | ||
| − | <!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> | + | Common names: Haspan flatsedge <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> , Shethed Flatsedge <ref name= "orzell" >Orzell, S. L. and E. L. Bridges (2006). "Floristic composition of the south-central Florida dry prairie landscape." Florida Ecosystem 1(3): 123-133. </ref><!-- Get the taxonomy information from the NRCS Plants database --> |
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| name = Cyperus haspan | | name = Cyperus haspan | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
===Habitat=== | ===Habitat=== | ||
Common habitats for ''C. haspan'' is in tidal marshes, low fields, ditches, and waterfowl impoundments. It requires full sunlight, it has littler tolerance for shaded regions.<ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> <ref name= "Weakley"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> | Common habitats for ''C. haspan'' is in tidal marshes, low fields, ditches, and waterfowl impoundments. It requires full sunlight, it has littler tolerance for shaded regions.<ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> <ref name= "Weakley"> Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Cyperus haspan'' has been found to grow well in subtropical and tropical climates and being of the most productive plants in the regions wetlands. <ref name= "akinbile"> Akinbile, C., et al. (2012). "Landfill leachate treatment using sub-surface flow constructed wetland by Cyperus | ||
| + | haspan." Elsevier. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Habitats also include wet prairies, broadleaf marshes, and wetland shrubs. They are found to germinate well in flooded environments. <ref name= "Wetzel"> Wetzel, P., et al. (2001). "Restoration of wetland vegetation on the Kissimmee River Floodplain: Potential role of seed banks." Wetlands 21(2): 189-198. </ref> | ||
<!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 19:48, 5 June 2018
Common names: Haspan flatsedge [1] , Shethed Flatsedge [2]
| Cyperus haspan | |
|---|---|

| |
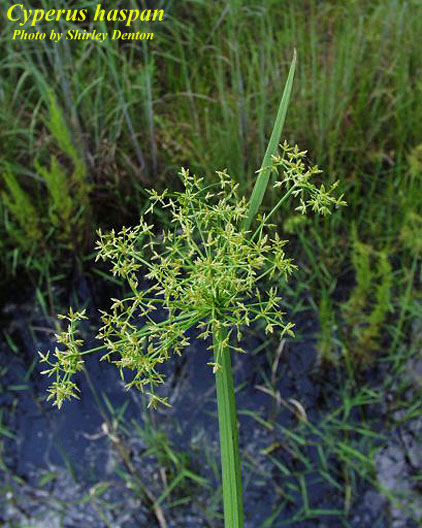
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Cyperaceae |
| Genus: | Cyperus |
| Species: | C. haspan |
| Binomial name | |
| Cyperus haspan L. | |
| |
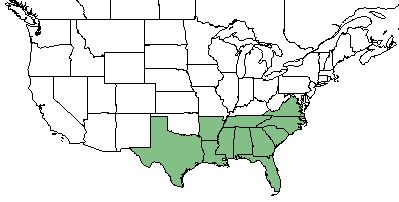
| Natural range of Cyperus haspan from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: none
Variety: C. americanus (Böckler)
Description
C. haspan is a perennial graminoid of the Cyperaceae family that is native to North America. [1]
Distribution
C. haspan is distributed across the southeastern region of the United States; from Florida north to Virginia and west to Texas. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
Common habitats for C. haspan is in tidal marshes, low fields, ditches, and waterfowl impoundments. It requires full sunlight, it has littler tolerance for shaded regions.[1] [3]
Cyperus haspan has been found to grow well in subtropical and tropical climates and being of the most productive plants in the regions wetlands. [4]
Habitats also include wet prairies, broadleaf marshes, and wetland shrubs. They are found to germinate well in flooded environments. [5]
Phenology
C. haspan commonly flowers between April and September. Seeds begin to disperse during the summer months. [1] [6]
Fire ecology
Cyperus haspan has a tolerance for low intensity fires.[1]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Has been used in landfill restoration areas. [7]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 USDA Plant Database
- ↑ Orzell, S. L. and E. L. Bridges (2006). "Floristic composition of the south-central Florida dry prairie landscape." Florida Ecosystem 1(3): 123-133.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ Akinbile, C., et al. (2012). "Landfill leachate treatment using sub-surface flow constructed wetland by Cyperus haspan." Elsevier.
- ↑ Wetzel, P., et al. (2001). "Restoration of wetland vegetation on the Kissimmee River Floodplain: Potential role of seed banks." Wetlands 21(2): 189-198.
- ↑ Pan Flora
- ↑ [Akinbile, C., et al. (2012). "Landfill leachate treatment using sub-surface flow constructed wetland by Cyperus haspan." Elsevier.]