Difference between revisions of "Ctenium aromaticum"
(→Ecology) |
(→Ecology) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| − | Seed germination starts in Map and June that develop into stalks that produce plentiful seeds. | + | Seed germination starts in Map and June that develop into stalks that produce plentiful seeds. <ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> |
===Fire ecology=== | ===Fire ecology=== | ||
| − | Seeds are produced after the region has been burned. | + | Seeds are produced after the region has been burned.<ref name= "USDA"> [https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=CEAM USDA Plant Database]</ref> |
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
===Use by animals=== | ===Use by animals=== | ||
Revision as of 19:53, 18 May 2018
| Ctenium aromaticum | |
|---|---|
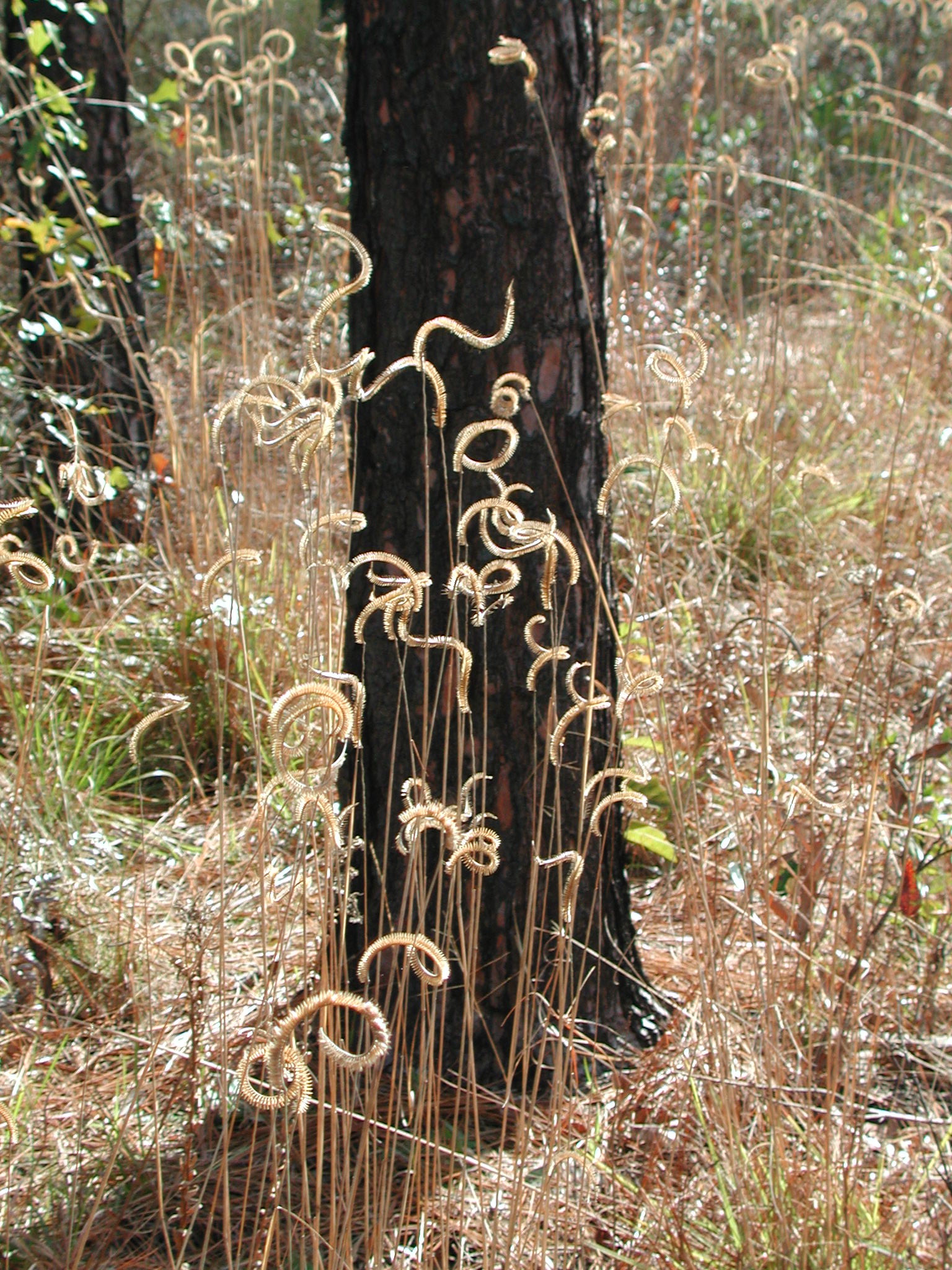

| |
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Ctenium |
| Species: | C. aromaticum |
| Binomial name | |
| Ctenium aromaticum Walter | |
| |
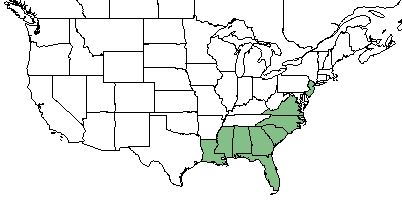
| Natural range of Ctenium aromaticum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: Campulosus aromaticus (Walter)
Variety: none
Description
C. aromaticum is a perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family native to North America. [1]
Distribution
C. aromaticum can be found in the southeastern part of the United States, specifically in Florida, Georgia, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana, South Carolina, North Carolina, and Virginia. [1]
Ecology
Habitat
Ideal habitats for the C. aromaticum are in moist clay that may have some standing water after heavy rains. It has adapted to extremely wet conditions with acidic soils. [1]
Seed bank and germination
Seed germination starts in Map and June that develop into stalks that produce plentiful seeds. [1]
Fire ecology
Seeds are produced after the region has been burned.[1]
Use by animals
This grass can be used for livestock to graze on. [1]