Difference between revisions of "Nothoscordum bivalve"
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, ''N. bivalve'' flowers from mid-March through mid-May and in September through December. Fruiting occurs in May through June and from October through January.<ref name=Weakley 2015"/> | + | In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, ''N. bivalve'' flowers from mid-March through mid-May and in September through December. Fruiting occurs in May through June and from October through January.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/> |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
Revision as of 12:00, 8 February 2018
| Nothoscordum bivalve | |
|---|---|

| |
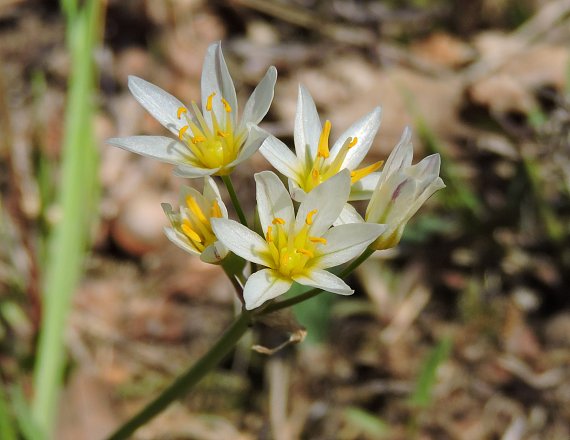
| Photo from the Illinois Wildflowers Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Liliaceae |
| Genus: | Nothoscordum |
| Species: | N. bivalve |
| Binomial name | |
| Nothoscordum bivalve L. | |
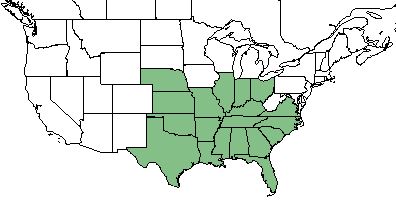
| |
| Natural range of Nothoscordum bivalve from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: grace garlic; false garlic;[1] crowpoison[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym: Allium bivalve[1]
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
N. bivalve occurs around granite flatrocks, in various glades and barrens, open woodlands, along roadsides, and in fields.[1]
Phenology
In the southeastern and mid-Atlantic United States, N. bivalve flowers from mid-March through mid-May and in September through December. Fruiting occurs in May through June and from October through January.[1]