Difference between revisions of "Cuscuta compacta"
(→Ecology) |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
In the southern and mid-Atlantic United States, ''C. compacta'' flowers from late July through November.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/><ref name="PanFlora">Nelson G (24 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/</ref> | In the southern and mid-Atlantic United States, ''C. compacta'' flowers from late July through November.<ref name="Weakley 2015"/><ref name="PanFlora">Nelson G (24 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/</ref> | ||
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| + | In Virginia, ''C. compacta'' has a very high percentage of seed set.<ref name="Musselman 1986"/> | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Pollination=== | ||
| + | While other species of ''Cuscuta'' are well adapted for insect pollination, ''C. compacta'' is well developed for autogamy.<ref name="Musselman 1986"/> | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 13:36, 25 January 2018
| Cuscuta compacta | |
|---|---|
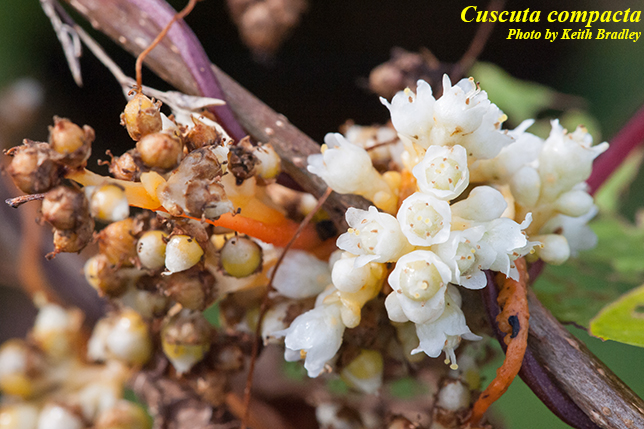

| |
| Photo by the Atlas of Florida Plants Database | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Cuscutaceae |
| Genus: | Cuscuta |
| Species: | C. compacta |
| Binomial name | |
| Cuscuta compacta Juss | |
| |
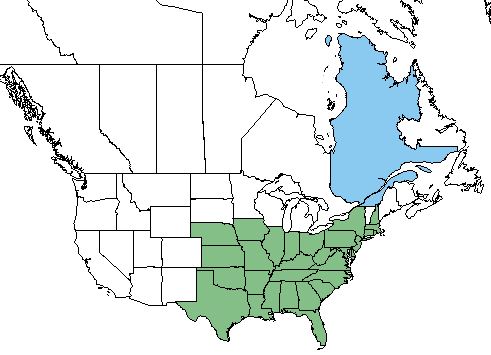
| Natural range of Cuscuta compacta from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name: compact dodder[1][2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Varieties: C. compacta var. compacta; C. compacta var. efimbriata[1][2]
Description
C. compacta is a parasitic dioecious perennial that grows as a forb/herb or a vine.[2] Stems are more than 2 mm in diameter. This species is typically a light green color, but there is considerable variation within the species.[3]
Distribution
C. compacta occurs from Nebraska, south to Texas, eastward to central peninsular Florida, and northward to Illinois, New York, and New Hampshire.[1][2] It has also been introduced in Quebec Canada.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
C. compacta is found on herbaceous and woody hosts in bottomland forests, stream banks, marshes, swamps, pine savannahs, wet fields, and other wet habitats.[1] This species has been reported parasitizing Vaccinium ashei and V. corymbosum in North Carolina[4] and Citrus sinensis in Florida.[5]
Phenology
In the southern and mid-Atlantic United States, C. compacta flowers from late July through November.[1][6]
===Seed bank and germination===--> In Virginia, C. compacta has a very high percentage of seed set.[3]
Pollination
While other species of Cuscuta are well adapted for insect pollination, C. compacta is well developed for autogamy.[3]
Use by animals
Pawnee Indians would use C. compacta to dye materials, such as feathers, orange. Maidens of the Pawnee would also use the parasite for divination to determine if their suitors sincerely loved them. A Mexican Indian has reported that rattlesnakes would take this plant into their dens for food.[7]
Diseases and parasites
C. compacta is reported to transmit the psorosis virus to 5% of sweet orange (Citrus sinensis) tested.[5]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 24 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Musselman LJ (1986) The genus Cuscuta in Virginia. Castanea 51(3):188-196.
- ↑ Monaco TJ, Mainland CM (1981) Cuscuta compacta on blueberries in North Carolina. Haustorium, Parasitic Plants Newsletter 7:1.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Price WC (1965) Transmission of psorosis virus by dodder. International organization of citrus virologists conference proceedings (1957-2010) 3(3):162-166.
- ↑ Nelson G (24 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/
- ↑ Gilmore MR (1919) Uses of plants by the indians of the Missouri river region. Smithsonian Institution, Bureau of American Ethnology, Annual Report 33.