Difference between revisions of "Smilax smallii"
(→Taxonomic Notes) |
|||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| + | ''S. smallii'' comprises 5-10% of the diets of large mammals, small mammals, and terrestrial birds.<ref name="Miller & Miller 1999">Miller JH, Miller KV (1999) Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Revision as of 14:01, 22 January 2018
| Smilax smallii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney hosted at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Smilacaceae |
| Genus: | Smilax |
| Species: | S. smalliis |
| Binomial name | |
| Smilax smallii Morong | |
| |
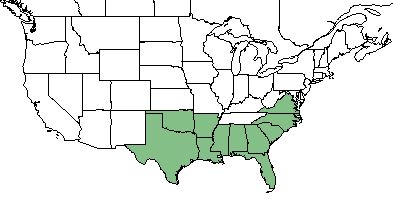
| Natural range of Smilax smallii from USDA NRCS [1]. | |
Common Name(s): Jackson-briar;[1] lanceleaf greenbrier[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym(s): S. maritima;[1] S. domingensis; S. lanceolata[2]
Description
Smilax smallii is a monoecious perennial that grows as a shrub or vine.[2]
Distribution
This species primarily occurs on the coastal plain from Virginia, south to central peninsular Florida, westward to Texas.[1][2] It can also be found in Puerto Rico.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
S. smallii is found in bottomland forests.[1]
Phenology
Flowering occurs from May through July[1][3] and fruits from April to June of the following year.[1]
Use by animals
S. smallii comprises 5-10% of the diets of large mammals, small mammals, and terrestrial birds.[4]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 22 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Nelson G (22 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/
- ↑ Miller JH, Miller KV (1999) Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.