Difference between revisions of "Sorghastrum nutans"
(→Cultivation and restoration) |
|||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
| + | Seeds collected in the fall can be propagated by sowing unstratified seeds in the fall or stratified seeds in the spring. Seeds require dry stratification.<ref name="Ladybird"/> | ||
| + | |||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Revision as of 14:37, 17 January 2018
| Sorghastrum nutans | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Hilty hosted at IllinoisWildflowers.info | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Sorghastrum |
| Species: | S. nutans |
| Binomial name | |
| Sorghastrum nutans (L.) Nash | |
| |
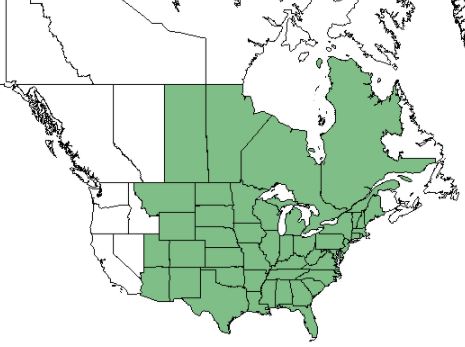
| Natural range of Sorghastrum nutans from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): yellow indiangrass;[1] indiangrass[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym(s): S. avenaceum;[1][2] Andropogon nutans[2]
Description
Sorghastrum nutans is a monoecious perennial graminoid.[2] It is a bunching sod-forming grass with broad blue-green blades and soft plume-like golden-brown seed heads. This species can reach heights of 3-8 ft (0.91-2.44 m).[3]
Distribution
This species can be found in 42 of the 48 lower United States, from Arizona, northward through Utah, Wyoming, and Montana, and all states eastward. It also occurs in parts of Quebec, Ontario, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan provinces of Canada and in Mexico.[1][2]
Ecology
Habitat
It is one of the dominant grasses of tall-grass prairies but can be found in xeric and mesic woodlands and forests, along powerline right-of-ways and roadbanks, and in open habitats and forested landscapes.[1]
Phenology
Flowering occurs from late August through October.[1] A report of flowering in November also exists.[4]
Use by animals
This species provides nesting material and structure for native bees to build their nests. Caterpillars, including those of the pepper and salt skipper (Amblyscirtes hegon) use it for food.[3]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Seeds collected in the fall can be propagated by sowing unstratified seeds in the fall or stratified seeds in the spring. Seeds require dry stratification.[3]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 17 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Plant database: Sorghastrum nutans. (17 January 2018) Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=SONU2
- ↑ Nelson G (17 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/