Difference between revisions of "Steinchisma hians"
(→Taxonomic Notes) |
(→Ecology) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
<!--===Pollination===--> | <!--===Pollination===--> | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| + | This grass is considered one of the top forage grasses in Louisiana woodlands.<ref name="Shiflet 1963">Shiflet TN (1963) A conservation program for grazing woodlands in the southeast. Journal of Range Management 16(1):18-21.</ref> | ||
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Revision as of 14:02, 16 January 2018
| Steinchisma hians | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John Gwaltney hosted at Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Steinchisma |
| Species: | S. hians |
| Binomial name | |
| Steinchisma hians (Elliott) Nash | |
| |
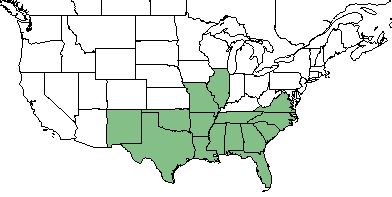
| Natural range of Steinchisma hians from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): gaping panic grass;[1] gaping grass[2]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonym(s): Panicum hians[1][2]
Description
Steinchisma hians" is a monoecious perennial graminoid.[2]
Distribution
S. hians is found from southeastern Virginia, south to Florida, west to Texas and Oklahoma, and south through Mexico and central America to Colombia. It is also found in southern South America.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
This species is found along the shores of streams, ponds, and lakes, as well as in low woods, cypress-gum ponds, floodplains, marshes, ditches, and seepage slopes.[1]
Phenology
Flowering occurs from May through October.[1]
Use by animals
This grass is considered one of the top forage grasses in Louisiana woodlands.[3]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley AS (2015) Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 USDA NRCS (2016) The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 16 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ Shiflet TN (1963) A conservation program for grazing woodlands in the southeast. Journal of Range Management 16(1):18-21.