Difference between revisions of "Tephrosia virginiana"
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| − | ''T. virginiana'' comprises 2-5% of the diets of some large mammals and terrestrial birds.<ref name="Miller & Miller 1999">Miller JH, Miller KV (1999) Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> | + | ''T. virginiana'' comprises 2-5% of the diets of some large mammals and terrestrial birds.<ref name="Miller & Miller 1999">Miller JH, Miller KV (1999) Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.</ref> In the past, it was used as a goat feed to increase milk production. However, this use stopped after tephrosin, an insecticide and fish poison, was found in it.<ref name="Ladybird"/> |
<!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | <!--==Diseases and parasites==--> | ||
Revision as of 14:17, 12 January 2018
| Tephrosia virginiana | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicots |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Genus: | Tephrosia |
| Species: | T. virginiana |
| Binomial name | |
| Tephrosia virginiana (L.) Pers. | |
| |
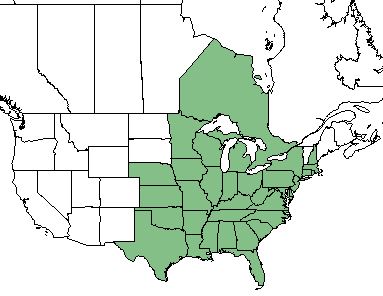
| Natural range of Tephrosia virginiana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): Virginia goat's-rue;[1] Virginia tephrosia;[2][3] goat's rue; devil's shoestring[3]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Varieties: T. virginiana var. glabra; T. virginiana var. virginiana[1]
Synonym(s): Cracca virginiana;[1][2] Cracca latidens; T. latidens[2]
Description
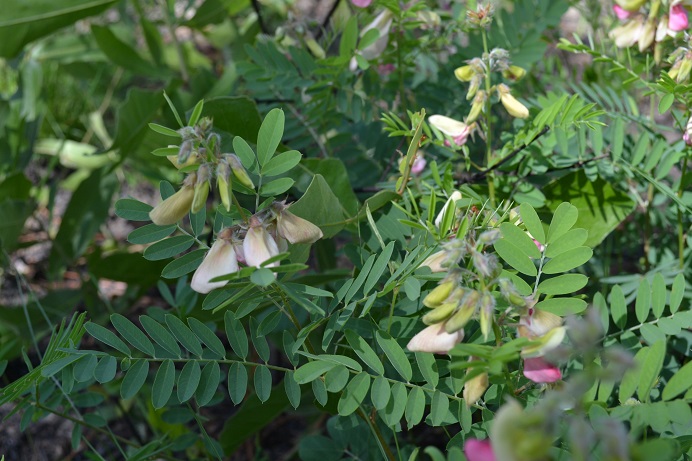
Tephrosia virginiana is covered with soft white hairs, which makes it silvery green in appearance. It grows to 1-3 ft (0.30-0.91 m) and has long stringy roots, from which it gets the name devil's shoestring. Leaves are pinnately compound with 8-15 pairs of leaflets. Flowers are bi-colored with pink and pale yellow and typically cluster at the tip of the stem. In southern portions of its range, flowers can initially be white but will change over time.[3]
Distribution
This species is found from Texas, eastward to Florida, northward to New Hampshire and New York, and inland to Minnesota and Nebraska.[1][2] It is also reported to occur in the Ontario province of Canada.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
T. virginiana is found in sandhills, other pinelands, xeric or rocky woodlands and forests, outcrops, shale barrens, other barrens, and dry roadbanks.[1]
Phenology
Flowering occurs from April through June.[1][4] Fruiting occurs from July through October.[1]
Use by animals
T. virginiana comprises 2-5% of the diets of some large mammals and terrestrial birds.[5] In the past, it was used as a goat feed to increase milk production. However, this use stopped after tephrosin, an insecticide and fish poison, was found in it.[3]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 12 January 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Plant database: Tephrosia virginiana. (12 January 2018) Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center. URL: https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=TEVI
- ↑ Nelson G. (12 January 2018) PanFlora. Retrieved from gilnelson.com/PanFlora/
- ↑ Miller JH, Miller KV (1999) Forest plants of the southeast and their wildlife uses. Southern Weed Science Society.