Difference between revisions of "Dichanthelium villosissimum"
(→Description) |
|||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | ''D. villosissimum'' is a monoecious perennial graminoid | + | ''D. villosissimum'' is a monoecious perennial graminoid<ref name="USDA"/> that can be found growing in small clumps.<ref>McClain W. E., Phillippe L. R., and Ebinger J. E. (2005). Floristic assessment of the Henry Allan Gleason Nature Preserve, Mason County, Illinois. Castanea 70(2):146-154.</ref> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Revision as of 17:01, 7 December 2017
| Dichanthelium villosissimum | |
|---|---|
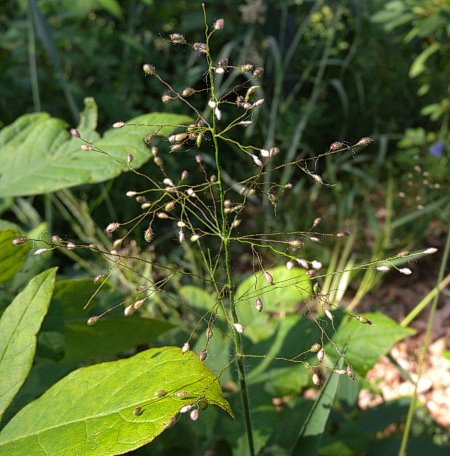

| |
| Photo by Illinois Wildflowers | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae - Grasses |
| Genus: | Dichanthelium |
| Species: | D. villosissimum |
| Binomial name | |
| Dichanthelium villosissimum (Nash) | |
| |
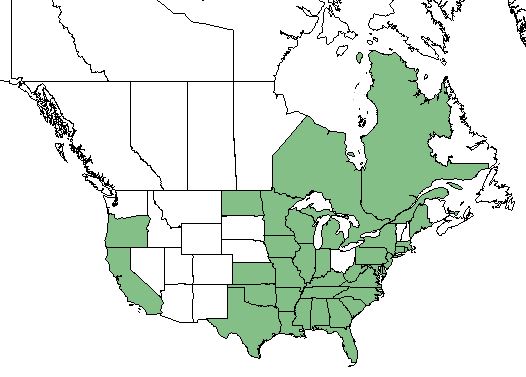
| Natural range of Dichanthelium villosissimum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name(s): white-haired witchgrass, whitehair rosette grass[1][2], hairy panic grass[3]
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Variation(s): Dichanthelium villosissimum var. villosissimum; D. villosissimum var. praecocius[1][2]
Description
D. villosissimum is a monoecious perennial graminoid[2] that can be found growing in small clumps.[4]
Distribution
This species is found from Maine and Massachusetts south to Florida and westward to Texas, the Dakota's, Nebraska, Kansas, and Oklahoma. It is also recorded in Oregon and California as well as eastern Canada and parts of Mexico and Mesoamerica.[1][2]
Ecology
Habitat
D. villosissimum is found in dry sandy soils of open woodlands and prairies.[1] In a study comparing mature dry sand prairies, 60 yr and 30 yr successional fields, frequency and average cover decreased with decreasing length of establishment. This suggests it colonizes slowly compared to other species.[3]
Phenology
Flowering and fruiting occur between April and September.[1]
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Weakley A. S.(2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC: University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 USDA, NRCS. (2016). The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 7 December 2017). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 McClain W. E., Schwegman J. E., Strole T. A., Phillippee L. R., and Ebinger J. E. (2008). Floristic study of sand prairie-scrub oak nature preserve, Mason County, Illinois. Castanea 73(1):29-39
- ↑ McClain W. E., Phillippe L. R., and Ebinger J. E. (2005). Floristic assessment of the Henry Allan Gleason Nature Preserve, Mason County, Illinois. Castanea 70(2):146-154.