Difference between revisions of "Vigna luteola"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) (→Taxonomic notes) |
||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
Synonyms: ''Vigna repens'' (Linnaeus) Kuntze; ''Vigna marina'' (Burmann) Merrill | Synonyms: ''Vigna repens'' (Linnaeus) Kuntze; ''Vigna marina'' (Burmann) Merrill | ||
| − | It is a member of the papilionoideae subfamily of the Fabaceae family<ref name="eol">[[http://eol.org/pages/649089/details]]Encyclopedia of Life. Accessed: March 21, 2016</ref> | + | It is a member of the papilionoideae subfamily of the Fabaceae family.<ref name="eol">[[http://eol.org/pages/649089/details]]Encyclopedia of Life. Accessed: March 21, 2016</ref> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
Revision as of 18:55, 18 August 2016
| Vigna luteola | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by John R. Gwaltney, Southeastern Flora.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Vigna |
| Species: | V. luteola |
| Binomial name | |
| Vigna luteola (Jacq.) Benth. | |
| |
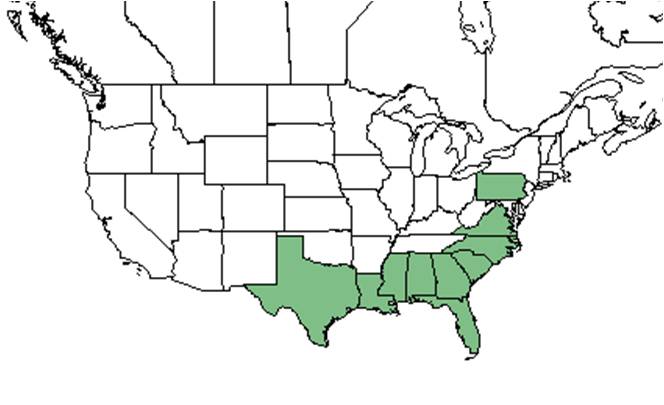
| Natural range of Vigna luteola from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: hairypod cowpea
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Vigna repens (Linnaeus) Kuntze; Vigna marina (Burmann) Merrill
It is a member of the papilionoideae subfamily of the Fabaceae family.[1]
Description
"Annual or perennial, trailing or climbing herbaceous vines (or occasionally erect). Leaves pinnately 3-foliolate; leaflets entire, stipellate. Racemes axillary usually long-pedunculate, with few to several closely clustered, papilionaceous flowers subtended by small, caduceus bracts and with paired, caduceus bractlets at or near the tops of the pedicels. Calyx campanulate, somewhat 2-lipped, the upper lobes partly or completely united, longer than the lateral but shorter than the lowermost lobe; petals yellow or purple, the keel petals curved but not spirally coiled, about as long as the wings and shorter than the auriculate standard; stamens diadelphous, 9 and 1; ovary sessile, style bearded along the upper surface. Legume linear, terete or slightly compressed." [2]
"Perennial with glabrous to retrorsely pubescent stems, 1-3 m long. Leaflets ovate or more commonly lanceolate to linear-lanceolate, 2-8 cm long, both surfaces more or less sparsely appressed-pubescent; stipules ovate-lanceolate to lanceolate, not extending below the point of attachment. Racemes on elongate peduncles usually several times longer than the subtending leaves and terminated by few to several, closely clustered flowers on retrorsely pubescent pedicels 1-3 mm long subtended by pubescent bracts 1-1.5 mm long and with pairs of 1-nerved, pubescent bractlets 1-1.5 mm long. Calyx the upper lobes united, 2 mm long, the lateral lobes ca. 1.5 mm long and the lowermost ca. 2.5 mm long; petals yellow, 1.4-1.8 cm long. Legume linear, 4-6.5 cm long, appressed-pubescent." [2]
Distribution
Found in the southeastern U.S., Texas; West Indies, Mexico, Central and South America[3].
Ecology
Habitat
Vigna luteola occurs along bays, river banks, palmetto hammocks, bordering mangrove swamps, lagoon shores, salt marsh banks, scrub oak-palmetto near the coast, along seepage slopes, and coastal sea oats grasslands. It has also can be found in disturbed areas such as cleared borders of slash pine flatwoods and disturbed beaches[4]. It can be used as a short term legume in pastures, green manure, or as ley in croplands[5]. Prefers moist soils which include loamy sand, sandy loam, and oyster shells[4]. It is a major component of intermediate marshes and can shade out other perennials[6]. This species nodulates freely and effectively and releases nitrogen when it dies that can improve the growth of associated grasses[7]. Associated species include Bidens laevis, Eupatorium perfoliatum, Aster puniceus, Rynchospora, Uniola paniculata, Helianthus debilis, and Paspalum[4].
Phenology
Flowers and fruits February through November[4].
It establishes a tripartite symbiosis with indigenous rhizobia and AM fungi for phosphorous uptake[8]. Hernandez et al. found that the most efficient fungus in promoting growth of V. luteola was Glomus mosseae[9].
Seed dispersal
The legume pods are dehiscent[5]. Animals who eat the legumes can spread the seed in dung under favorable conditions of warmth and moisture[7].
Fire ecology
It has been observed growing in recently burned pine woodlands[4].
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Vigna luteola at Archbold Biological Station. [10]
Halictidae: Halictus poeyi
Megachilidae: Anthidium maculifrons, Coelioxys sayi, Dianthidium floridiense, Megachile brevis pseudobrevis, M. exilis parexilis, M. mendica
Use by animals
V. luteola is a source of food for white-tailed deer[1].
Diseases and parasites
This species can suffer from damage from catterpillars (Prodenia spp.) and jassids (Cicadellidae: Homoptera). In Australia, it can suffer from the peanut mottle virus.[5]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
It can be used for as a short term legume in pastures, green manure, or ley in croplands[5].
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 [[1]]Encyclopedia of Life. Accessed: March 21, 2016
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 639. Print.
- ↑ [[2]]Regional Conservation. Accessed: March 21, 2016
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, K.E. Blum, Sidney T. Brinson, Jane Brockmann, D. Burch, A.F. Clewell, C. Craighead, M. Darst, Delzie Demaree, Robert K. Godfrey, James W. Hardin, W.F. Humphrey, Norlan C. Henderson, Ann F. Johnson, Robert Kral, R.L. Lazor, Robert J. Lemaire, H. Loftin, Sidney McDaniel, Mary E. Nolan, Jackie Patman, Elmer C. Prichard, Paul Redfearn, William Reese, Alberto S. Taylor, S.D. Todd, Alfred Traverse, Edwin L. Tyson, D.B. Ward, Sarah V. Yinger. States and Counties: Alabama: Baldwin. Florida: Bay, Brevard, Clay, Dade, Flagler, Franklin, Hillsborough, Indian River, Lee, Manatee, Monroe, Palm Beach, Pinellas, Putnam, Sarasota, Volusia. Countries: Panama. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 [[3]]Tropical Forages. Accessed: March 21, 2016
- ↑ White, D. A. and M. J. Simmons (1988). "Productivity of the Marshes at the Mouth of the Pearl River, Louisiana." Castanea 53(3): 215-224
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 [[4]]Accessed: March 21, 2016
- ↑ Izaguirre-Mayoral, M. L., S. Flores, et al. (2011). "Rhizophagus manihotis promotes the growth of rhizobia-nodulated Vigna luteola L in phosphorus deficient acid montane soils devoid of ground cover vegetation." Symbiosis 55(1): 1-9.
- ↑ Hernández, G., G. Cuenca, et al. "Behaviour of arbuscular-mycorrhizal fungi on Vigna luteola growth and its effect on the exchangeable (32P) phosphorus of soil." Biology and Fertility of Soils 31(3): 232-236.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.