Difference between revisions of "Licania michauxii"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | Habitats of ''L. michauxii'' include pine-palmetto woods; dry pine barrens; sandhills; scrub above wetland depression; shrubby boarders of depression marshes; and wooded slopes of ravines. It has been found in disturbed sites such as cutover flatwoods and dirt roads and is a good soil stabalizer <ref name="dave"/> | + | Habitats of ''L. michauxii'' include pine-palmetto woods; dry pine barrens; sandhills; scrub above wetland depression; shrubby boarders of depression marshes; and wooded slopes of ravines. It has been found in disturbed sites such as cutover flatwoods and dirt roads and is a good soil stabalizer.<ref name="dave"/> Associated species include ''Pinus palustris, Quercus laevis, Aristida stricta, Rhynchosia, Bumelia tenax, Juniperus silicicola, Myrica cerifera, Pinus clausa, Quercus geminata, Sabal palmetto'' and ''Chrysoma''. Soils include those of Astatula (Typic Quartzipsamments) and Paola (Spodic Quartzipsamments) types.<ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
In dense patches of ''L. michauxii'' hogs selectively forage and destroy lichens in large quantities. <ref name=hm> Hawkes, C. V. and E. S. Menges (2003). "Effects of Lichens on Seedling Emergence in a Xeric Florida Shrubland." Southeastern Naturalist 2(2): 223-234.</ref> | In dense patches of ''L. michauxii'' hogs selectively forage and destroy lichens in large quantities. <ref name=hm> Hawkes, C. V. and E. S. Menges (2003). "Effects of Lichens on Seedling Emergence in a Xeric Florida Shrubland." Southeastern Naturalist 2(2): 223-234.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 20:10, 17 August 2016
| Licania michauxii | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Chrysobalanaceae |
| Genus: | Licania |
| Species: | L. michauxii |
| Binomial name | |
| Licania michauxii Prance | |
| |
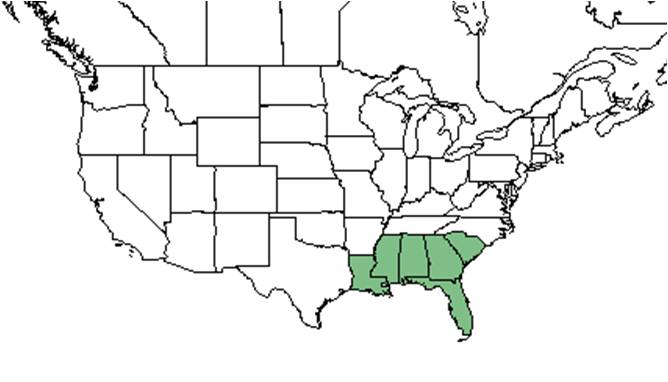
| Natural range of Licania michauxii from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: gopher apple
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Chrysobalanus oblongifolius Michaux; Geobalanus oblongifolius (Michaux) Small; Geobalanus pallidus Small
This species was named for the French botanist Andre Michaux, who discovered this plant in the late 1700's. [1]
Description
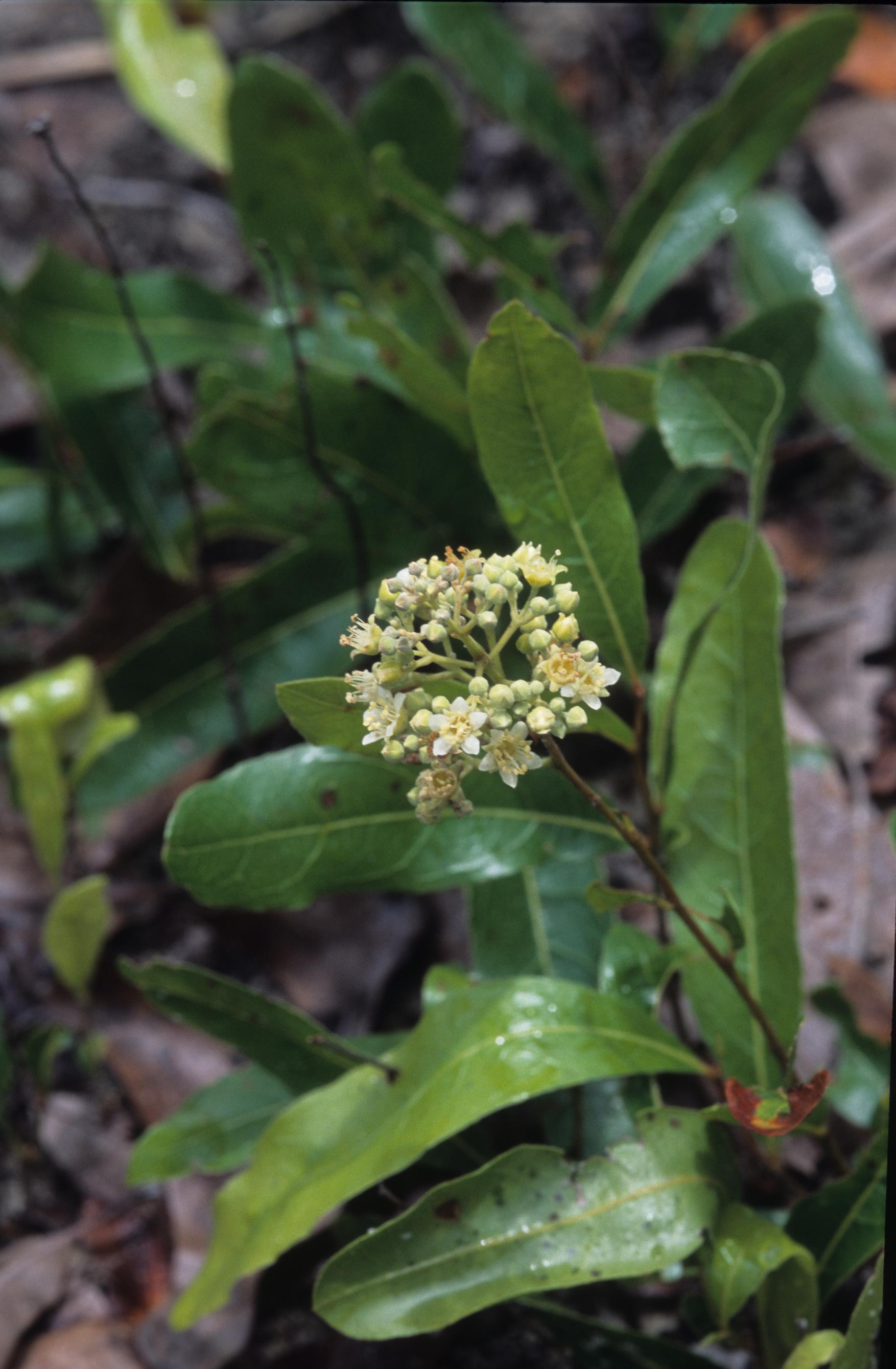
L. michauxii is a perennial, woody groundcover species, with mature stems only reaching 20 centimeters above the ground. [2] The leathery, long, dark green leaves makes this species resemble an oak seedling. [1] It is often found in thickets on poor, dry, sandy soils [3] and easily spreads by rhizomes that grow 1 to 10 centimeters below the soil (Bell and Taylor 1982, Taylor 1992). The flowers of L. michauxii are small, yellow, and clustered in triangular shaped terminal cymes. [4]
"Low shrub to ca. 4 dm tall, with an extensive underground stem system. The stems above ground very slender, rarely more than 5 mm in diam. While the underground stems frequently measures as much as 5 cm in diam. Leaves simple, alternate, evergreen, oblanceolate, 4-10 cm long, 1.3-5 cm wide, finely undulate, entire, glabrous and lustrous; stipules very small. Inflorescence a terminal panicle of cymes. Hypanthium and sepals pubescent. Sepals 1-1.5 mm long; petals white, 1.5-2.5 cm long, densely pubescent; stamens 10-15; style 1. Drupe ellipsoid, 2-3 cm long." [5]
Distribution
It is distributed throughout the southeastern U.S., south to Monroe County, Florida. The Monroe County population is disjunct from the Miami-Dade county to the pine rocklands of Big Pine Key. [6]
Ecology
Habitat
Habitats of L. michauxii include pine-palmetto woods; dry pine barrens; sandhills; scrub above wetland depression; shrubby boarders of depression marshes; and wooded slopes of ravines. It has been found in disturbed sites such as cutover flatwoods and dirt roads and is a good soil stabalizer.[3] Associated species include Pinus palustris, Quercus laevis, Aristida stricta, Rhynchosia, Bumelia tenax, Juniperus silicicola, Myrica cerifera, Pinus clausa, Quercus geminata, Sabal palmetto and Chrysoma. Soils include those of Astatula (Typic Quartzipsamments) and Paola (Spodic Quartzipsamments) types.[7]
In dense patches of L. michauxii hogs selectively forage and destroy lichens in large quantities. [8]
Phenology
Flowers March through June and fruits June through October. [7] The fruit is an elliptical drupe and is edible
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by being consumed by vertebrates (being assumed). [9]
Fire ecology
This species is found in habitats that experience fire annually or in long intervals. Ward and Taylor (1999) found a stand of L. michauxii that consists of many tree-form plants that reach over a meter tall. [10] This stand is found on Merritt Island on a narrow strip of land between Mosquito Lagoon to the east and the Indian River to the west and bounded by a dredge canal to the north. These surrounding features protect this stand from any naturally occurring wildfires and records show no historical fires in this area.
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Licania michauxii at Archbold Biological Station: [11]
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Epeolus glabratus, E. zonatus
Colletidae: Colletes sp. A
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochlorella aurata, Augochloropsis metallica, A. sumptuosa, Lasioglossum nymphalis, Sphecodes heraclei
Leucospididae: Leucospis robertsoni, L. slossonae
Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis, M. rugifrons
Pompilidae: Anoplius relativus, Paracyphonyx funereus
Sphecidae: Ammophila urnaria, Bembecinus nanus floridanus, Bembix sayi, Bicyrtes quadrifasciata, Cerceris blakei, C. flavofasciata floridensis, C. fumipennis, Microbembex monodonta, Stictiella serrata
Vespidae: Euodynerus castigatus rubrivestris, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus salcularis rufulus, Stenodynerus fundatiformis
Use by animals
The fruit is eaten by gopher tortoises, raccoons, opossums, and foxes. [12]
Diseases and parasites
Galls made by Lopesia can be found on the subterranean stems of the gopher apple. [2]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
This species tolerates a wide range of soil pH [13] but does not tolerate long term flooding by salt or brackish water. [6] It is extremely difficult to transplant.[12]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 [[1]] Eat the Weeds. Accessed: January 19, 2016
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Gagné, Raymond J., and Kenneth L. Hibbard. “A New Species of Cecidomyia (diptera: Cecidomyiidae) Feeding on Resin of Baldcypress”. The Florida Entomologist 91.3 (2008): 431–435.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 [[2]]Dave's Garden. Accessed: January 19, 2016
- ↑ [[3]] Floridata. Accessed: January 19, 2016
- ↑ Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 569. Print.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 [[4]] Accessed: January 19, 2016
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: Collectors: States and Counties: Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Hawkes, C. V. and E. S. Menges (2003). "Effects of Lichens on Seedling Emergence in a Xeric Florida Shrubland." Southeastern Naturalist 2(2): 223-234.
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.
- ↑ Ward, D. B. and W. K. Taylor (1999). "Discovery of Tree-Form Gopher Apple (Licania michauxii), with Implication of an Arboreous Ancestor." Castanea 64(3): 263-265.
- ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 [[5]] Sharon's Florida. Accessed: January 19, 2016
- ↑ [[6]] University of Florida Extension. Accessed: January 19, 2016