Difference between revisions of "Solidago auriculata"
(→Conservation and Management) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''S. auriculata'' can be found in limestone glades, limestone outcrops, limestone woodlands, in between limestone glades, mixed hardwood forests and oak-hickory woodlands | + | In the Coastal Plain in Florida, ''S. auriculata'' can be found in limestone glades, limestone outcrops, limestone woodlands, in between limestone glades, mixed hardwood forests and oak-hickory woodlands. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Angus Gholson, R. F. Thorne, R. A. Davidson, R. Kral, Ann F. Johnson, Wilson Baker. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Jackson. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> Substrates include dry loam, sandy loam, and calcareous areas. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> Associated species include ''Quercus, Carya, Schoenus nigricans, Aristida longespica, Houstonia nigricans, Rhynchospora divergens, Scleria verticillata,'' and ''Juniperus.'' <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | Flowers and fruits August through November | + | Flowers and fruits August through November. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
<!--===Seed dispersal===--> | <!--===Seed dispersal===--> | ||
<!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> | ||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
Revision as of 19:57, 8 August 2016
| Solidago auriculata | |
|---|---|

| |
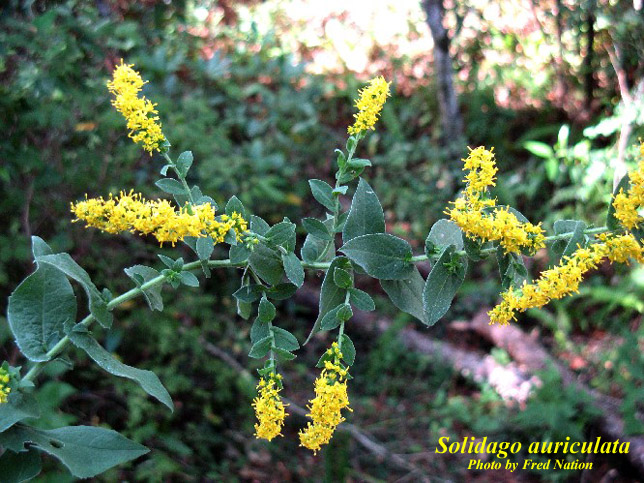
| Photo by Fred Nation, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Solidago |
| Species: | S. auriculata |
| Binomial name | |
| Solidago auriculata Shuttlw. ex S.F. Blake | |
| |
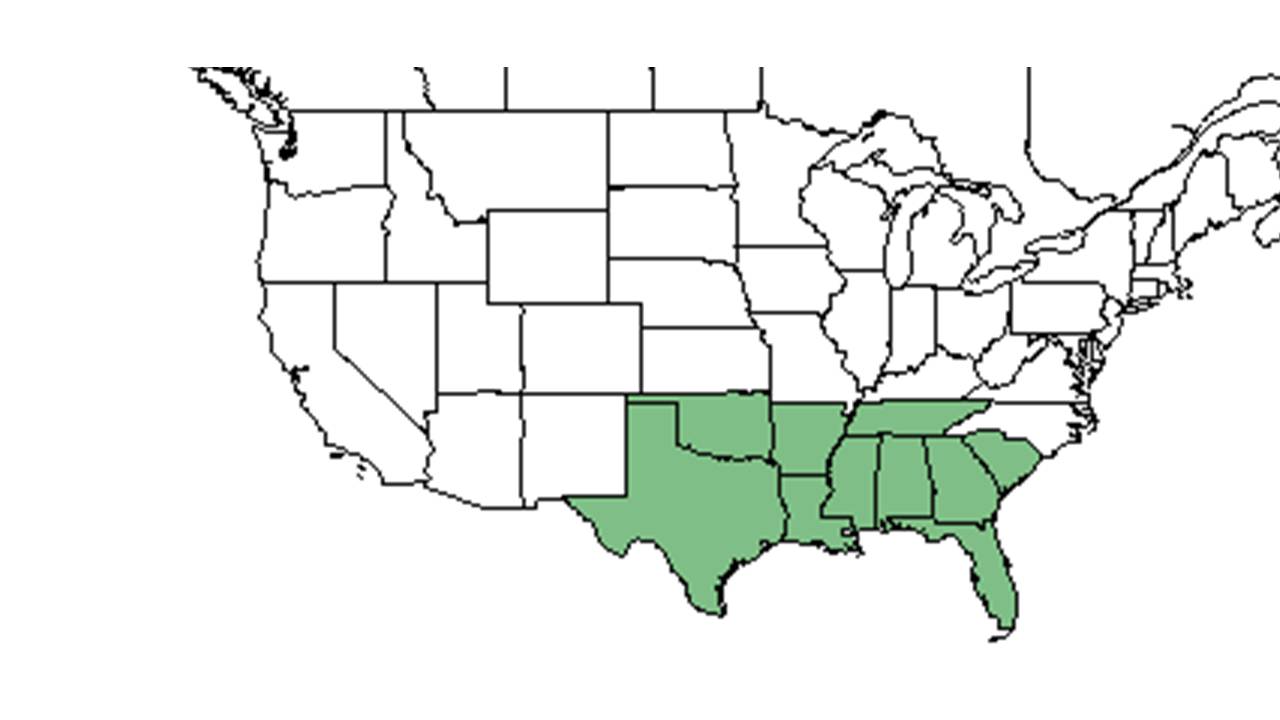
| Natural range of Solidago auriculata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: eared goldenrod
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Solidago notabilis Mackenzie
Description
A description of Solidago auriculata is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, S. auriculata can be found in limestone glades, limestone outcrops, limestone woodlands, in between limestone glades, mixed hardwood forests and oak-hickory woodlands. [1] Substrates include dry loam, sandy loam, and calcareous areas. [1] Associated species include Quercus, Carya, Schoenus nigricans, Aristida longespica, Houstonia nigricans, Rhynchospora divergens, Scleria verticillata, and Juniperus. [1]
Phenology
Flowers and fruits August through November. [1]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Angus Gholson, R. F. Thorne, R. A. Davidson, R. Kral, Ann F. Johnson, Wilson Baker. States and Counties: Florida: Gadsden, Jackson. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.