Difference between revisions of "Polanisia tenuifolia"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| − | Habitats of ''P. tenuifolia'' include longleaf pine/scrub oak ridges, sandhills, and dry pinelands <ref name="eol"/> | + | Habitats of ''P. tenuifolia'' include longleaf pine/scrub oak ridges, sandhills, and dry pinelands. <ref name="eol"/> <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Angus Gholson Jr., Robert K. Godfrey. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty, Putnam. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.</ref> Associated species include ''Balduina angustifolia, Licania michauxii, Conradina canescens, Opuntia humifusa, O. pusilla, Froelichia floridana, Cypersus retrosus, Stipulicida setacea, Polygonella gracilis, Diodia teres, Triplasis americana'',and ''Heterotheca subaxillaris'' (UF Herbarium). |
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
<!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Polanisia tenuifolia'' at Archbold Biological Station | + | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Polanisia tenuifolia'' at Archbold Biological Station: <ref name="Deyrup 2015">Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.</ref> |
Halictidae: ''Augochloropsis metallica, Lasioglossum nymphalis'' | Halictidae: ''Augochloropsis metallica, Lasioglossum nymphalis'' | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 12:41, 8 August 2016
| Polanisia tenuifolia | |
|---|---|

| |
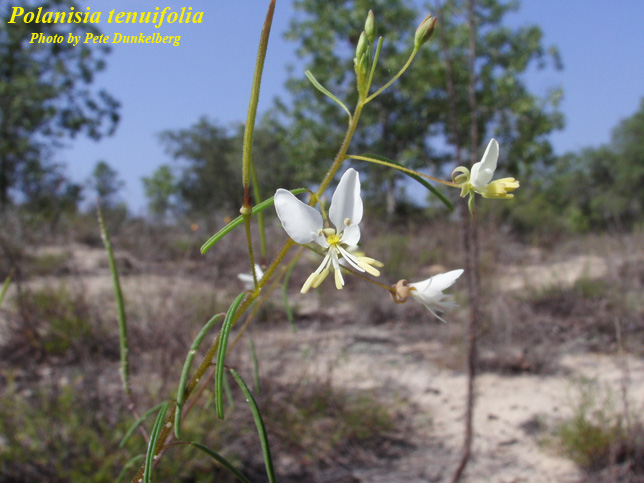
| Photo by Pete Dunkelberg, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Brassicales |
| Family: | Cleomaceae |
| Genus: | Polanisia |
| Species: | P. tenuifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Polanisia tenuifolia Torr. & A. Gray | |
| |
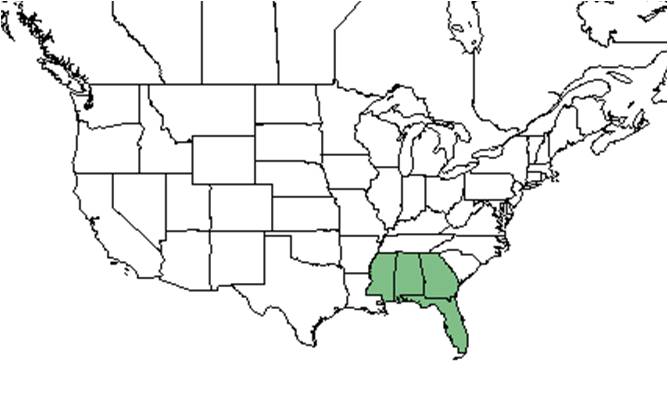
| Natural range of Polanisia tenuifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Slenderleaf clammyweed
Contents
[hide]Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Aldenella tenuifolia (Torrey & A. Gray) Greene
Description
A description of Polanisia tenuifolia is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
It is a regional endemic found in the Florida panhandle to southeast Mississippi[1].
Ecology
Habitat
Habitats of P. tenuifolia include longleaf pine/scrub oak ridges, sandhills, and dry pinelands. [1] [2] Associated species include Balduina angustifolia, Licania michauxii, Conradina canescens, Opuntia humifusa, O. pusilla, Froelichia floridana, Cypersus retrosus, Stipulicida setacea, Polygonella gracilis, Diodia teres, Triplasis americana,and Heterotheca subaxillaris (UF Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
This species has vertically dangling pods called siliques, which open gradually dispenses seeds[3].
Seed bank and germination===
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Polanisia tenuifolia at Archbold Biological Station: [4]
Halictidae: Augochloropsis metallica, Lasioglossum nymphalis
Megachilidae: Dolichostelis louisae, Megachile brevis pseudobrevis
Sphecidae: Cerceris blakei, Ectemnius rufipes ais, Tachysphex similis
Vespidae: Leptochilus krombeini, Microdynerus monolobus, Stenodynerus histrionalis rufustus
Use by animals
It produces glandular hairs which are believed to deter insect feeding and creeping[3].
Conservation and management
Loss of habitat of dunes to vacation homes and resorts is threatening this species[1].
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 [[1]]Encyclopedia of Life. Accessed: February 21, 2016
- Jump up ↑ Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Angus Gholson Jr., Robert K. Godfrey. States and Counties: Florida: Liberty, Putnam. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ Jump up to: 3.0 3.1 [[2]]Treasure Coast Natives. Accessed: February 21, 2016
- Jump up ↑ Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.