Difference between revisions of "Hypericum microsepalum"
(→Taxonomic notes) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
''Hypericum microsepalum'' is an evergreen, arborescent plant that occurs along coastal ecoclines of the Florida panhandle (nomenclature follows Godfrey 1988). | ''Hypericum microsepalum'' is an evergreen, arborescent plant that occurs along coastal ecoclines of the Florida panhandle (nomenclature follows Godfrey 1988). | ||
| − | “Usually glabrous herbs or shrubs. Leaves usually punctate, simple, opposite, entire, usually sessile or subsessile, exstipulate. Inflorescence basically cymose; flowers perfect, regular, bracteates, subsessile or short-pedicellate, sepals 2, 4, or 5, persistent; petals 4 or 5, usually marcescent, yellow or pink; stamens 5-numerous, separate or connate basally forming 3-5 clusters or fascicles, filaments usually persistent; carpels 2-5, stigmas and styles separate or fused, ovary superior, 1-locular or partly or wholly 2-5 locular, placentation axile or parietal. Capsules basically ovoid, longitudinally dehiscent, styles usually persistent; seeds numerous, lustrous, areolate, cylindric or oblong. In general our species form a polymorphic complex with many intergrading taxa.” | + | “Usually glabrous herbs or shrubs. Leaves usually punctate, simple, opposite, entire, usually sessile or subsessile, exstipulate. Inflorescence basically cymose; flowers perfect, regular, bracteates, subsessile or short-pedicellate, sepals 2, 4, or 5, persistent; petals 4 or 5, usually marcescent, yellow or pink; stamens 5-numerous, separate or connate basally forming 3-5 clusters or fascicles, filaments usually persistent; carpels 2-5, stigmas and styles separate or fused, ovary superior, 1-locular or partly or wholly 2-5 locular, placentation axile or parietal. Capsules basically ovoid, longitudinally dehiscent, styles usually persistent; seeds numerous, lustrous, areolate, cylindric or oblong. In general our species form a polymorphic complex with many intergrading taxa.” <ref name="Radford et al 1964">Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 709. Print.</ref> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
''Hypericum microsepalum'' is associated with upland, drier pine savannas where fires are frequent, having a 2–3 year fire frequency <ref name="Crandall 2013">Crandall, R. M. and W. J. Platt (2012). "Habitat and fire heterogeneity explain the co-occurrence of congeneric resprouter and reseeder ''Hypericum'' spp. along a Florida pine savanna ecoline." Plant Ecology 213: 1643-1654.</ref> It is found in Pine savanna and seepage bog community types of Florida.<ref name="Drewa et al 2002">Drewa, P., W. Platt, et al. (2002). "Community Structure along Elevation Gradients in Headwater Regions of Longleaf Pine Savannas." Plant Ecology 160(1): 61-78.</ref> ''H. microsepalum'' is also one of the most abundant seepage, savanna shrubs that resprouts from the root crowns.<ref name="Drewa et al 2006">Drewa, P. B., J. M. Thaxton, et al. (2006). "Responses of root-crown bearing shrubs to differences in fire regimes in ''Pinus palustris'' (Longleaf pine) savannas: exploring old-growth questions in second-growth systems." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 27-36.</ref> | ''Hypericum microsepalum'' is associated with upland, drier pine savannas where fires are frequent, having a 2–3 year fire frequency <ref name="Crandall 2013">Crandall, R. M. and W. J. Platt (2012). "Habitat and fire heterogeneity explain the co-occurrence of congeneric resprouter and reseeder ''Hypericum'' spp. along a Florida pine savanna ecoline." Plant Ecology 213: 1643-1654.</ref> It is found in Pine savanna and seepage bog community types of Florida.<ref name="Drewa et al 2002">Drewa, P., W. Platt, et al. (2002). "Community Structure along Elevation Gradients in Headwater Regions of Longleaf Pine Savannas." Plant Ecology 160(1): 61-78.</ref> ''H. microsepalum'' is also one of the most abundant seepage, savanna shrubs that resprouts from the root crowns.<ref name="Drewa et al 2006">Drewa, P. B., J. M. Thaxton, et al. (2006). "Responses of root-crown bearing shrubs to differences in fire regimes in ''Pinus palustris'' (Longleaf pine) savannas: exploring old-growth questions in second-growth systems." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 27-36.</ref> | ||
| − | It generally occurs in sandy soil, and in addition to the native habitat types as mentioned above, it can be found in some disturbed habitats such as roadsides | + | It generally occurs in sandy soil, and in addition to the native habitat types as mentioned above, it can be found in some disturbed habitats such as roadsides. <ref name="FSU Herbarium">Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: John Jensen, Carl Noedman, Preston Adams, Robert K. Godfrey. Sidney McDaniel, Mark A Garland, Preston Adams, Walter S. Judd, Kent D. Perkins, Scott Zona, Loran C. Anderson, William P. Adams, Robert Kral, H. E. Grelen, M. Knott, L. B. Trott, Steve L. Orzell, M. Davis, K. M. Meyer, and A. Townesmith. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Dixie, Franklin, Gulf, Jackson, Jefferson, Lafayette, Liberty, Madison, Marianna, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, Taylor, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Thomas.</ref> |
| − | Associated species includes ''Cyrilla parvifolia, Vaccinium darrowi, V. myrsinites, Ilex glabra, Polygala lutea, P. nana, Xyris brevifolia, Lyonia mariana, Myrica cerifera, Gaylussacia nana, Lobelia paludosa, Salix caroliniana Hypericum galioides, Myrica, Vaccinium, Aristida stricta, Ilex glabra, Pinus palustris,'' and ''Serenoa repens'' | + | Associated species includes ''Cyrilla parvifolia, Vaccinium darrowi, V. myrsinites, Ilex glabra, Polygala lutea, P. nana, Xyris brevifolia, Lyonia mariana, Myrica cerifera, Gaylussacia nana, Lobelia paludosa, Salix caroliniana Hypericum galioides, Myrica, Vaccinium, Aristida stricta, Ilex glabra, Pinus palustris,'' and ''Serenoa repens''. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | Flowering and fruiting have been observed in January through May, as well as in July | + | Flowering and fruiting have been observed in January through May, as well as in July. <ref name="FSU Herbarium"/> |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 13:52, 29 July 2016
| Hypericum microsepalum | |
|---|---|
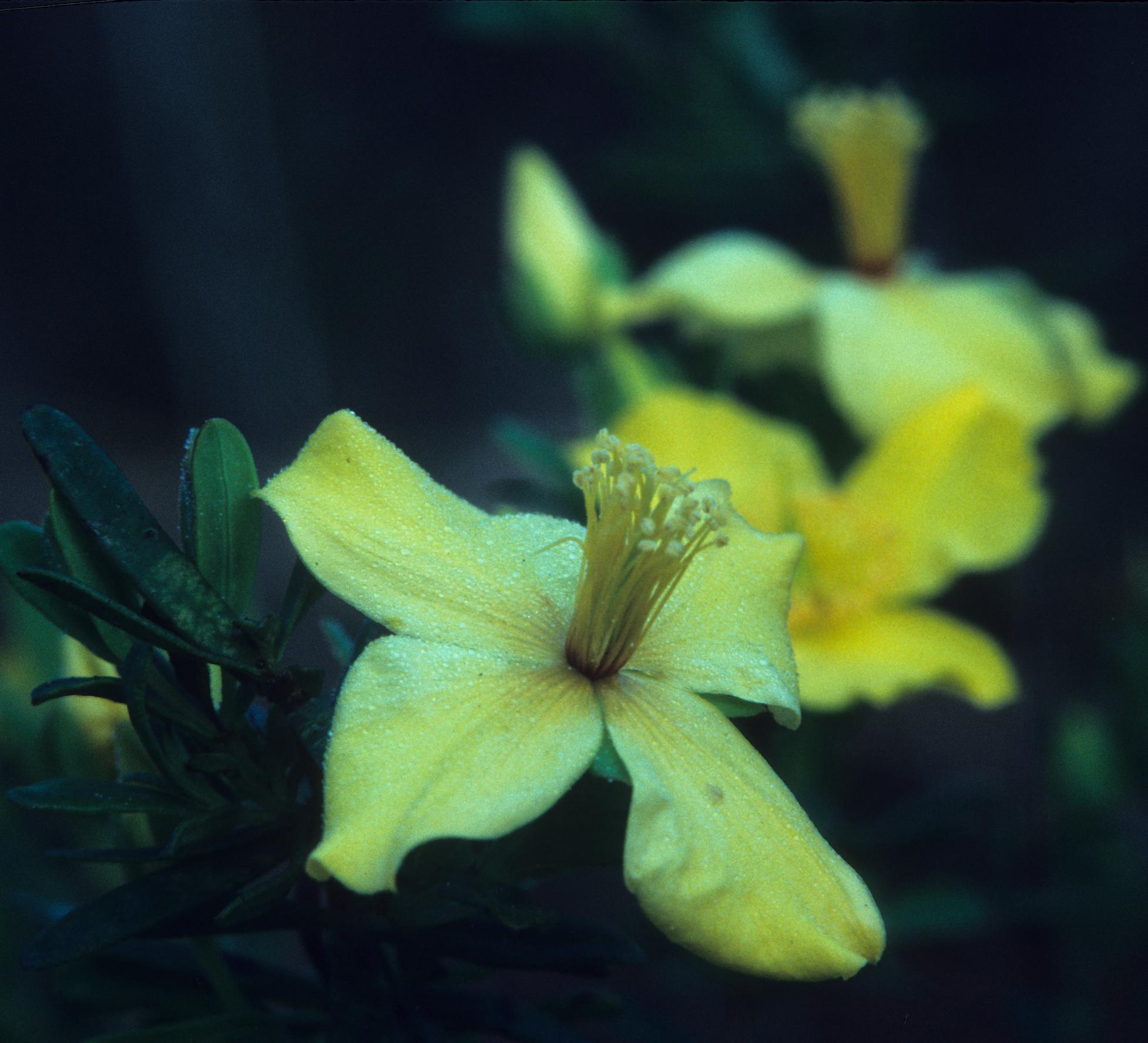

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Theales |
| Family: | Clusiaceae ⁄ Guttiferae |
| Genus: | Hypericum |
| Species: | H. microsepalum |
| Binomial name | |
| Hypericum microsepalum (Torr. & A. Gray) A. Gray ex S. Watson | |
| |
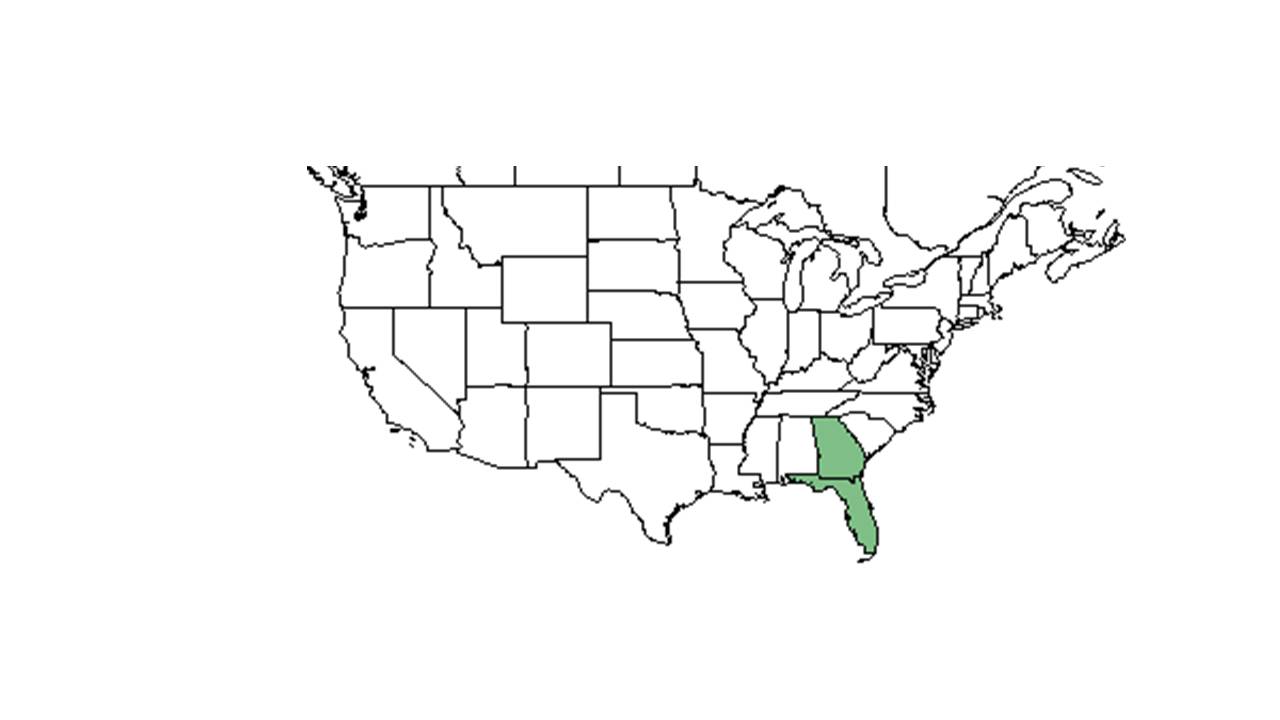
| Natural range of Hypericum microsepalum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: flatwoods St. Johnswort
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Crookea microsepala (Torr. & A. Gray) Small
Description
Hypericum microsepalum is an evergreen, arborescent plant that occurs along coastal ecoclines of the Florida panhandle (nomenclature follows Godfrey 1988).
“Usually glabrous herbs or shrubs. Leaves usually punctate, simple, opposite, entire, usually sessile or subsessile, exstipulate. Inflorescence basically cymose; flowers perfect, regular, bracteates, subsessile or short-pedicellate, sepals 2, 4, or 5, persistent; petals 4 or 5, usually marcescent, yellow or pink; stamens 5-numerous, separate or connate basally forming 3-5 clusters or fascicles, filaments usually persistent; carpels 2-5, stigmas and styles separate or fused, ovary superior, 1-locular or partly or wholly 2-5 locular, placentation axile or parietal. Capsules basically ovoid, longitudinally dehiscent, styles usually persistent; seeds numerous, lustrous, areolate, cylindric or oblong. In general our species form a polymorphic complex with many intergrading taxa.” [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Hypericum microsepalum and H. brachyphyllum are both shrubby in habit, producing multiple shoots from the base whereas H. chapmanii produces a single stem with thick, flaky bark [2]. Hypericum microsepalum has a high survival rate when transplanted in lowland areas however the populations quickly decline in the absence of fire.[2]
Habitat
Hypericum microsepalum is associated with upland, drier pine savannas where fires are frequent, having a 2–3 year fire frequency [2] It is found in Pine savanna and seepage bog community types of Florida.[3] H. microsepalum is also one of the most abundant seepage, savanna shrubs that resprouts from the root crowns.[4]
It generally occurs in sandy soil, and in addition to the native habitat types as mentioned above, it can be found in some disturbed habitats such as roadsides. [5]
Associated species includes Cyrilla parvifolia, Vaccinium darrowi, V. myrsinites, Ilex glabra, Polygala lutea, P. nana, Xyris brevifolia, Lyonia mariana, Myrica cerifera, Gaylussacia nana, Lobelia paludosa, Salix caroliniana Hypericum galioides, Myrica, Vaccinium, Aristida stricta, Ilex glabra, Pinus palustris, and Serenoa repens. [5]
Phenology
Flowering and fruiting have been observed in January through May, as well as in July. [5]
Seed dispersal
All species produce perfect flowers and the dehiscent, septicidal capsules contain numerous seeds. Seeds are dispersed by gravity and occasionally by birds. [3]
Seed bank and germination
All species have life spans 10 years and persistent seed banks.[2]
Fire ecology
Different fire seasons influences the growth of Hypericum microsepalum as recorded by Drewa (2006). Stem densities were greater post dormant-season fires than growing-season fires. When compared to the initial levels of densities, the density of H. microspealum grew up to 7X greater after multiple dormant-season fires. Overall, densities were much more greater after repeated dormant-season fires than growing-season fires, however the difference was not significant. [4]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 709. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Crandall, R. M. and W. J. Platt (2012). "Habitat and fire heterogeneity explain the co-occurrence of congeneric resprouter and reseeder Hypericum spp. along a Florida pine savanna ecoline." Plant Ecology 213: 1643-1654.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Drewa, P., W. Platt, et al. (2002). "Community Structure along Elevation Gradients in Headwater Regions of Longleaf Pine Savannas." Plant Ecology 160(1): 61-78.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Drewa, P. B., J. M. Thaxton, et al. (2006). "Responses of root-crown bearing shrubs to differences in fire regimes in Pinus palustris (Longleaf pine) savannas: exploring old-growth questions in second-growth systems." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 27-36.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: John Jensen, Carl Noedman, Preston Adams, Robert K. Godfrey. Sidney McDaniel, Mark A Garland, Preston Adams, Walter S. Judd, Kent D. Perkins, Scott Zona, Loran C. Anderson, William P. Adams, Robert Kral, H. E. Grelen, M. Knott, L. B. Trott, Steve L. Orzell, M. Davis, K. M. Meyer, and A. Townesmith. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Dixie, Franklin, Gulf, Jackson, Jefferson, Lafayette, Liberty, Madison, Marianna, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, Taylor, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Thomas.