Difference between revisions of "Solanum carolinense"
(→Conservation and Management) |
|||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation and management== |
| + | |||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
Revision as of 16:59, 7 July 2016
| Solanum carolinense | |
|---|---|
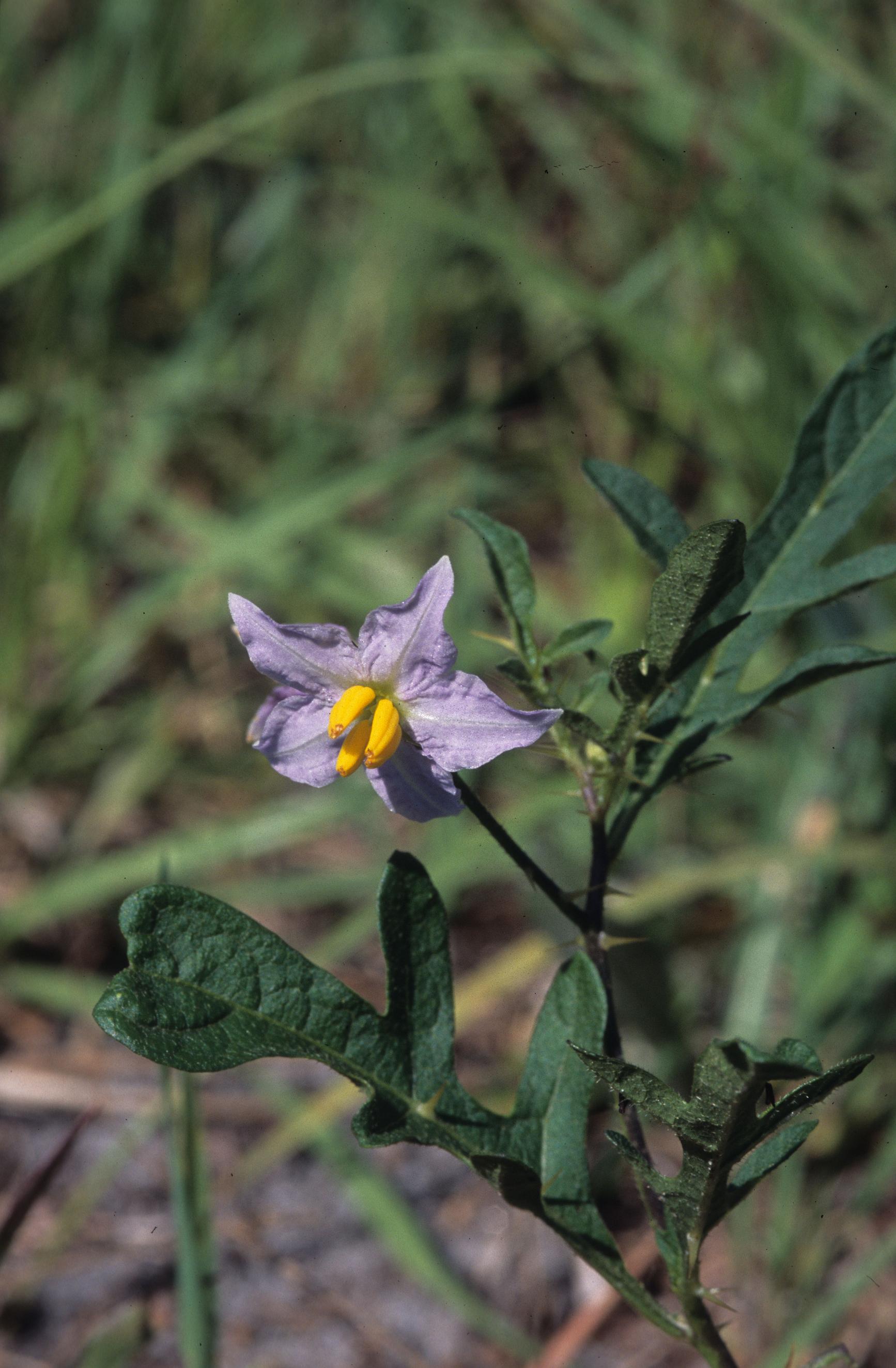

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Solanaceae |
| Genus: | Solanum |
| Species: | S. carolinense |
| Binomial name | |
| Solanum carolinense L. | |
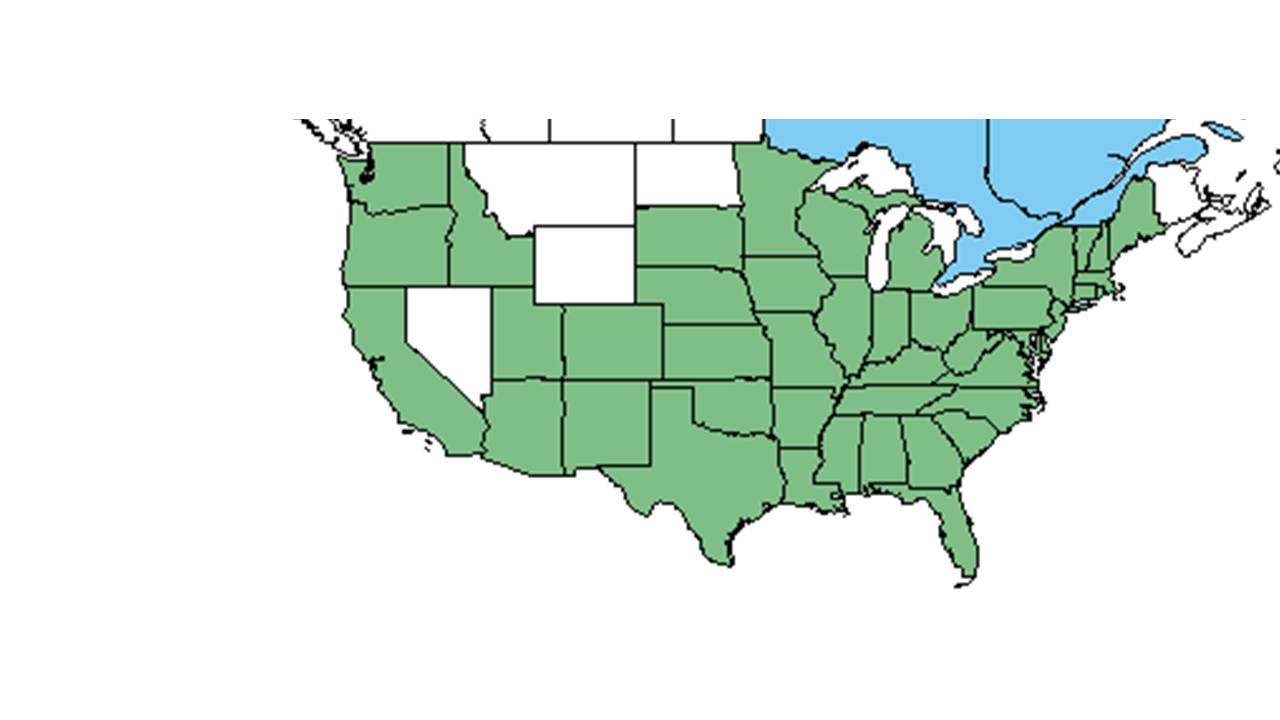
| |
| Natural range of Solanum carolinense from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Carolina horsenettle
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Solanum carolinense Linnaeus var. carolinense
Description
"Annual or perennial herbs or vines, often armed. Leaves petiolate, entire to pinnatifid. Corolla rotate, 5 parted, the lobes spreading or reflexed. Anthers exserted, erect and connivent or sometimes spreading, opening by two terminal pores, filaments short, often pubescent. Berry 2-locular, mealy or fleshy." [1] "Erect, armed, weakly branched, stellate pubescent perennial, 2-8 dm tall. Leaves ovate to elliptic-lanceolate, 7-12 cm long, 3-8 cm wide, irregularly sinuate, lobed, or parted, both surfaces beset with sessile, stellate trichomes with 5-7 spreading rays and an elongate central ray. Racemes terminal, few-flowered; calyx tube 2-3 mm long, calyx lobes acuminate, 3-6 mm long depending on age; corolla white to purple, 2.3-3.1 cm broad, lobes ovate, spreading or reflexed; anthers erect, connivent, 7-9 mm long. Berry yellow, 1-1.5 cm in diam."[1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
S. carolinense can be found in pinelands, floodplains, floodplain clearings, pine-oak woods, upland oak-hickory forests, grassy turf of berms, pine-palmetto flatwoods, wet hammocks, deciduous woodlands, river banks, bordering marshes, and seasonally wet depressions within thickets (FSU Herbarium). It can also occur at boat landings, roadsides, shrubby lake margins, cultivated watermelon fields, under bridges, roadside depressions, cultivated flower beds, powerline corridors, old fields, along hiking trails, disturbed slash pine woodlands, and cowpea fields. Associated species include Richardia scabra, Croton glandulosus, Ambrosia artemisifolia, Datura stramonium, Phytolacca, Amaranthus, Cyperus, Passiflora, Rubus, Ilex, Baccharis, Myrica, horsemint, morning glory, and evening primrose (FSU Herbarium). Soils include sandy soils, limestone, sandy loam, loamy sand, alluvial sands, black organic clay (FSU Herbarium) and calcareous soils. [2]
Phenology
Flowers and fruits April through November (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by being consumed by vertebrates (being assumed). [3]
Fire ecology
S. carolinense dominated the canopy coverage on herbicide-treated plots during the first year after treatment. [4]
Use by animals
It is an important summer food for bobwhites.[5]
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: John B. Nelson, Loran C. Anderson, Gwynn W. Ramsey, Richard S. Mitchell, Robert K. Godfrey, John Morrill, Bruce Hansen, Angus Gholson, Jr., Nancy Caswell, S. W. Leonard, Kathy Craddock Burks, Kristen Coleman, Sarah Braun, Stacy Halpern, Andre F. Clewell, R. Komarek, R. F. Doren, ,-- Sherman, ,-- Shamblee, Geo M. Merrill, R. L. Lazor, N. C. Henderson, R. Kral, A Traverse, A. E. Radford, Nora E. Mullens, C. Leland Rodgers, J. B. Nelson, Windler, Keenan, Carl Blomberg, Norlan C. Henderson, Richard D. Houk, W. G. D'Arcy, Paul L. Redfearn, Jr., George T. Jones, Rufus Crane, H F.L. Rock, Roomie Wilson, Wm. H. Ellis, J. Cohn, WM D Countryman, Billy Bailey, Sidney McDaniel, Gerould Wilhelm, L. B. Trott, J. M. Kane. States and Counties: Alabama: DeKalb. Arkansas: Pulaski. Florida: Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Jackson, Jefferson, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Nassau, Okaloosa, St. Johns, Taylor, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Chattahoochee, Grady, Thomas. Illinois: Lawrence, Porter. Louisiana: Lincoln, Ouachita, Tangipahoa. Maryland: Harford. Massachusetts: Bristol. Michigan: Allegan. Mississippi: Amite. Missouri: Barton, Bates, Buchanan, Douglas, Greene, Lafayette, Lincoln, Ozark, Shannon. Ohio: Delaware, Erie. South Carolina: Anderson, Greenville, Richland. Tennessee: Anderson, Cumberland. Texas: Harris, Van Zandt. Vermont: Washington. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 932. Print.
- ↑ Engle, D. M., M. W. Palmer, et al. (2000). "Influence of late season fire on early successional vegetation of an Oklahoma prairie." Journal of Vegetation Science 11: 135-144.
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.
- ↑ Madison, L. A., T. G. Barnes, et al. (2001). "Effectiveness of fire, disking, and herbicide to renovate tall fescue fields to northern bobwhite habitat." Wildlife Society Bulletin 29: 706-712.
- ↑ Jones, J. D. J. and M. J. Chamberlain (2004). "Efficacy of herbicides and fire to improve vegetative conditions for northern bobwhites in mature pine forests." Wildlife Society Bulletin 32: 1077-1084.