Difference between revisions of "Pleopeltis michauxiana"
(→Taxonomic notes) |
(→Conservation and Management) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
<!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | <!--===Use by animals===--> <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
<!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | ||
| − | ==Conservation and | + | ==Conservation and management== |
| + | |||
==Cultivation and restoration== | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
Revision as of 20:04, 29 June 2016
| Pleopeltis michauxiana | |
|---|---|
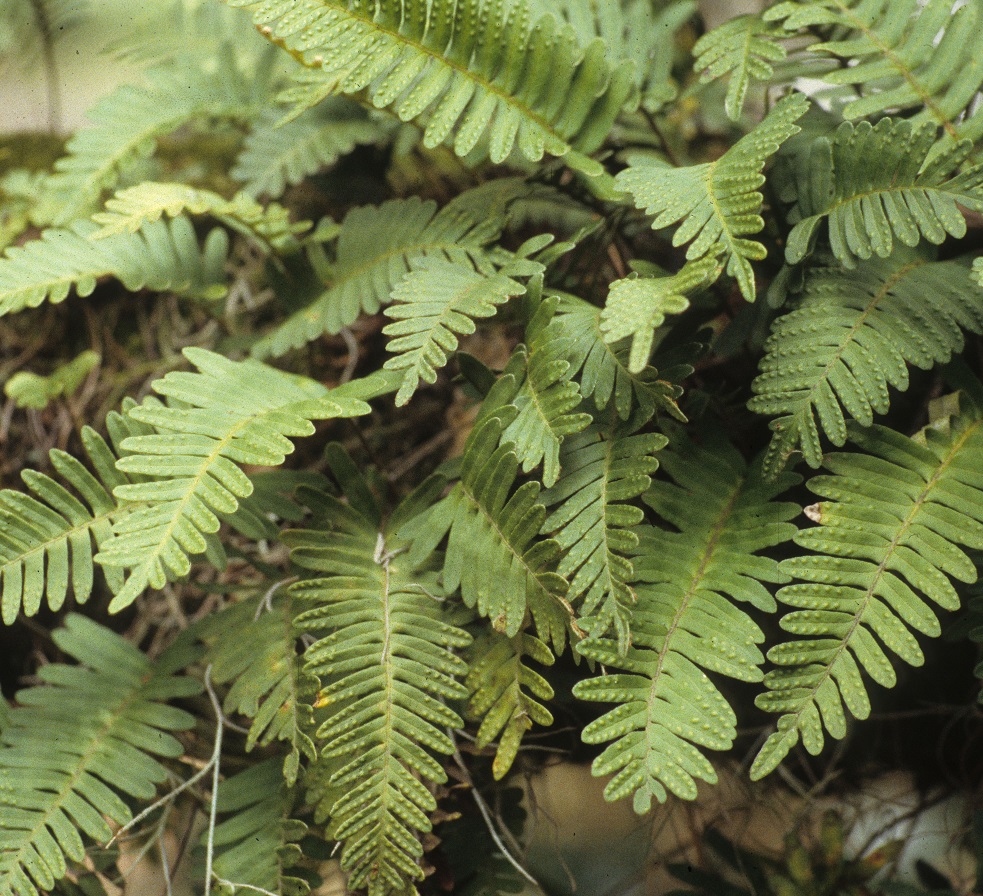

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Pteridophyta – Ferns |
| Class: | Filicopsida |
| Order: | Polypodiales |
| Family: | Polypodiaceae |
| Genus: | Pleopeltis |
| Species: | P. michauxiana |
| Binomial name | |
| Pleopeltis michauxiana (Weatherby) Hickey & Sprunt | |
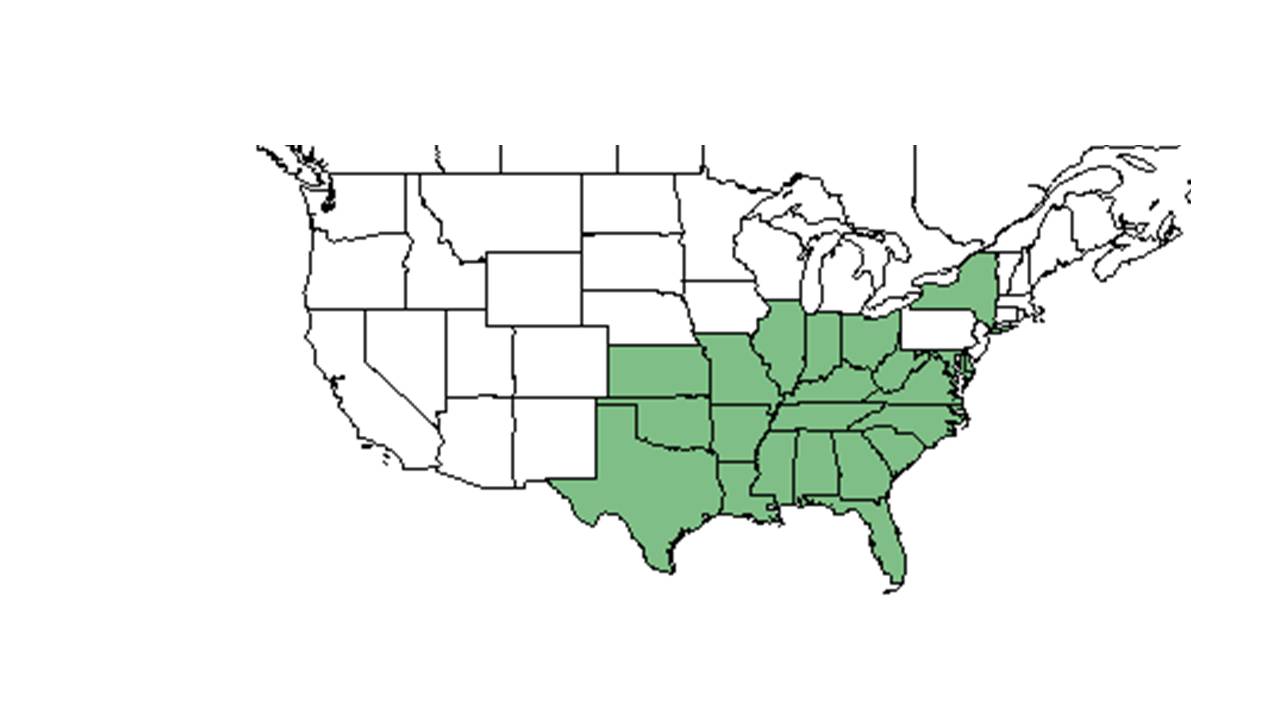
| |
| Natural range of Pleopeltis michauxiana from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: resurrection fern
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Pleopeltis polypodioides; Pleopeltis polypodioides (Linnaeus) E.G. Andrews & Windham var. michauxiana (Weatherby) E.G. Andrews & Windham; Polypodium polypodioides (Linnaeus) Watt; Polypodium polypodioides (Linnaeus) Watt var. michauxianum Weatherby; Marginaria polypodioides (Linnaeus) Tidestrom; Pleopeltis polypodioides ssp. michauxiana
Description
A description of Pleopeltis michauxiana is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, P. michauxiana is an epiphytic plant that can be found in cabbage palm hammocks, trunks of sand live oaks, live oaks, ravines, old fallen logs, limestone fern grottos, cherry trees, and upland trees (FSU Herbarium). It can also be found on shaded roadside banks, hiking trails in mixed hardwood forests, and on clay bank roadsides. This epiphytic fern lacks soil which puts it at a high risk of desiccation although it is able to survive a significant amount of time without any water source (Dubuission et al. 2009). Associated species include Pinus clausa, Quercus geminata, Quercus falcata and Quercus virginiana (FSU Herbarium).
Conservation and management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Dubuisson, J.-Y., H. Schneider, et al. (2009). "Epiphytism in ferns: diversity and history." Comptes Rendus Biologies 332: 120-128.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: July 2015. Collectors: : Cecil R Slaughter, Loran C. Anderson, Robert K. Godfrey, Robert Kral, C. Jackson, Gwynn W. Ramsey, Sidney McDaniel, Patricia Elliot, J. P. Gillespie, Ira L. Wiggins, Dorothy B. Wiggins, Kathy Craddock Burks, B. Auld, B. Moore, P. L. Redfearn, Jr., R. F. Thorne, A. Gholson Jr., Wilson Baker, Susanne Cooper, Richard S. Mitchell, S. W. Leonard, C. H. Beck, Robert J Lemaire, Tiffani Floyd, Roy Komarek, J. B. Nelson, Chris Cooksey, Richard Gaskalla, David Printiss. States and Counties: Florida: Brevard, Citrus, Dixie, Flagler, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Hernando, Indian River, Jackson, Jefferson, Lafayette, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Martin, Okaloosa, Pasco, Pinellas, Santa Rosa, Taylor, Wakulla, Washington. Georgia: Grady. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.