Difference between revisions of "Agalinis divaricata"
Krobertson (talk | contribs) (→References and notes) |
Krobertson (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
==Conservation and Management== | ==Conservation and Management== | ||
''A. divaricata'' requires fire or other vegetation-removing disturbance to maintain high light levels in the habitat which also reduces competition. It does not appear to be common in areas with a great deal of soil disturbance, although it occurs along roadsides and ditches<ref name="fsu"/>. This species is highly threatened by land-use conversion, habitat fragmentation and forest management practices<ref name="natureserve"/>. | ''A. divaricata'' requires fire or other vegetation-removing disturbance to maintain high light levels in the habitat which also reduces competition. It does not appear to be common in areas with a great deal of soil disturbance, although it occurs along roadsides and ditches<ref name="fsu"/>. This species is highly threatened by land-use conversion, habitat fragmentation and forest management practices<ref name="natureserve"/>. | ||
| − | ==Cultivation and restoration== | + | <!--==Cultivation and restoration==--> |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
Revision as of 18:25, 17 May 2016
| Agalinis divaricata | |
|---|---|

| |
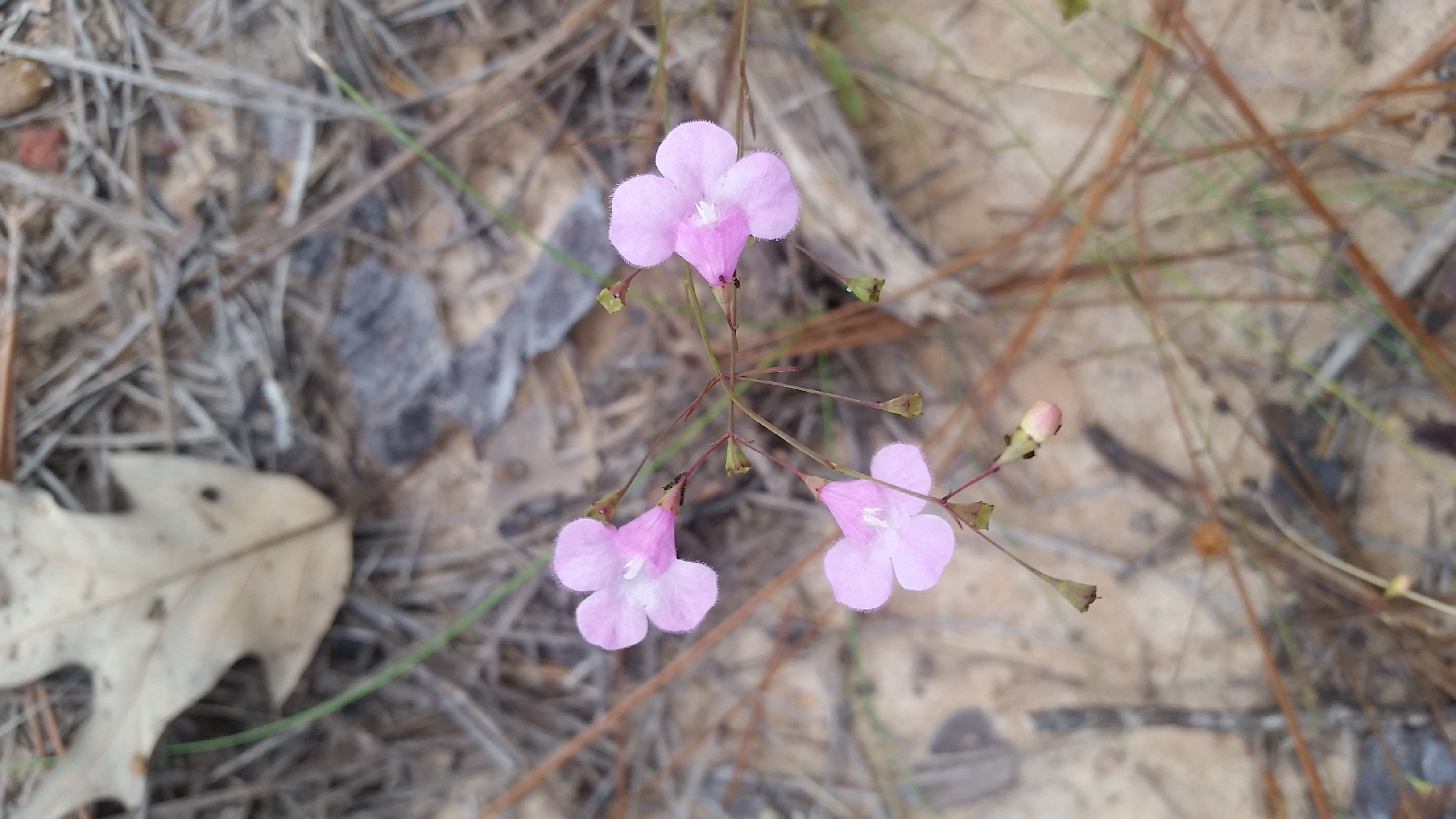
| Photo by Michelle Smith at Torreya State Park | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Orobancheaceae |
| Genus: | Agalinis |
| Species: | A. divaricata |
| Binomial name | |
| Agalinis divaricata (Chapm.) Pennell | |
| |
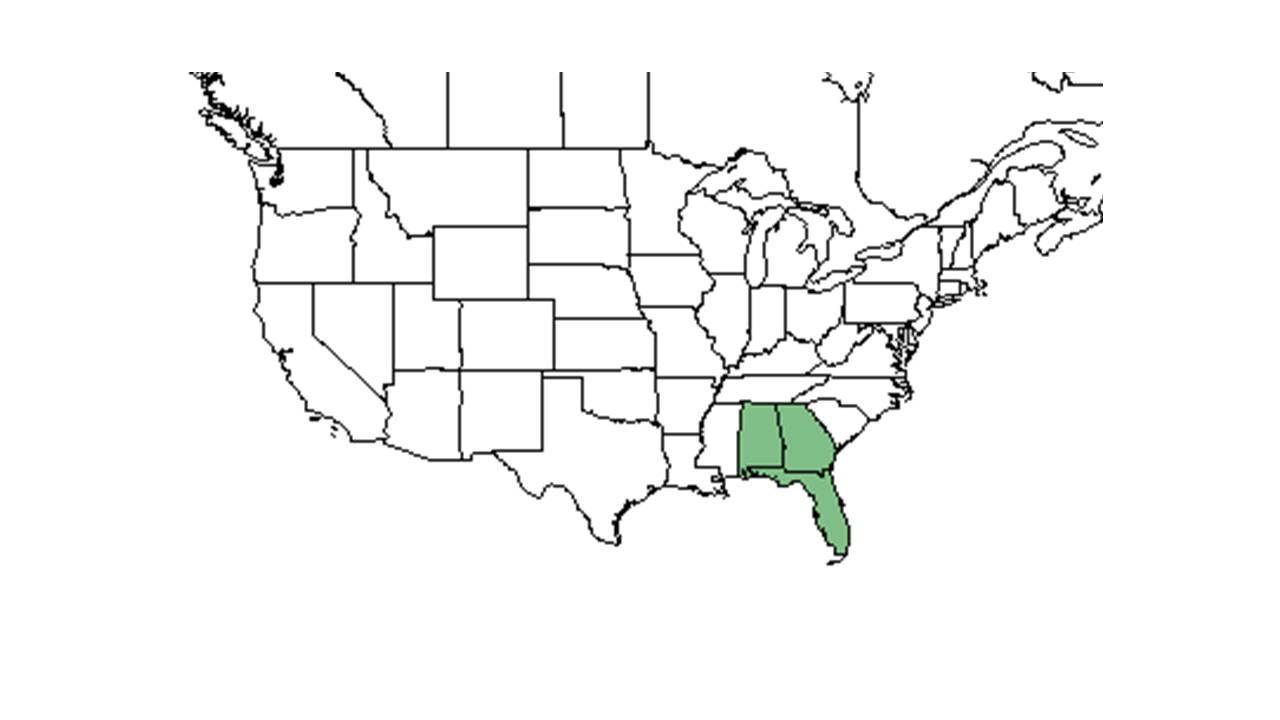
| Natural range of Agalinis divaricata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Pineland False Foxglove; Little Gerardia
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: Gerardia divaricata Chapm.
Description
It is an annual and flowers in the fall[1]. It flowers summer to fall[2].
Distribution
It is infrequent in central, north, and west Florida. Found from: West to Mississippi, east to Alabama[1]. Listed as critically imperiled in Alabama and Georgia[3].
Ecology
Habitat
It occurs primarily in well drained sands and loamy sands of pine-oak sandhill communities, sand dunes and interdune hollows (Entisols), and pine flatwoods communities (Spodosols). It thrives in frequently burned areas[4]. It is found in dry, scrub pinelands[1]. It is found in dry pine-oak savannas, sandhills, and mesic bog margins[2]. Found in dry loamy sands, well drained sands, deep coarse sands, and loamy sand areas[4]. A. divaricata is also fund in human disturbed areas such as pine plantations, old fields, and along roadside edges and ditches. It does well in high levels of light.
Associated species: Myrica, Pinus, Quercus, Liatris, Pityopsis, Agalinis pulchella, Agalinis aphylla, Agalinis tenuifolia, Agalinis plukenetii, Quercus laevis, Aristida stricta, Andropogon spp.; Polygonella, Chrysopsis, Haplopappus, Opuntia, Eupatorium, Dicerandra, Trichostema, Liatris gracilis, and others[4].
Fire ecology
It thrives in frequently burned areas; and occurs in areas with extremely xeric conditions (such as sand dunes) which limit competition with other vegetation[4].
Conservation and Management
A. divaricata requires fire or other vegetation-removing disturbance to maintain high light levels in the habitat which also reduces competition. It does not appear to be common in areas with a great deal of soil disturbance, although it occurs along roadsides and ditches[4]. This species is highly threatened by land-use conversion, habitat fragmentation and forest management practices[3].
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Hall, David W. Illustrated Plants of Florida and the Coastal Plain: based on the collections of Leland and Lucy Baltzell. 1993. A Maupin House Book. Gainesville. 341. Print.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Wunderlin, Richard P. and Bruce F. Hansen. Guide to the Vascular Plants of Florida. Second edition. 2003. University Press of Florida: Gainesville/Tallahassee/Tampa/Boca Raton/Pensacola/Orlando/Miami/Jacksonville/Ft. Myers. 546. Print.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 [[1]]NatureServe. Accessed: March 21, 2016
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 .Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Sidney McDaniel, Andre F. Clewell, Robert K. Godfrey, Paul O. Schallert, J. M. Canne, John Morrill, Loran C. Anderson, J. Hays, Robert Kral, Jean W. Wooten, H. E. Grelen, John C. Semple, L. Brouillet, Wilson Baker, H. Roth, V Craig, Bill Boothe, Marcia Boothe, R. A. Norris, and T. MacClendon. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Jackson, Leon, Liberty, Levy, Okaloosa, Santa Rosa, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington.