Difference between revisions of "Croton argyranthemus"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→Ecology) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→Pollination) |
||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | Pollinated mostly by small bees<ref name= | + | Pollinated mostly by small bees<ref name=hawthorn/>. |
| + | |||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Ants are an agent of seed dispersal<ref name=cumberland/>. ''C. argyranthemus'' is an important game food plant: it is consumed by doves, quail, and deer.<ref name="Hebb 1971">Hebb, E. A. (1971). "Site preparation decreases game food plants in Florida sandhills." Journal of Wildlife Management 35: 155-162.</ref>. It is the larval food plant for the goateed leafwing butterfly. It produces a milky sap to help defend from herbivory<ref name=hawthorn>[[http://hawthornhillwildflowers.blogspot.com/2010/06/silver-croton-croton-argyranthemus.html]]Native Florida Wildflowers. Accessed: April 15, 2016</ref>. | Ants are an agent of seed dispersal<ref name=cumberland/>. ''C. argyranthemus'' is an important game food plant: it is consumed by doves, quail, and deer.<ref name="Hebb 1971">Hebb, E. A. (1971). "Site preparation decreases game food plants in Florida sandhills." Journal of Wildlife Management 35: 155-162.</ref>. It is the larval food plant for the goateed leafwing butterfly. It produces a milky sap to help defend from herbivory<ref name=hawthorn>[[http://hawthornhillwildflowers.blogspot.com/2010/06/silver-croton-croton-argyranthemus.html]]Native Florida Wildflowers. Accessed: April 15, 2016</ref>. | ||
Revision as of 17:10, 15 April 2016
| Croton argyranthemus | |
|---|---|

| |
| photo by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Euphorbiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Croton |
| Species: | C. argyranthemus |
| Binomial name | |
| Croton argyranthemus Michx. | |
| |
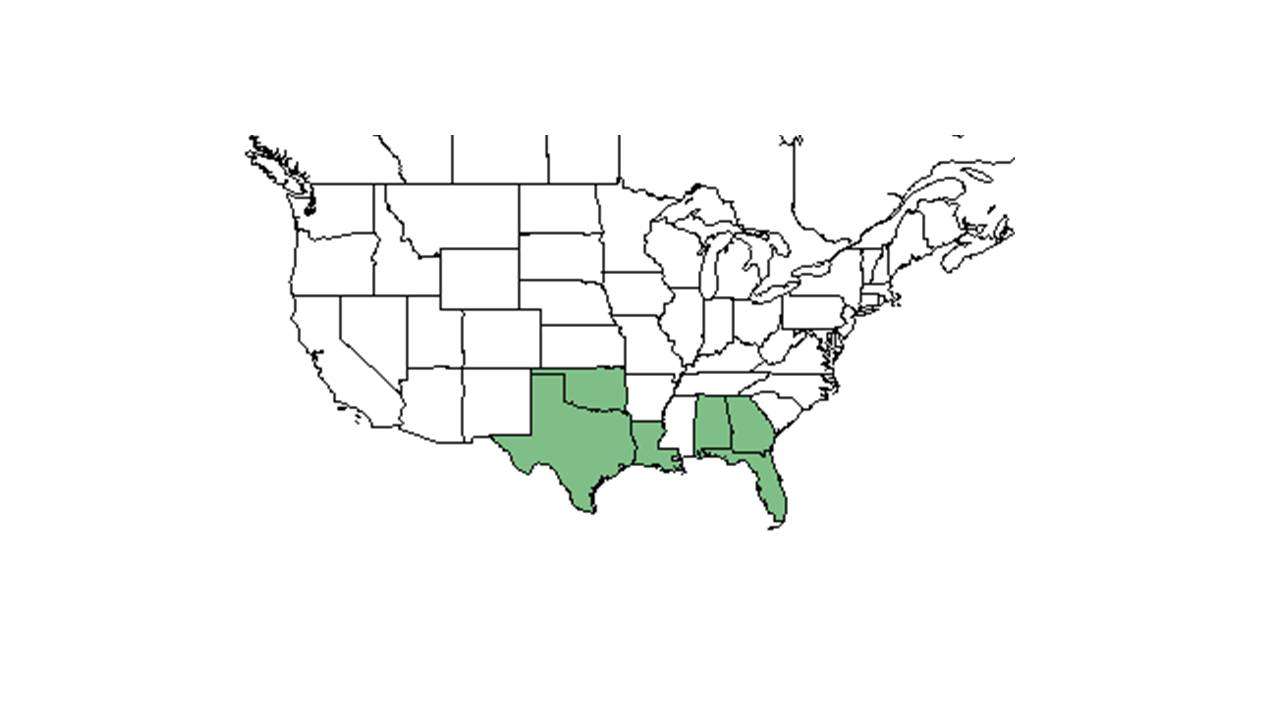
| Natural range of Croton argyranthemus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: healing croton
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It is extremely vulnerable to disturbance. One reason for this might be that it relies too much on native species of ants for dispersal.[1] It can be found in longleaf pine communities.[2] It can also be found in sandhill communities.[3] It has been found on the edges of sandy oak-palmetto scrub, clobbered, cutover flatwoods, and pine-turkey oak flatwoods and sand ridges[4]. It has also been found to grow along disturbed areas like the wooded edges of powerline corridors. Growing in either moderate shade to full sun, this species grows in drying sandy loam in the uplands.
Associated species includes Crotonopsis, Paronychia, Tetragonotheca, Berlandiera, and Onosmodium[4].
Phenology
It is a summer forb.[1] This species has been observed to flower from April to October and to fruit from April to September[4].
Seed dispersal
Seeds have elaiosomes, and can be dispersed by ants such as fire ants[2]. It can also be dispersed explosively[1]. Three of the ballistic euphorbs (C. stimulosus, C. argyranthemus and S. sylvatica) produce seeds with elaiosomes and all of the ballistic species are collected by ants, in particular Pogonomyrex badius Latreille (Long and Lakela 1971; N.E. Stamp and J. R. Lucas, personal observation).”[3] According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by explosion mechanisms or by ants. [5]
Fire ecology
This species is fire tolerant and is included in the flowering plant survery – post burn – in Heuberger’s study.[6]
Pollination
Pollinated mostly by small bees[7].
Use by animals
Ants are an agent of seed dispersal[2]. C. argyranthemus is an important game food plant: it is consumed by doves, quail, and deer.[8]. It is the larval food plant for the goateed leafwing butterfly. It produces a milky sap to help defend from herbivory[7].
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Kirkman, L. K., K. L. Coffey, et al. (2004). "Ground cover recovery patterns and life-history traits: implications for restoration obstacles and opportunities in a species-rich savanna." Journal of Ecology 92(3): 409-421.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Cumberland, M. S. and L. K. Kirkman (2013). "The effects of the red imported fire ant on seed fate in the longleaf pine ecosystem." Plant Ecology 214: 717-724.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Stamp, N. E. and J. R. Lucas (1990). "Spatial patterns and dispersal distances of explosively dispersing plants in Florida sandhill vegetation." Journal of Ecology 78: 589-600.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, D. Burch, Andre F. Clewell, M. Davis, Patricia Elliot, Robert K. Godfrey, C. Jackson, Walter Kittredge, Gary R. Knight, Robert Kral, Robert L. Lazor, Sidney McDaniel, John Morrill, John B. Nelson, R. A. Norris, Cecil R. Slaughter, John K. Small, S. S. Ward, E. West, Ira L. Wiggins, and Dorothy B. Wiggins. States and Counties: Florida: Alachua, Bay, Clay, Columbia, Escambia, Franklin, Gadsden, Gilchrist, Holmes, Jackson, Leon, Levy, Liberty, Madison, Marion, Okaloosa, Polk, Santa Rosa, Taylor, Walton, and Washington.
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.
- ↑ Heuberger, K. A. and F. E. Putz (2003). "Fire in the suburbs: ecological impacts of prescribed fire in small remnants of longleaf pine (Pinus palustris) sandhill." Restoration Ecology 11: 72-81.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 [[1]]Native Florida Wildflowers. Accessed: April 15, 2016
- ↑ Hebb, E. A. (1971). "Site preparation decreases game food plants in Florida sandhills." Journal of Wildlife Management 35: 155-162.