Difference between revisions of "Lechea minor"
(→References and notes) |
|||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
<!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | <!--===Phenology===--> <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | + | ===Seed dispersal=== | |
| + | According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by being consumed by vertebrates (being assumed). <ref name="KK"> Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015. </ref> | ||
| + | |||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
Several short-lived perennial forbs also have a seed bank persistent for at least several years.<ref>Platt, W. J., S. M. Carr, et al. (2006). "Pine savanna overstorey influences on ground-cover biodiversity." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 37-50.</ref> | Several short-lived perennial forbs also have a seed bank persistent for at least several years.<ref>Platt, W. J., S. M. Carr, et al. (2006). "Pine savanna overstorey influences on ground-cover biodiversity." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 37-50.</ref> | ||
Revision as of 14:48, 8 April 2016
| Lechea minor | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Violales |
| Family: | Cistaceae |
| Genus: | Lechea |
| Species: | L. minor |
| Binomial name | |
| Lechea minor L. | |
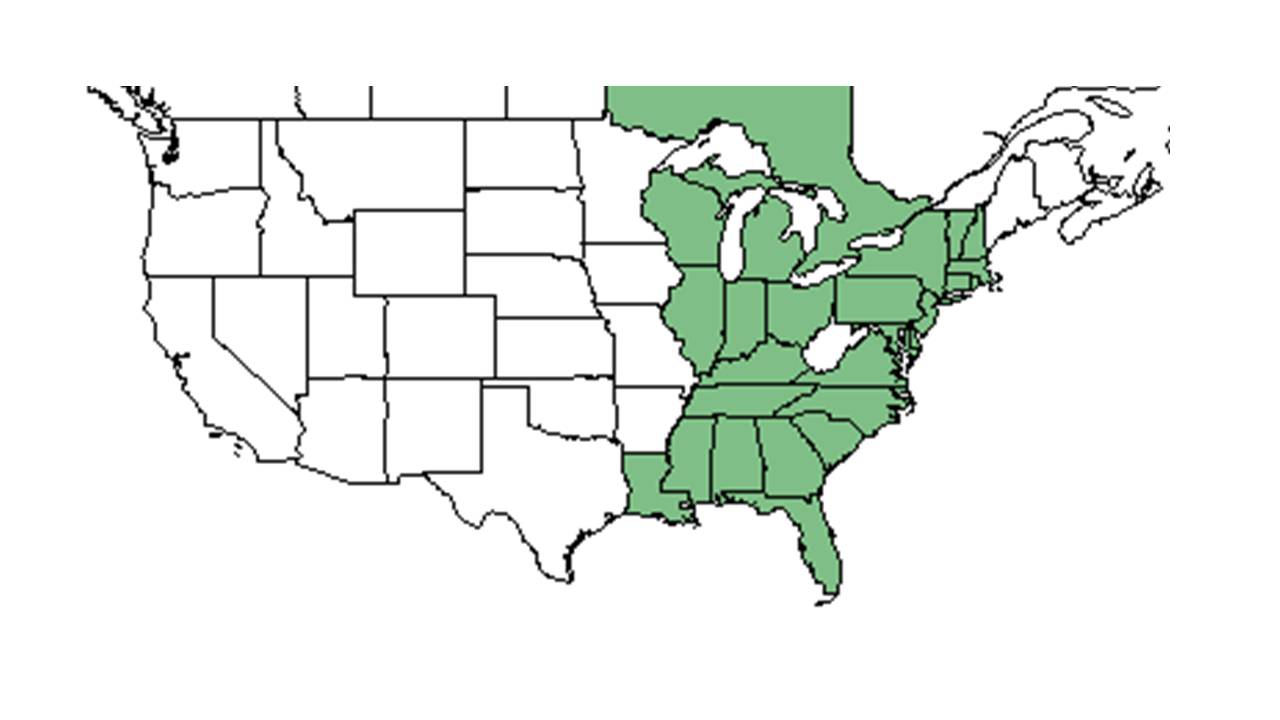
| |
| Natural range of Lechea minor from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: thymeleaf pinweed
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Lechea thymifolia Michaux
Description
This species can be frequent where it occurs (FSU Herbarium).
"Perennial herbs with tap roots and basal rosettes of procumbent, leafy stems late in the season; early stems erect, several from a crown, freely branched above, appressed or spreading pubescent. Leaves opposite, subopposite, whorled or subverticillate on lower part of stem, usually alternate above, usually short-petiolate; leaves of the winter rosettes usually whorled or subverticillate. Inflorescence of scroppoid cymes or racemes in a panicle or theyrse. Sepals 5, outer 2 linear, inner 3 elliptic to ovate; petals 3, reddish or maroon, usually shorter than the sepals; stamens mostly 5-15; stigmas 3, red, plumose. Capsule 1-3 seeded; seeds reddish brown or brown ca. 1 mm long." [1]
"Stems appressed pubescent, 2-7 dm tall with mostly spreading ascending branches; principal stems 1-2 mm in diam. Leaves oblong to elliptic, spreading to spreading-ascending, 6-12 mm long, 1-3 mm wide, glabrous above, ciliate, pubescent beneath mostly on the midrib and near the margins; leaf arrangement similar to no. , but opposite and whorled arrangement often higher into the inflorescence; petioles ca. 1 mm long. Inner sepals shorter than the capsule, 1-1.5 mm long, outer slightly longer. Capsule ellipsoid 1.2-1.7 mm long, 0.7-1 mm broad, 3-seeded." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
This species can be found in sandy soils in open fields, open bogs, and longleaf pine forests (FSU Herbarium). It also occurs in human disturbed areas such as powerline corridors and in old roadbeds (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Longleaf pine and wiregrass (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
According to Kay Kirkman, a plant ecologist, this species disperses by being consumed by vertebrates (being assumed). [2]
Seed bank and germination
Several short-lived perennial forbs also have a seed bank persistent for at least several years.[3]
Fire ecology
Can grow in areas that are annually burned (FSU Herbarium)
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Robert K. Godfrey, Kevin Oakes, and R. Komarek. States and Counties: Florida: Leon and Franklin. Georgia: Baker, Grady, and Thomas.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 720-1. Print.
- ↑ Kay Kirkman, unpublished data, 2015.
- ↑ Platt, W. J., S. M. Carr, et al. (2006). "Pine savanna overstorey influences on ground-cover biodiversity." Applied Vegetation Science 9: 37-50.