Difference between revisions of "Desmodium strictum"
(→Description) |
|||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | Generally, for ''Desmodium'' genus, they are "annual or perennial herbs, shrubs or small trees. Leaves 1-5 foliolate, pinnately 3-foliolate in ours or rarely the uppermost or lowermost 1-foliolate; leaflets entire, usually stipellate; stipules caduceus to persistent, ovate to subulate, foliaceous to setaceous, often striate. Inflorescence terminal and from the upper axils, paniculate or occasionally racemose; pedicel of each papilionaceous flower subtended by a secondary bract or bractlet, the cluster of 1-few flowers subtended by a primary bract. Calyx slightly to conspicuously 2-lipped, the upper lip scarcely bifid, the lower lip 3-dentate; petals pink, roseate, purple, bluish or white; stamens monadelphous or more commonly diadelphous and then 9 and 1. Legume a stipitate loment, the segments 2-many or rarely solitary, usually flattened and densely uncinated-pubescent, separating into 1-seeded, indehiscent segments." | + | Generally, for ''Desmodium'' genus, they are "annual or perennial herbs, shrubs or small trees. Leaves 1-5 foliolate, pinnately 3-foliolate in ours or rarely the uppermost or lowermost 1-foliolate; leaflets entire, usually stipellate; stipules caduceus to persistent, ovate to subulate, foliaceous to setaceous, often striate. Inflorescence terminal and from the upper axils, paniculate or occasionally racemose; pedicel of each papilionaceous flower subtended by a secondary bract or bractlet, the cluster of 1-few flowers subtended by a primary bract. Calyx slightly to conspicuously 2-lipped, the upper lip scarcely bifid, the lower lip 3-dentate; petals pink, roseate, purple, bluish or white; stamens monadelphous or more commonly diadelphous and then 9 and 1. Legume a stipitate loment, the segments 2-many or rarely solitary, usually flattened and densely uncinated-pubescent, separating into 1-seeded, indehiscent segments." <ref name =Radford> Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 604-9. Print. </ref> |
| − | Specifically, for ''D.strictum'' species, they are "erect perennial; stems 0.5-1.2 m tall, sparsely to densely uncinulate-puberulent and short-pubescent, often becoming glabrate below. Terminal leaflets linear to narrowly oblong, often 6-10 X as long as wide, 3-7 cm long, glabrate or minutely puberulent or sparsely short-pubescent especially along the veins beneath, fine reticulate; stipules linear-subulate, 2-4 mm long; stipels persistent. Inflorescence usually paniculate, densely uncinulate-puberulent; pedicels (4) 6-11 mm long. Calyx densely puberulent and sparsely short-pubescent; petals purplish, 3-5 mm long, stamens diadelphous. Loments of 1-3 suborbicular to weakly obovate segments, each 4-6 mm long, 3-4 mm broad, upper suture of each segment slightly concave or indented, densely uncinlate-puberulent on both sutures and sides; stipe 1-2 mm long, about as long as calyx but shorter than stamina remnants." | + | Specifically, for ''D.strictum'' species, they are "erect perennial; stems 0.5-1.2 m tall, sparsely to densely uncinulate-puberulent and short-pubescent, often becoming glabrate below. Terminal leaflets linear to narrowly oblong, often 6-10 X as long as wide, 3-7 cm long, glabrate or minutely puberulent or sparsely short-pubescent especially along the veins beneath, fine reticulate; stipules linear-subulate, 2-4 mm long; stipels persistent. Inflorescence usually paniculate, densely uncinulate-puberulent; pedicels (4) 6-11 mm long. Calyx densely puberulent and sparsely short-pubescent; petals purplish, 3-5 mm long, stamens diadelphous. Loments of 1-3 suborbicular to weakly obovate segments, each 4-6 mm long, 3-4 mm broad, upper suture of each segment slightly concave or indented, densely uncinlate-puberulent on both sutures and sides; stipe 1-2 mm long, about as long as calyx but shorter than stamina remnants." <ref name=Radford/> |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Revision as of 13:49, 8 April 2016
| Desmodium strictum | |
|---|---|

| |
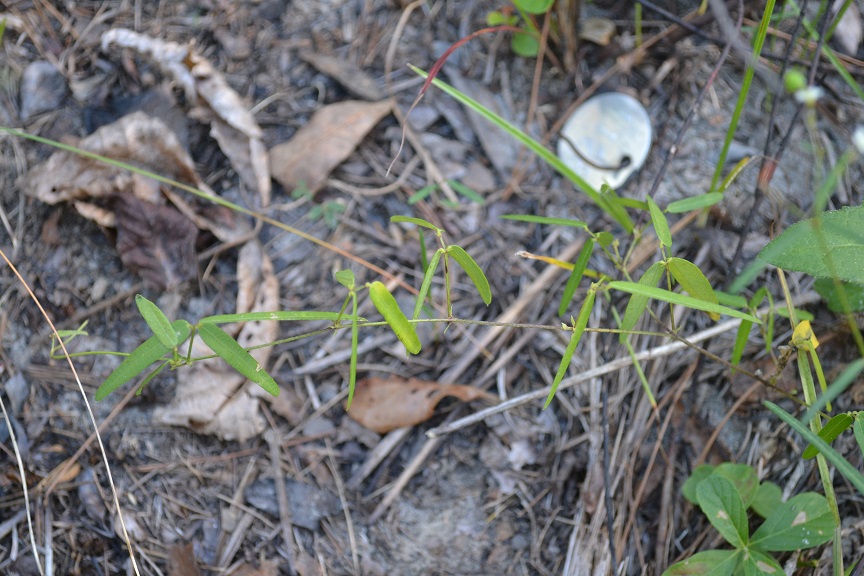
| Photo taken by Kevin Robertson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Desmodium |
| Species: | D. strictum |
| Binomial name | |
| Desmodium strictum (Pursh) DC. | |
| |
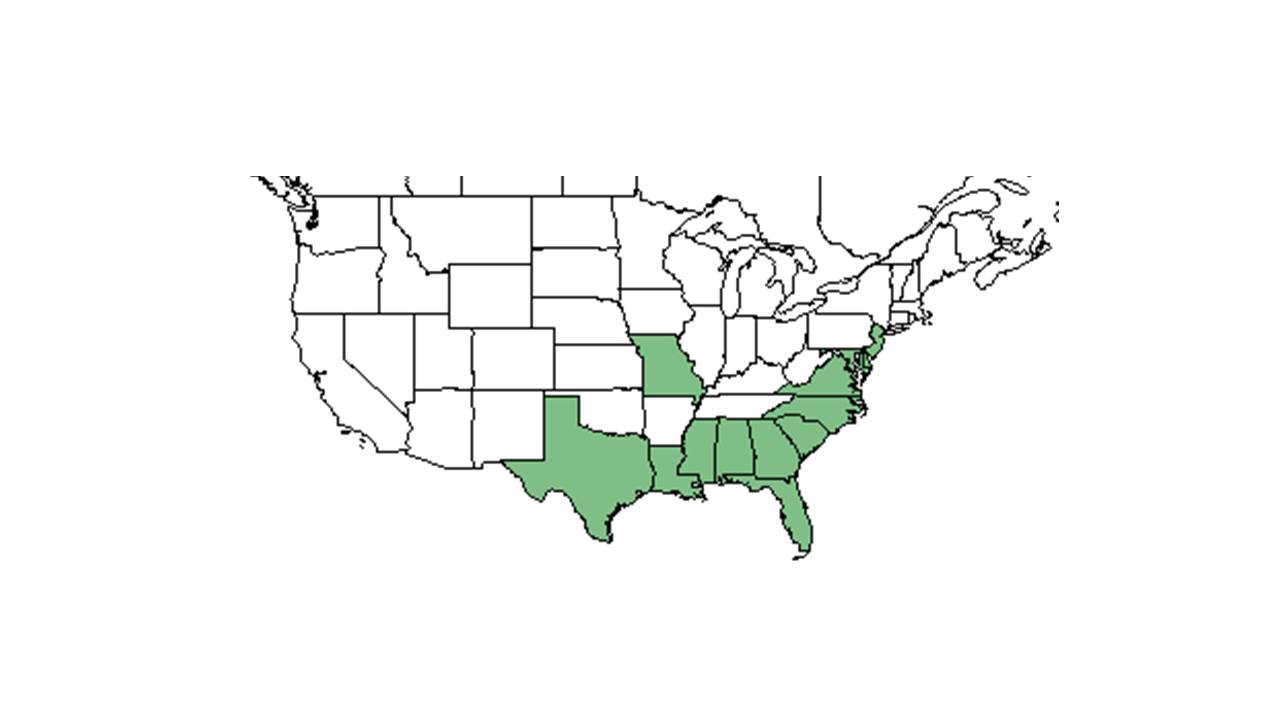
| Natural range of Desmodium strictum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: pine barren ticktrefoil
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Meibomia stricta (Pursh) Kuntze
Description
Generally, for Desmodium genus, they are "annual or perennial herbs, shrubs or small trees. Leaves 1-5 foliolate, pinnately 3-foliolate in ours or rarely the uppermost or lowermost 1-foliolate; leaflets entire, usually stipellate; stipules caduceus to persistent, ovate to subulate, foliaceous to setaceous, often striate. Inflorescence terminal and from the upper axils, paniculate or occasionally racemose; pedicel of each papilionaceous flower subtended by a secondary bract or bractlet, the cluster of 1-few flowers subtended by a primary bract. Calyx slightly to conspicuously 2-lipped, the upper lip scarcely bifid, the lower lip 3-dentate; petals pink, roseate, purple, bluish or white; stamens monadelphous or more commonly diadelphous and then 9 and 1. Legume a stipitate loment, the segments 2-many or rarely solitary, usually flattened and densely uncinated-pubescent, separating into 1-seeded, indehiscent segments." [1]
Specifically, for D.strictum species, they are "erect perennial; stems 0.5-1.2 m tall, sparsely to densely uncinulate-puberulent and short-pubescent, often becoming glabrate below. Terminal leaflets linear to narrowly oblong, often 6-10 X as long as wide, 3-7 cm long, glabrate or minutely puberulent or sparsely short-pubescent especially along the veins beneath, fine reticulate; stipules linear-subulate, 2-4 mm long; stipels persistent. Inflorescence usually paniculate, densely uncinulate-puberulent; pedicels (4) 6-11 mm long. Calyx densely puberulent and sparsely short-pubescent; petals purplish, 3-5 mm long, stamens diadelphous. Loments of 1-3 suborbicular to weakly obovate segments, each 4-6 mm long, 3-4 mm broad, upper suture of each segment slightly concave or indented, densely uncinlate-puberulent on both sutures and sides; stipe 1-2 mm long, about as long as calyx but shorter than stamina remnants." [1]
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
It occurs throughout the southeastern United States, from Texas to New Jersey (NRCS Plants Database). It thrives in open, frequently burned areas such as longleaf pine and shortleaf pine old field habitats (ultisols) (Coffee and Kirkman 2006, FSU Herbarium). It also occurs in longleaf pine-turkey oak sandhills (entisols), and in longleaf pine and slash pine flatwoods (spodosols) (FSU Herbarium). It occurs in habitats dominated by ultisol soil types with average temperatures from 11 to 27° Celsuis, and with 132 cm of annual rainfall (Coffey and Kirkman 2006). It is seen in habitats with soil types of sandy loam to eroded sandy clayey areas (FSU Herbarium).
Associated species: Other plants that occur in the same area as Desmodium strictum when collected include D. viridiflorum, D. floridanum, D. glabellum, D. canescens, D. marilandicum, wiregrass, longleaf pine, and slash pine (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowers in from September to October and fruits from September to November (FSU Herbarium).
Seed bank and germination
Because Desmodium strictum lacks a hard seed coat, it is not capable of forming long-term persistent seed banks, but rather germinates readily within one year following dispersal (Coffey and Kirkman 2006). This suggests that D. strictum does not exhibit the strong physical dormancy attributed to an impermeable seed coat that many other legumes do (it lacks a hard seed coat) (Coffey and Kirkman 2006).
Fire ecology
It thrives in frequently burned (1-2 year interval) habitats (Coffey and Kirkman 2006, FSU Herbarium).
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
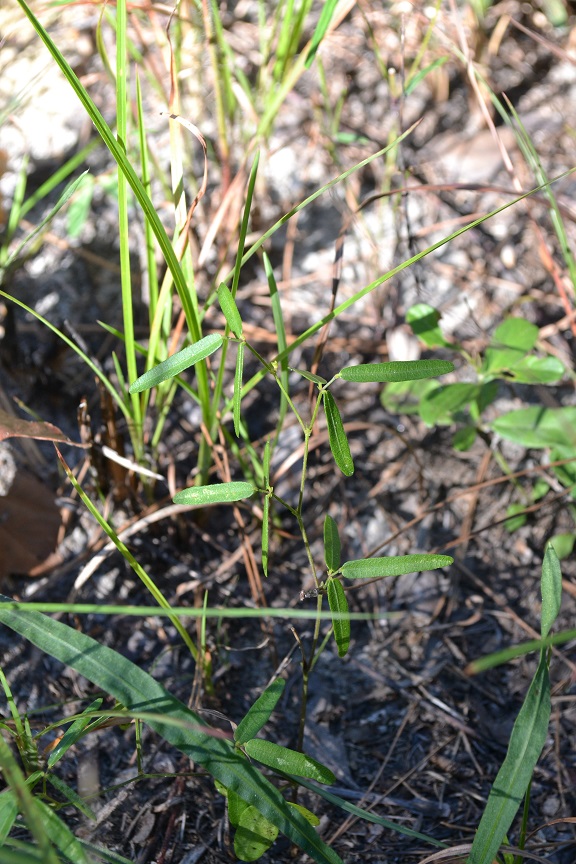
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Coffey, K. L. and L. K. Kirkman (2006). "Seed germination strategies of species with restoration potential in a fire-maintained pine savanna." Natural Areas Journal 26: 289-299.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: L. C. Anderson, R. K. Godfrey, V. Sullivan, J. Wooten, R. Kral, James R. Ray Jr., John Morrill, Robert L. Lazor, Andre F. Clewell, and T. MacClendon. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Bradford, Franklin, Gadsden, Hernando, Jackson, Leon, Putnam, Taylor, Wakulla, and Walton. Georgia: Baker, Grady, and Thomas.
NRCS Plants Database http://plants.usda.gov/java
Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 604-9. Print.
