Difference between revisions of "Sisyrinchium xerophyllum"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| − | Flowers March through November and fruits May through November | + | Flowers have six blue tepals, yellow bases and usually aristae tips. Flowers March through November and fruits May through November<ref name="fsu"/>. |
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
Revision as of 18:22, 16 March 2016
| Sisyrinchium xerophyllum | |
|---|---|
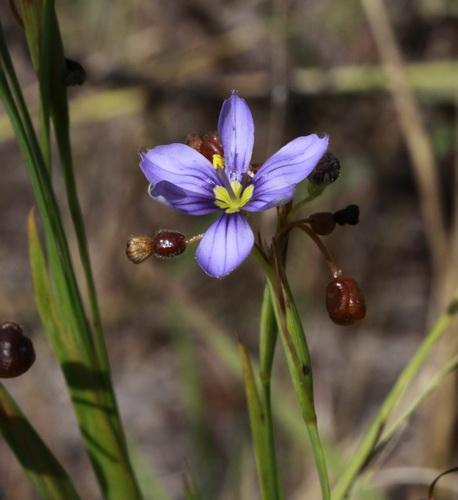

| |
| Photo by Shirley Denton (Copyrighted, use by photographer’s permission only), Nature Photography by Shirley Denton | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Liliales |
| Family: | Iridaceae |
| Genus: | Sisyrinchium |
| Species: | S. xerophyllum |
| Binomial name | |
| Sisyrinchium xerophyllum Greene | |
| |
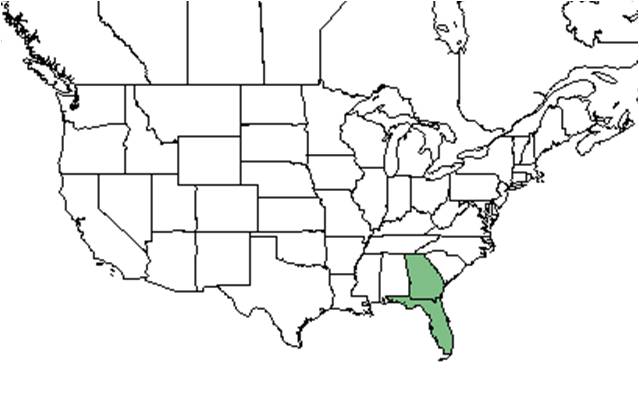
| Natural range of Sisyrinchium xerophyllum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: jeweled blue-eyed grass
Contents
Taxonomic notes
The specific epithet xerophyllum refers to the habitat this species grows in , well-drained sandy uplands[1].
Description
A description of Sisyrinchium xerophyllum is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, S. xerophyllum occurs surrounding limestone glades with wiregrass, open barrens, scrub oak-wiregrass sand ridges, pine-turkey oak flats, and interdune swales. It has also can be found in disturbed areas such as sandy parking lots and roadsides. Soils include sandy loam, loamy sand, sand, and loam. It grows in shaded environments. Associated species include Carex fissa, C. vexans, Chrysopsis linearifolia, Andropogon virginicus, Aristida stricta, Pteridium aquilinum var. subcaudatum, Smilax auriculata and Panicum virgatum [2].
Phenology
Flowers have six blue tepals, yellow bases and usually aristae tips. Flowers March through November and fruits May through November[2].
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Sisyrinchium xerophyllum at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Halictidae: Lasioglossum nymphalis, L. placidensis
Megachilidae: Anthidiellum perplexum, Megachile brevis pseudobrevis
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Billy Bailey, Wilson Baker, J. Beckner, Robert K. Godfrey, Beverly Judd, Walter S. Judd, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, Robert Kral, O. Lakela, Hugh O’Neill, Daniel B. Ward. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Franklin, Highlands, Jackson, Leon, Marion, Marin, Polk, Wakulla, Walton. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ [[1]]Native Florida Wildflowers. Accessed: March 16, 2016
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Billy Bailey, Wilson Baker, J. Beckner, Robert K. Godfrey, Beverly Judd, Walter S. Judd, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, Robert Kral, O. Lakela, Hugh O’Neill, Daniel B. Ward. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Franklin, Highlands, Jackson, Leon, Marion, Marin, Polk, Wakulla, Walton. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.