Difference between revisions of "Sideroxylon tenax"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→References and notes) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
Common name: tough bully | Common name: tough bully | ||
| − | ==Taxonomic notes== | + | <!--==Taxonomic notes==--> |
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
Seeds are dispersed by animals. | Seeds are dispersed by animals. | ||
| − | ===Seed bank and germination=== | + | <!--===Seed bank and germination===--> |
| − | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | + | <!--===Fire ecology===--> <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> |
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Sideroxylon tenax'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Sideroxylon tenax'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Fruits are eaten by fallow deer <ref name=Morse">Morse, B. W., M. L. McElroy, et al. (2009). "Seasonal Diets of an Introduced Population of Fallow Deer on Little St. Simons Island, Georgia." Southeastern Naturalist 8(4): 571-586.</ref> and birds<ref name="rufino"/>. | Fruits are eaten by fallow deer <ref name=Morse">Morse, B. W., M. L. McElroy, et al. (2009). "Seasonal Diets of an Introduced Population of Fallow Deer on Little St. Simons Island, Georgia." Southeastern Naturalist 8(4): 571-586.</ref> and birds<ref name="rufino"/>. | ||
| − | + | <!--===Diseases and parasites===--> | |
| − | ===Diseases and parasites=== | + | <!--==Conservation and Management==--> |
| − | ==Conservation and Management== | + | <!--==Cultivation and restoration==--> |
| − | ==Cultivation and restoration== | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
<gallery widths=180px> | <gallery widths=180px> | ||
Revision as of 15:04, 16 March 2016
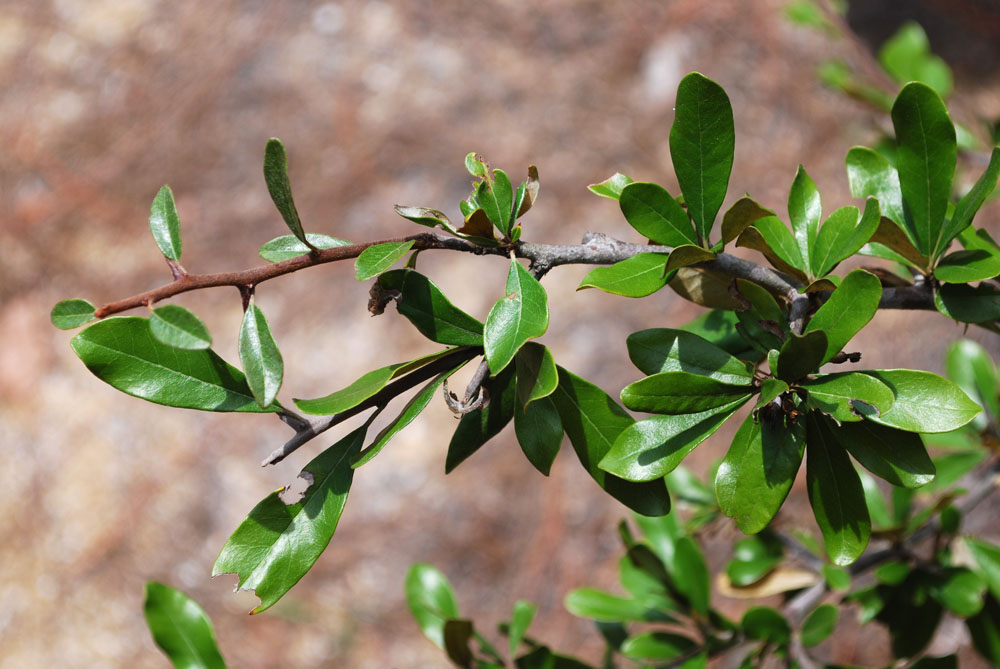
| Sideroxylon tenax | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo by Wayne Matchett, SpaceCoastWildflowers.com | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Ebenales |
| Family: | Sapotaceae |
| Genus: | Sideroxylon |
| Species: | S. tenax |
| Binomial name | |
| Sideroxylon tenax L. | |
| |
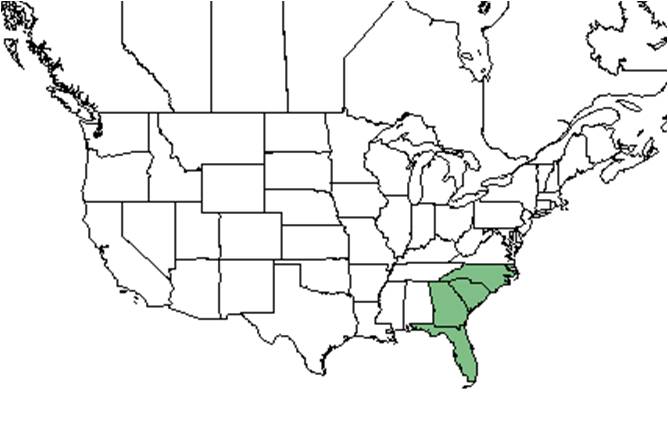
| Natural range of Sideroxylon tenax from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: tough bully
Contents
Description
A description of Sideroxylon tenax is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Tough bully is native to North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and Florida. In Florida, it is absent from the panhandle[1].
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain, S. tenax has occurred in longleaf pine-Carya floridana-oak woods, longleaf pine-turkey oak-wiregrass sandhills, scrub oaks, hydric hammocks, sand dunes, coastal scrubs, scrub oak/cabbage palm communities, saw palmetto thickets, Pinus clausa scrubs, salt marsh edges, tidal marsh borders, and river floodplains. It has also occurred on roadside disturbed sand dunes[2]. This species prefers moist to dry, well-drained sandy soil with a humusy top layer[3] and has been found in sand, loamy sand, and calcareous loamy sand[2]. Associated species include Ceratiola ericoides, Pinus clausa, Quercus chapmanii, Q. geminata, Q. myrtifolia, Garberia heterophylla, , Sabal etonia, Lyonia ferruginea, Vitis rotundifolia, Bumelia, Smilax, Selaginella arenicola, Rhynchospora megalocarpa, Ximenia americana, Juniperus silicicola, Myrica cerifera, Celtis, Xanthoxylum fagara, Persea littoralis, Ardisia escallonioides, Rapanea guianesis, Parthenocissus quinquefolia, Plumbago scandens, Bumelia, Forestiera and Sageretia minutiflora.
This species mostly grow in xeric habitats, it has adapted a dense coat of hair to slow down the water loss through transpiration[1].
Phenology
The berries are dark purple, spherical to egg shaped and about 10 mm across[4]; they have a sweetish pulp that is eaten by large birds and mammals[1]. Flowers are borne in groups of up to 40 flower[4]. Flowers June through October and fruits June through November[2].
Seed dispersal
Seeds are dispersed by animals.
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Sideroxylon tenax at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens
Colletidae: Colletes francesae
Halictidae: Augochlora pura, Augochlorella aurata, Augochloropsis metallica, A. sumptuosa, Lasioglossum nymphalis
Leucospididae: Leucospis robertsoni
Pompilidae: Episyron conterminus posterus
Sphecidae: Bicyrtes quadrifasciata, Cerceris fumipennis, Ectemnius rufipes ais, Isodontia exornata, Oxybelus decorosum, Stictia carolina, Tachysphex apicalis
Vespidae: Monobia quadridens, Pachodynerus erynnis, Parancistrocerus fulvipes rufovestris, Stenodynerus histrionalis rufustus
Use by animals
Fruits are eaten by fallow deer [5] and birds[1].
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 [[1]]Accessed: March 17, 2016
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: James R. Allison, Harry E. Ahles, J. Ambrose, Loran C. Anderson, D.F. Austin, C.R. Bell, J. Bowers, N. Coile, A.H. Curtiss, A.R. Darr, R.J. Eaton, Angus Gholson, Robert K. Godfrey, Ann F. Johnson, Samuel b. Jones, Walter Judd, H. Kurz, Olga Lakela, Robert J. Lemaire, S.W. Leonard, Sidney McDaniel, K.M. Meyer, M. Moore, Gil Nelson, S. Parker, A.B. Pittman, Elmer C. Prichard, James D. Ray Jr., B. Reed, J. Simmons, R.W. Simons, C.E. Smith, R.R. Smith, A. Townesmith, Eric Van De Genachte, D.B. Ward, R. D. Whetstone, D. White, B. Winn, C.W. Wood, B. Zoodsma. States and Counties: Florida: Brevard, Collier, Duval, Flagler, Highlands, Indian River, Lake, Marion, Martin, Nassau, Palm Beach, St. Johns, St. Lucie, Volusia. Georgia: Bryan, Charlton, Chatham, Liberty, McIntosh. South Carolina: Beaufort, Charleston, Colleton, Hampton, Jasper. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
- ↑ [[2]]Regional Conservation. Accessed March 16, 2016
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 [[3]]Encyclopedia of Life. Accessed: March 17, 2016
- ↑ Morse, B. W., M. L. McElroy, et al. (2009). "Seasonal Diets of an Introduced Population of Fallow Deer on Little St. Simons Island, Georgia." Southeastern Naturalist 8(4): 571-586.