Difference between revisions of "Crocanthemum carolinianum"
(→References and notes) |
(→Description) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
Generally, for the ''Crocanthemum'' genus, they are erect, heraceous or suffrutescent perennials with alternate, stellate-pubescent leaves. There are two types of flowers, chasmogamous and cleistogamous. Chasmogamous flowers are on the pedicels that elongate to usually more than 1 cm long with large showy, tallow petals; there are numerous stamens and large sepals. The cleistogamous flowers are on the pedicels are usually less than 3 mm long, where the petals are absent, the stamens are few and the sepals are smaller than those of the chasmogamous flowers. The sepals are in 2 whorls, the outer are narrower than the inner. The capsule is 3-locular (Radford 1964). | Generally, for the ''Crocanthemum'' genus, they are erect, heraceous or suffrutescent perennials with alternate, stellate-pubescent leaves. There are two types of flowers, chasmogamous and cleistogamous. Chasmogamous flowers are on the pedicels that elongate to usually more than 1 cm long with large showy, tallow petals; there are numerous stamens and large sepals. The cleistogamous flowers are on the pedicels are usually less than 3 mm long, where the petals are absent, the stamens are few and the sepals are smaller than those of the chasmogamous flowers. The sepals are in 2 whorls, the outer are narrower than the inner. The capsule is 3-locular (Radford 1964). | ||
| − | Specifically, for ''Crocanthemum carolinianum'' species, the roots have tuberous thickenings, the | + | Specifically, for ''Crocanthemum carolinianum'' species, the roots have tuberous thickenings, the stems grow 1-3 dm tall, are pilose, arising from a basal rosettes of leaves. The leaves are widely elliptic to obovate, or nearly lanceolate, growing 2-5 cm long, and 0.7-2 cm wide, stellate pubescent on both surfaces, with longer trichomes above; basal leaves are often somewhat erose,usually larger than the stem leaves; the petioles grow 1-3 mm long. The cleistogamous flowers are absent. The chasmogamous flowers are solitary, are opposite a leaf (or appearing internodal). There are 6 sepals, the outer 3 linear, growing 5-10 mm long, are acute to acuminate, stellate pubescent; the petals growing 1.5-2 cm long. The capsules are globose to subglobose, growing 7-9 mm long. The seeds are reddish black in color, papillose, and growing 0.8-1 mm long (Radford 1964). |
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
Revision as of 20:41, 19 January 2016
| Crocanthemum carolinianum | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Violales |
| Family: | Cistaceae |
| Genus: | Crocanthemum |
| Species: | C. carolinianum |
| Binomial name | |
| Crocanthemum carolinianum (Walter) Michx. | |
| |
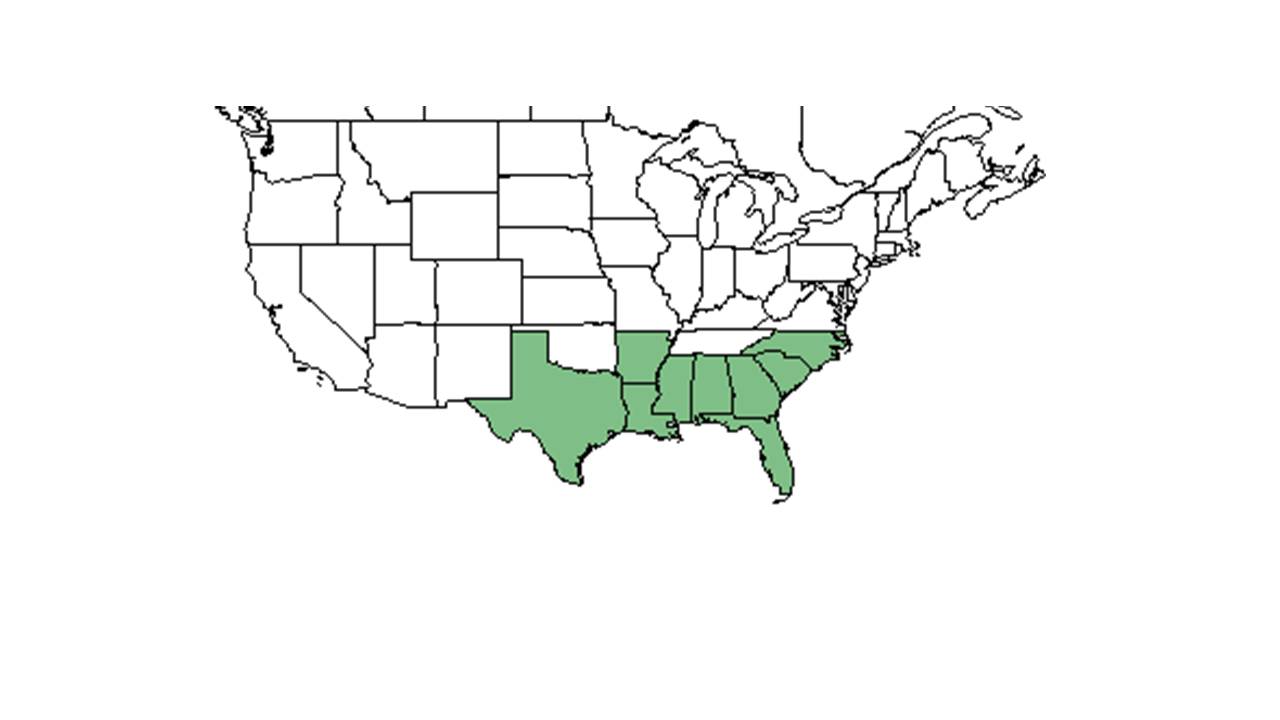
| Natural range of Crocanthemum carolinianum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Carolina frostweed
Synonym: Helianthemum carolinianum
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
Crocanthemum carolinianum is a perennial herbaceous species.
Generally, for the Crocanthemum genus, they are erect, heraceous or suffrutescent perennials with alternate, stellate-pubescent leaves. There are two types of flowers, chasmogamous and cleistogamous. Chasmogamous flowers are on the pedicels that elongate to usually more than 1 cm long with large showy, tallow petals; there are numerous stamens and large sepals. The cleistogamous flowers are on the pedicels are usually less than 3 mm long, where the petals are absent, the stamens are few and the sepals are smaller than those of the chasmogamous flowers. The sepals are in 2 whorls, the outer are narrower than the inner. The capsule is 3-locular (Radford 1964).
Specifically, for Crocanthemum carolinianum species, the roots have tuberous thickenings, the stems grow 1-3 dm tall, are pilose, arising from a basal rosettes of leaves. The leaves are widely elliptic to obovate, or nearly lanceolate, growing 2-5 cm long, and 0.7-2 cm wide, stellate pubescent on both surfaces, with longer trichomes above; basal leaves are often somewhat erose,usually larger than the stem leaves; the petioles grow 1-3 mm long. The cleistogamous flowers are absent. The chasmogamous flowers are solitary, are opposite a leaf (or appearing internodal). There are 6 sepals, the outer 3 linear, growing 5-10 mm long, are acute to acuminate, stellate pubescent; the petals growing 1.5-2 cm long. The capsules are globose to subglobose, growing 7-9 mm long. The seeds are reddish black in color, papillose, and growing 0.8-1 mm long (Radford 1964).
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
C. carolinianum can be found in longleaf pine-wiregrass savannas, as well as some disturbed areas, like mowed areas and fields (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowering has been observed in February, March, and April (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
This species occurs in habitat that burns frequently (FSU Herbarium).
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Robert K. Godfrey, Chris Cooksey, R. Komarek, Loran C. Anderson, and Richard R. Clinebell II. States and Counties: Florida: Leon. Georgia: Grady and Thomas.
Radford, Albert E., Harry E. Ahles, and C. Ritchie Bell. Manual of the Vascular Flora of the Carolinas. 1964, 1968. The University of North Carolina Press. 718-9. Print.