Difference between revisions of "Cirsium nuttallii"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→References and notes) |
|||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{taxobox | {{taxobox | ||
| name = Cirsium nuttallii | | name = Cirsium nuttallii | ||
| − | | image = | + | | image = Cirs_nutt.jpg |
| − | | image_caption = | + | | image_caption = Photo by Matthew Merritt, [http://www.florida.plantatlas.usf.edu/Plant.aspx?id=1018&display=photos Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants] |
| regnum = Plantae | | regnum = Plantae | ||
| divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | | divisio = Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants | ||
Revision as of 17:58, 19 January 2016
| Cirsium nuttallii | |
|---|---|
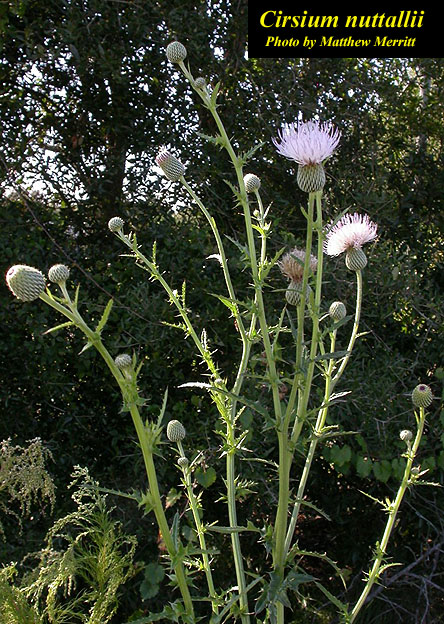

| |
| Photo by Matthew Merritt, Atlas of Florida Vascular Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Cirsium |
| Species: | C. nuttallii |
| Binomial name | |
| Cirsium nuttallii DC. | |
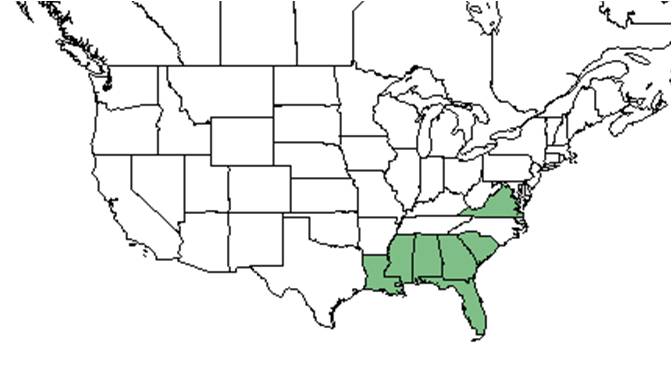
| |
| Natural range of Cirsium nuttallii from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Nuttall's thistle
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Carduus nuttallii
Description
A description of Cirsium nuttallii is provided in The Flora of North America.
C. nuttallii is a biennial species that develops a deep taproot and basal rosette the first year, then shoots up a single, erect, glabrous stem [1][2]. It can be distinguished from other Cirsium by having branched and many-headed stems (Krings et al. 2002).
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida and Georgia, C. nuttallii can be found in loamy sand of pine savannas, Hymenachne depressions, and freshwater marsh banks. It will grow in sunny, open and disturbed habitats such as roadsides, railroad tracks, pastures, levees, highways, and upland fallow fields [1] (FSU Herbarium). Soils include loamy sand and sandy loam (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Cirsium nuttallii can be found flowering May through July with white to pink flowers [1].
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
It produces a large number of seeds and has been observed to self-sow freely [1][3].
Fire ecology
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Cirsium nuttallii at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus griseocollis
Halictidae: Halictus poeyi
Megachilidae: Lithurgus gibbosus
Use by animals
The seeds are eaten by birds, but avoids herbivory from deer[4]. It is the larval host to the little metalmark butterfly [5].
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Global Conservation Status: G5[6].
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, James R. Birkhaulter, D. Burch, Emily Earp, R.K. Godfrey, R. Komarek, Marc Minno, Paul L. Redfearn Jr., Cecil R. Slaughter, L.B. Trott, D.B. Ward. States and Counties: Florida: Brevard, Escambia, Gadsden, Jefferson, Lee, Leon, Palm Beach, Polk, Putnam, Taylor, Wakulla. Georgia: Grady. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Krings, Alexander, Randy Westbrooks, and Janine Lloyd. “CIRSIUM NUTTALLII (ASTERACEAE: CYNAREAE) NEW TO NORTH CAROLINA AND AN ILLUSTRATED KEY TO SOUTHEASTERN CONGENERS”. SIDA, Contributions to Botany 20.2 (2002): 845–848.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 [Native Florida Wildflowers]Accessed:December 7, 2015
- ↑ [Encyclopedia of Life] Accessed: December 7, 2015
- ↑ [Dave's Garden]Accessed: December 7, 2015
- ↑ [Naturescapes of Beaufort, SC]Accessed: December 7, 2015
- ↑ [What Florida Native Plant is Blooming Today]Accessed: December 7, 2015
- ↑ [NatureServe]Accessed: December 7, 2015