Difference between revisions of "Bidens alba"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→Seed dispersal) |
||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
| + | The seed has two prongs that stick on to passing by animals, making dispersal zoochorous <ref name="Eat"/>. | ||
| + | |||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
Revision as of 18:41, 2 December 2015
| Bidens alba | |
|---|---|

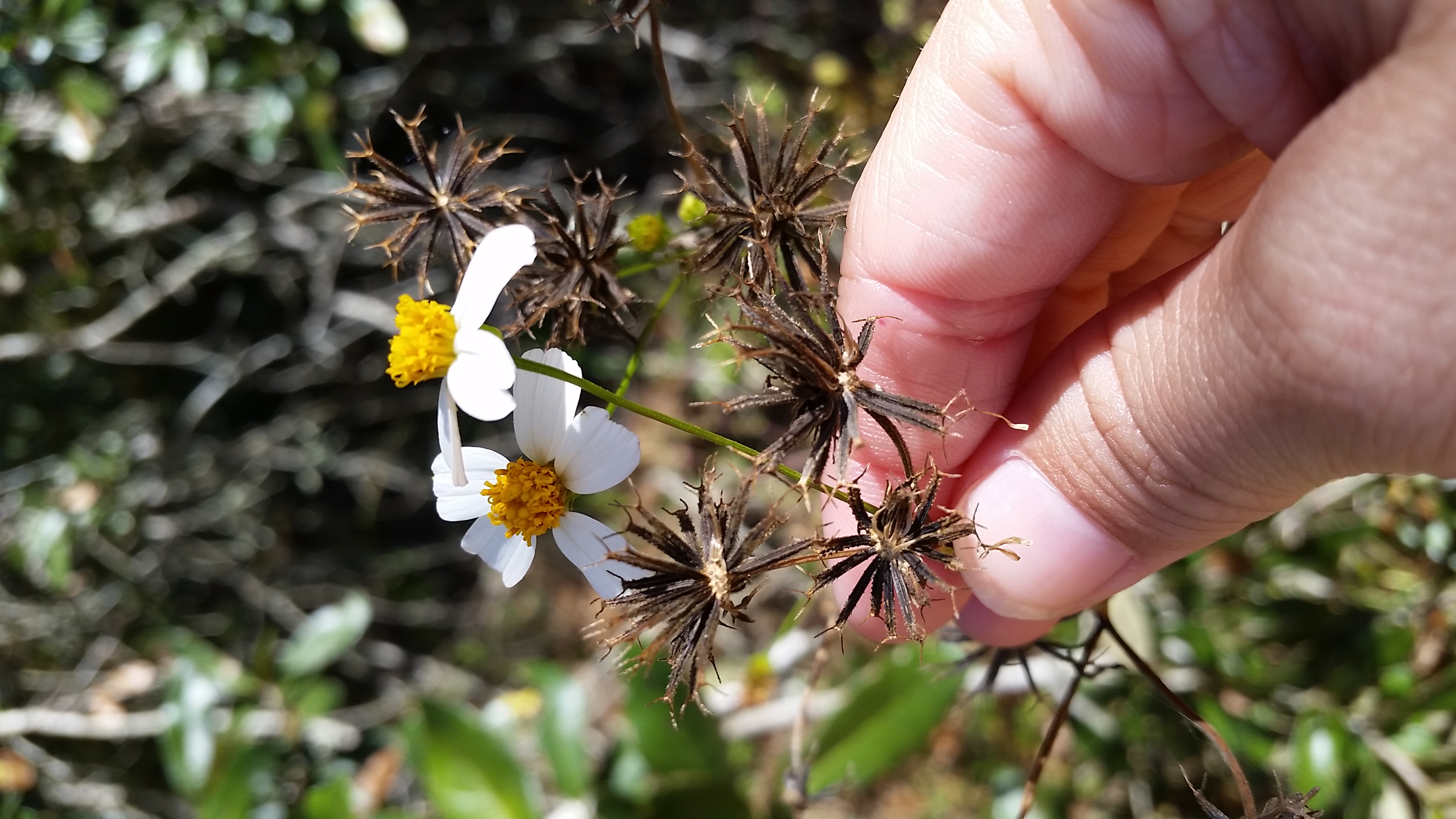
| |
| Photo taken by Michelle Smith | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae ⁄ Compositae |
| Genus: | Bidens |
| Species: | B. alba |
| Binomial name | |
| Bidens alba (L.) DC. | |
| |
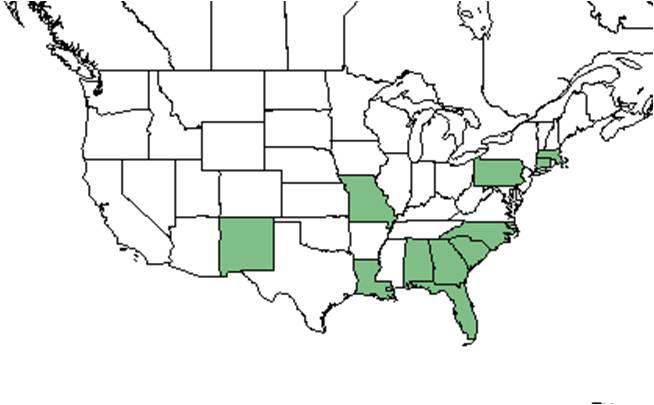
| Natural range of Bidens alba from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: Romerillo
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
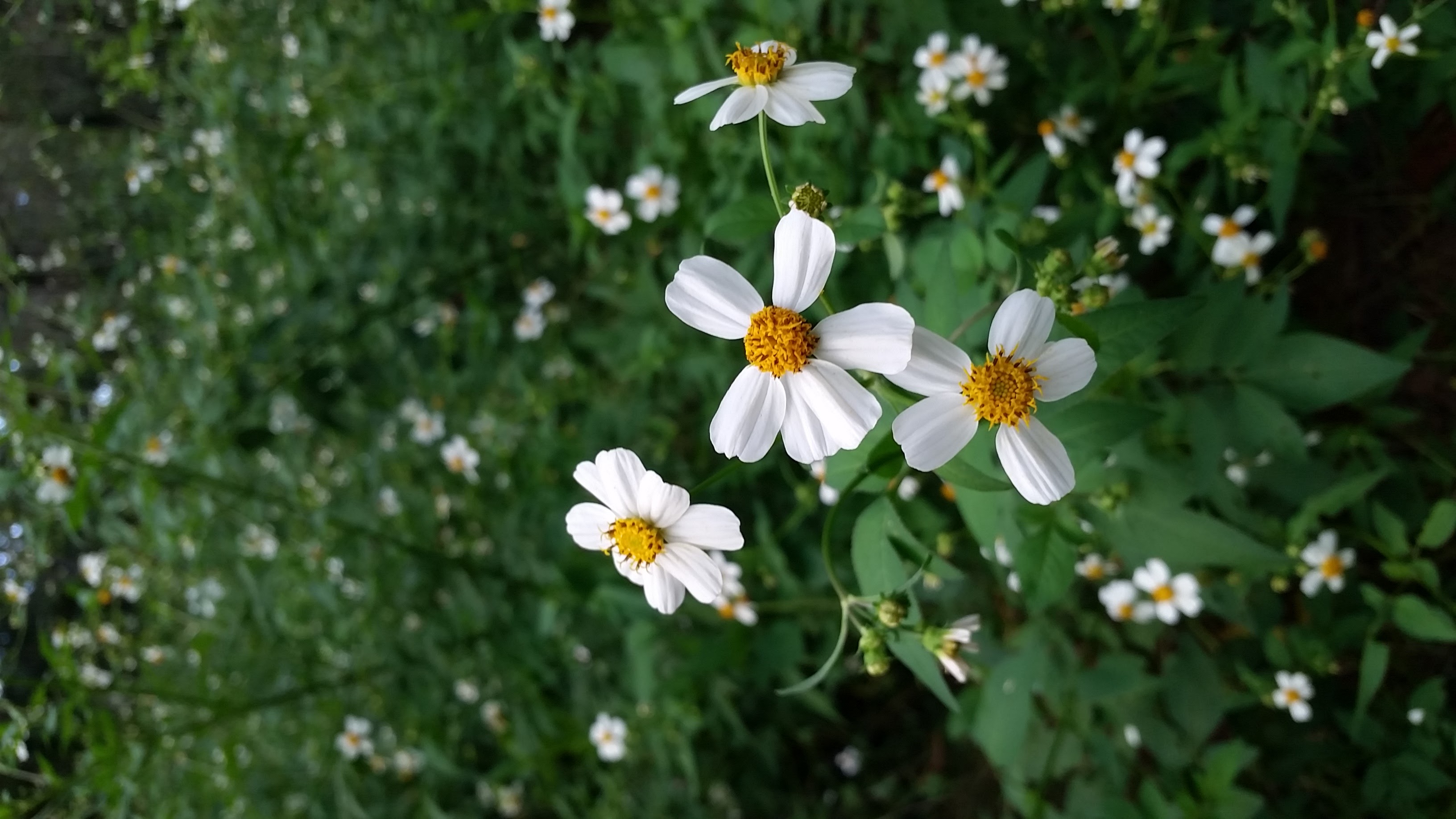
B. alba is a weedy annual or a short lived perennial that has vertical roots [1] [2]. Leaves are arranged opposite with depressed midveins [1].
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain in Florida, B. alba can be found in pine-oak woodlands (FSU Herbarium). It has been found to be common in disturbed areas such as railroads, citrus orchards, soil dumps and empty lots (FSU Herbarium; Ramirez et al. 2012). It has been observed to grow in loamy sand (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Andropogon, Euphorbia, and Ambrosia (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It has been recorded flowering January and May through November (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
The seed has two prongs that stick on to passing by animals, making dispersal zoochorous [2].
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Bidens alba at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Apidae: Apis mellifera, Bombus impatiens, B. pennsylvanicus, Mellisodes communis, M. comptoides, Nomada fervida
Halictidae: Agapostemon splendens, Augochlora pura, Augochlorella aurata, A. gratiosa, Augochloropsis metallica, Dieunomia heteropoda, Halictus poeyi, Lasioglossum pectoralis
Megachilidae: Anthidiellum notatum rufomaculatum, A. perplexum, Coelioxys dolichos, C. modesta, C. octodentata, C. sayi, Dolichostelis louisae, Heriades leavitti, Megachile albitarsis, M. brevis pseudobrevis, M. exilis parexilis, M. inimica, M. mendica, M. petulans, M. rugifrons, M. xylocopoides
Sphecidae: Ammophila pictipennis, A. urnaria, Bicyrtes capnoptera, Cerceris blakei, Isodontia exornata, Microbembex monodonta, Philanthus ventilabris
Vespidae: Eumenes smithii, Pachodynerus erynnis, Stenodynerus fundatiformis
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Deyrup, M.A. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: October 2015. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Ed Keppner, Lisa Keppner, R. Kral, Annie Schmidt, Kyle W. Shankle. States and Counties: Florida: Bay, Gulf, Indian River, Leon, Liberty, Martin, Wakulla. Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
