Difference between revisions of "Aureolaria pectinata"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→References and notes) |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. | + | Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Robert K. Godfrey. States and Counties: Florida: Wakulla. |
| + | |||
| + | University of Florida Herbarium database. URL: [https://www.flmnh.ufl.edu/herbarium/]. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Steven P. Christman, Nancy Coile, Brenda Herring, Robin B. Huck, Jean Huffman. States and Counties: Florida: Collier, Sarasota, Suwannee, Wakulla. South Carolina: Aiken. | ||
Revision as of 19:21, 30 November 2015
| Aureolaria pectinata | |
|---|---|

| |
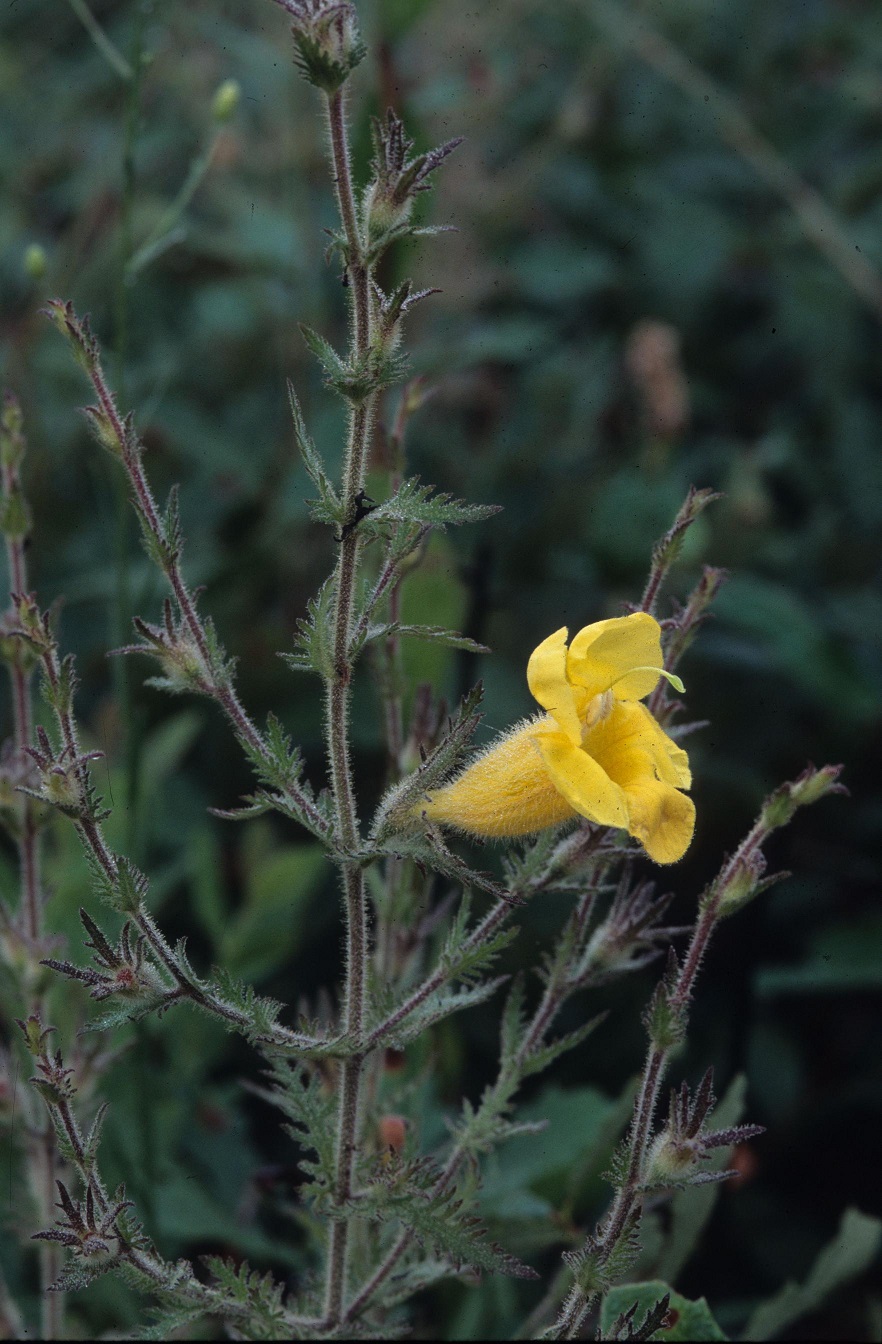
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Scrophulariaceae |
| Genus: | Aureolaria |
| Species: | A. pectinata |
| Binomial name | |
| Aureolaria pectinata (Nutt.) Pennell | |
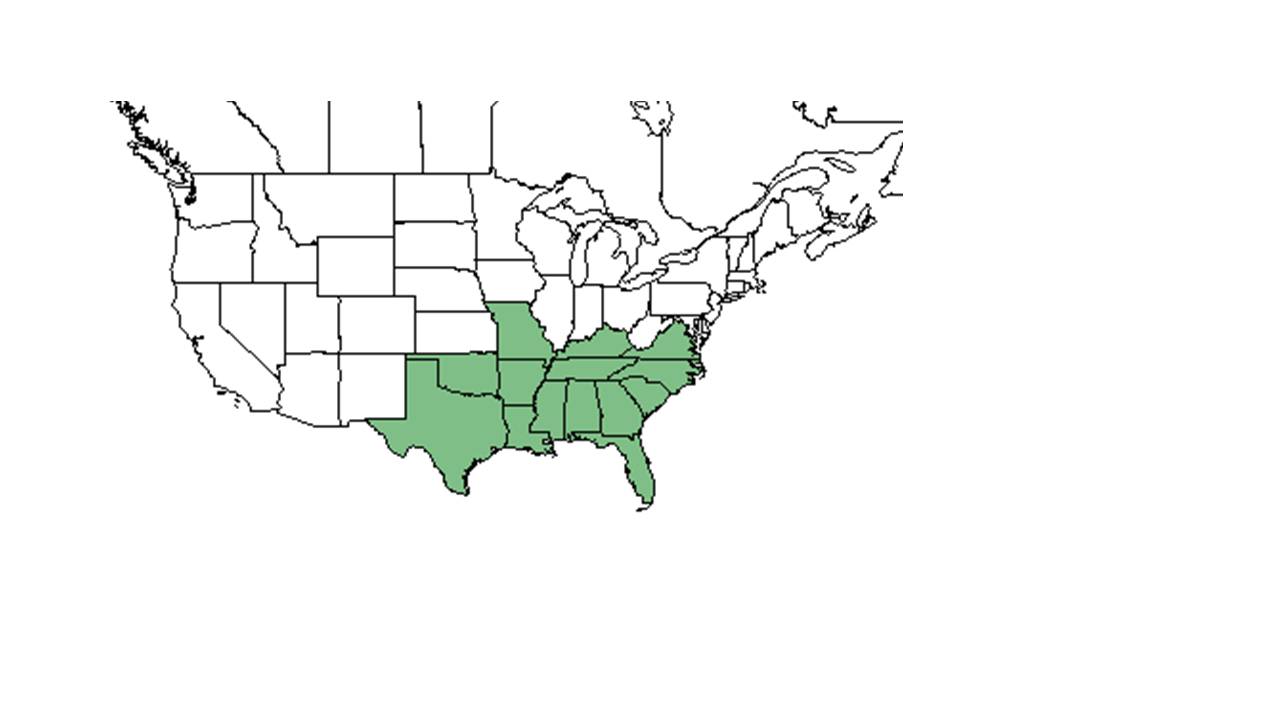
| |
| Natural range of Aureolaria pectinata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common Name: Combleaf Yellow False Foxglove
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonym: Gerardia pectinata
Description
A. pectinata has opposite, fern like leaves which are pinnately incised, with sticky glandular hairs [1]. It is a hemiparasitic plant that attaches modified roots to the roots of host plants, such as oaks [2].
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
A. pectinata can occur in turkey oak sandhills, longleaf pine communities, upland hardwood forests, savannas, glades, stream banks and slash pineland [3] [1] (FSU Herbarium).
Associated species include Pinus elliottii, Serenoa repens, Quercus geminata, Q. myrtifolia, Q. chapmanii, Liatris elegans, L. tenuifolia, and Salvia azurea (UF Herbarium).
Phenology
A. pectinata has bisexual, yellow flowers that bloom spring, summer, and fall. The ovary is superior and fruits in a capsule summer and fall [1]. The flower buds have a reddish tip, while the calyx is densely hairy [2].
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Studies have observed that A. pectinata does not occur in unburned sites, but does occur in burned sites (Harrod et al. 2000; Kush et al. 2000). Kush et al. (2000) found that A. pectinata occurred in biennially burned longleaf pine stands regardless of burning season. In Harrod et al. (2000) it was observed growing in a burned xeric hardwood site.
Pollination
Hummingbirds and bumblebees pollinate Aureolaria pectinata [2].
Use by animals
It is the larval host plant for the Baltimore checkerspot butterfly (Euphydryas phaeton)[2].
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Conservation status: Global: G5 [4].
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Robert K. Godfrey. States and Counties: Florida: Wakulla.
University of Florida Herbarium database. URL: [1]. Last accessed: November 2015. Collectors: Steven P. Christman, Nancy Coile, Brenda Herring, Robin B. Huck, Jean Huffman. States and Counties: Florida: Collier, Sarasota, Suwannee, Wakulla. South Carolina: Aiken.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 [Native and Naturalized Plants of the Carolinas and Georgia] Accessed November 30, 2015.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 [Arkansas Native Plant Society] Accessed November 30, 2015
- ↑ [Missouri Department of Conservation] Accessed November 30, 2015
- ↑ [NatureServe] Accessed November 30, 2015