Difference between revisions of "Tephrosia spicata"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
| + | It has been recorded flowering and fruiting May through October (FSU Herbarium). | ||
| + | |||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
It is dispersed by gravity (Kirkman et al 2004). | It is dispersed by gravity (Kirkman et al 2004). | ||
Revision as of 13:54, 3 November 2015
| Tephrosia spicata | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Tephrosia |
| Species: | T. spicata |
| Binomial name | |
| Tephrosia spicata (Walter) Torr. & A. Gray | |
| |
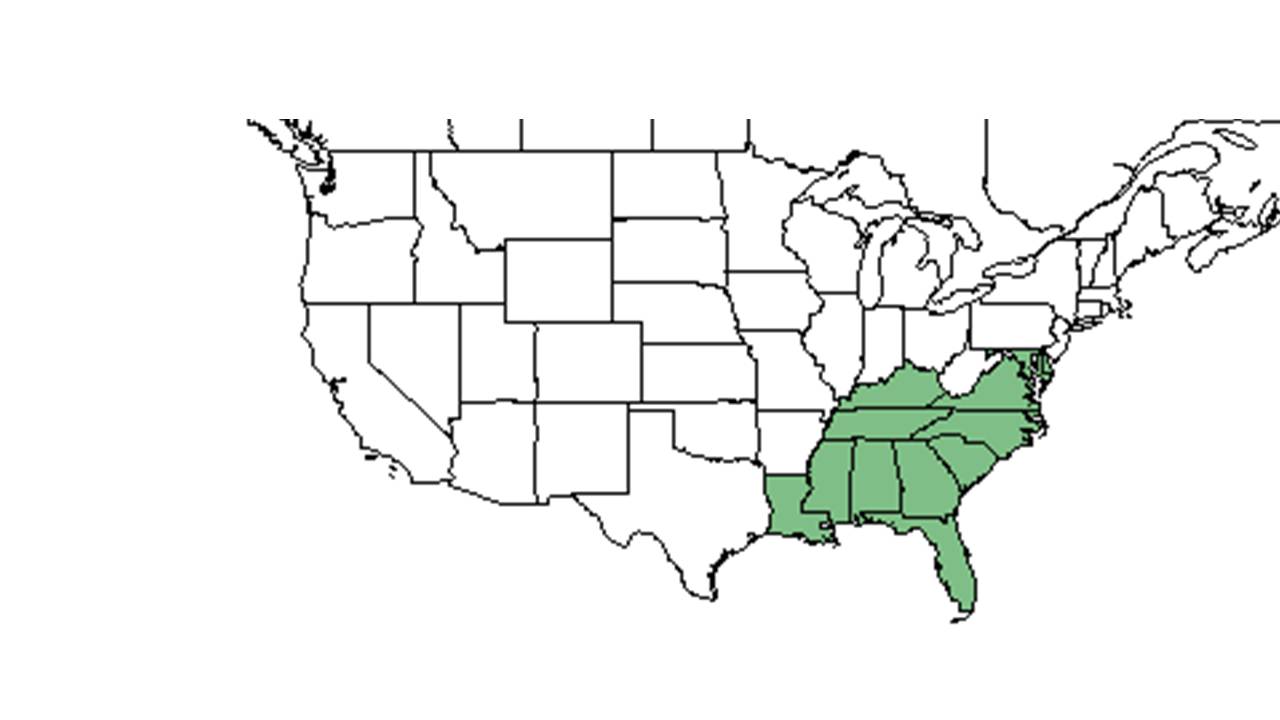
| Natural range of Tephrosia spicata from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: spiked hoarypea
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Tephrosia spicata can be found in coastal hammocks; wiregrass/pine communities; pine savannas; mixed hardwood forests; longleaf pine-turkey oak hills; turkey oak barrens; and longleaf pine scrub oak sand ridges (FSU Herbarium; Kirkman et al. 2004). It has been found in human disturbed areas such as railroad beds, cut over pine flatwoods, and roadsides. Soil types include loamy sand, sandy loam, clay soil, sand, sandy peat, and sandy clay (FSU Herbarium). Associated species include Phlox floridana, Calamintha dentata, Canna, Sambucus, Aristida stricta, Rhynchospora, Tephrosia floridana and T. chrysophylla (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It has been recorded flowering and fruiting May through October (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
It is dispersed by gravity (Kirkman et al 2004).
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Kirkman, L.K., K.L. Coffey, R.J. Mitchell, and E.B. Moser. 2004. Ground Cover Recovery Patterns and Life-History Traits: Implications for Restoration Obstacles and Opportunities in a Species-Rich Savanna. Journal of Ecology 92:409-421