Difference between revisions of "Symphyotrichum concolor"
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) |
KatieMccoy (talk | contribs) (→References and notes) |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| + | Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: [http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu]. Last accessed: Collectors: States and Counties: Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy. | ||
| + | |||
Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems. | Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems. | ||
Revision as of 12:51, 13 October 2015
| Symphyotrichum concolor | |
|---|---|
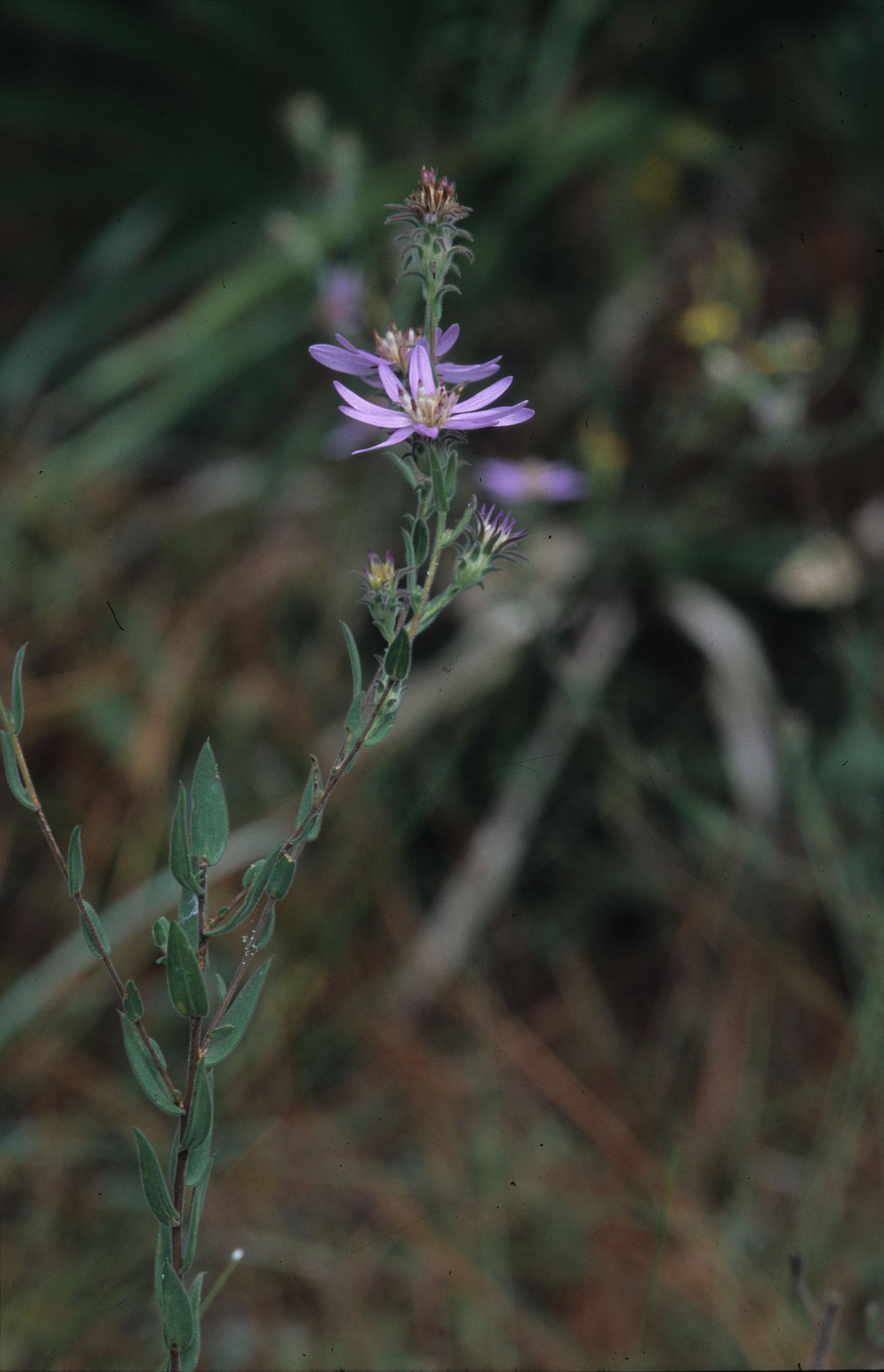

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida - Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteracae/Compositae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Species: | S. concolor |
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum concolor (L.) G.L. Nesom | |
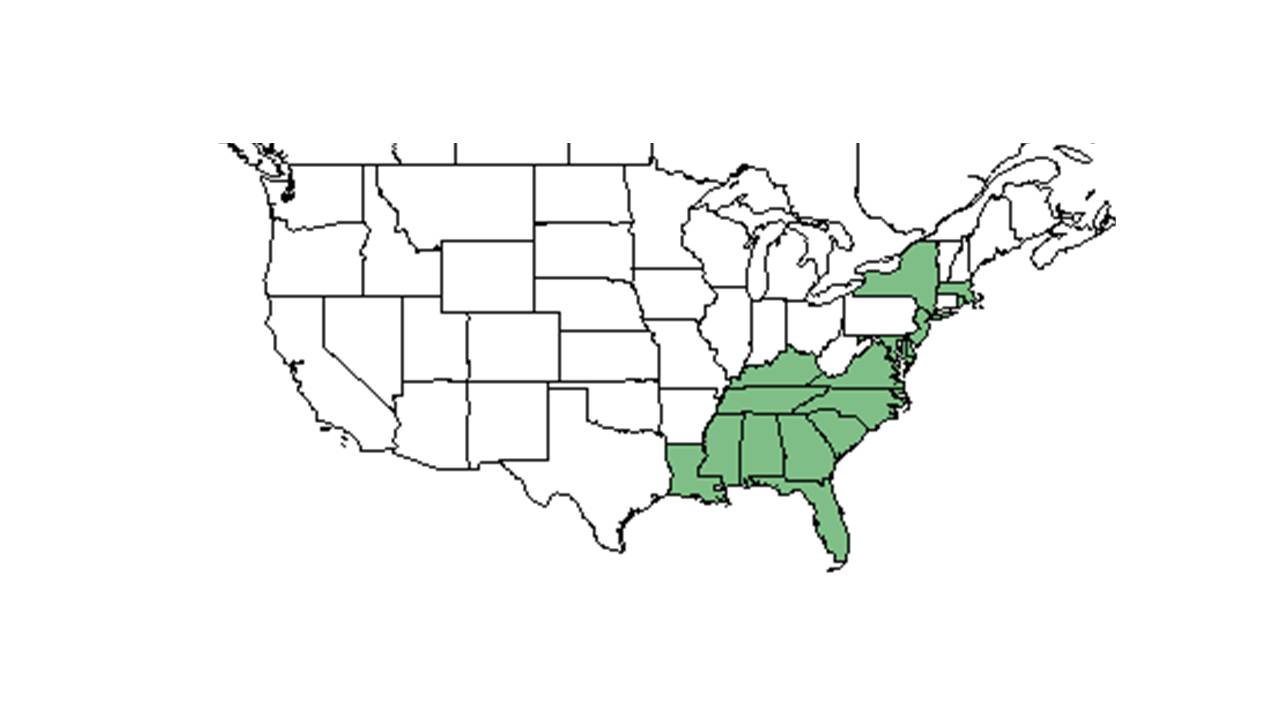
| |
| Natural range of Symphyotrichum concolor from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: eastern silver aster
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Description
A description of Symphyotrichum concolor is provided in The Flora of North America.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
In the Coastal Plain region, S. concolor can be found at the edges of limestone glades, longleaf pine-wiregrass flatwoods, pine-oak-hickory woods, scrub oak sand ridges, edges of brackish marshes, annually burned pinelands, former longleaf pine savannas, longleaf pine-scrub oaks, sandhills, and along roadways (FSU Herbarium). It is restricted to native groundcover and can be found in upland pines of South Georgia (Ostertag and Robertson 2007). Associated species include Schoenus nigricans, Muhlenbergia capillaris, Quercus laevis, Q. incana, Q. minima, Q. margaretta, Aristida stricta, Polygonella gracilis, Smilax auriculata, Licania michauxii, Eupatorium compositifolium, Pinus taeda, Aster adnatus, Ilex vomitoria, Pteridium aquilinum, Polygonella gracilis, Solidago puberula, Liatris gracilis, Chrysopsis lanuginosa, Vaccinium darrow, Warea sessilifolia, Pityopsis graminifolia var. tenuifolia, Liatris chapmanii, Aster linarrifolius, Andropogon, Schizachyrium, Serenoa repens, Smilax auriculata, Solidago odora, Helianthus radula, Tridens ambiguous, Ilex opaca, Baptisia lanceolata, Lespedeza hirta, Petalostemum carolinianum, Agaritina aromatica, Pityopsis aspera var. adenolepsi, and Vaccinium lanuginosa (FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
Flowers and fruits in November and October (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: Collectors: States and Counties: Compiled by Tall Timbers Research Station and Land Conservancy.
Ostertag, T.E., and K.M. Robertson. 2007. A comparison of native versus old-field vegetation in upland pinelands managed with frequent fire, South Georgia, USA. Pages 109–120 in R.E. Masters and K.E.M. Galley (eds.). Proceedings of the 23rd Tall Timbers Fire Ecology Conference: Fire in Grassland and Shrubland Ecosystems.