Difference between revisions of "Andropogon arctatus"
Annjohnson (talk | contribs) |
Annjohnson (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| − | It is maintained by fire. <ref name="Kral et al 1983">Kral, R. (1983). Andropogon arctatus Chapm. A report on some rare, threatened or endangered forest-related vascular plants of the South. R. Kral. Atlanta, GA, USDA Forest Service, Paper 183: 40-43.</ref> flowers in fall only after fire the same year.[[annjohnson]]<ref>ann johnson black creek bog phenological data 1993-2015<ref | + | It is maintained by fire. <ref name="Kral et al 1983">Kral, R. (1983). Andropogon arctatus Chapm. A report on some rare, threatened or endangered forest-related vascular plants of the South. R. Kral. Atlanta, GA, USDA Forest Service, Paper 183: 40-43.</ref> flowers in fall only after fire the same year.[[annjohnson]]<ref>ann johnson black creek bog phenological data 1993-2015</ref> |
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
Revision as of 15:43, 18 August 2015
| Andropogon arctatus | |
|---|---|
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida – Monocotyledons |
| Order: | Cyperales |
| Family: | Poaceae ⁄ Gramineae |
| Genus: | Andropogon |
| Species: | A. arctatus |
| Binomial name | |
| Andropogon arctatus Chapm. | |
| |
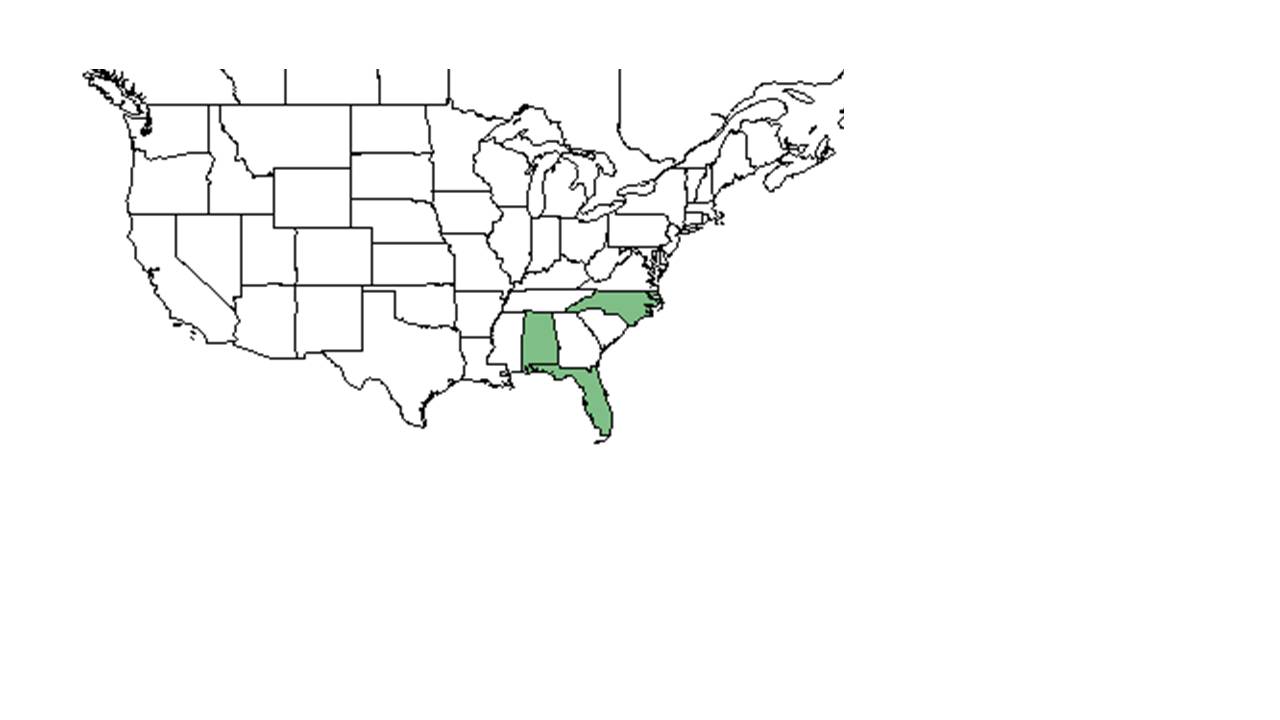
| Natural range of Andropogon arctatus from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common names: Pinewoods Bluestem
Contents
Description
It is a perennial (Hall 1978). This species grows scattered but it is mostly very abundant in areas it is seen (FSU Herbarium).
Distribution
It is occasionally found in northern and central peninsula of Florida; central and western panhandle (Wunderlin and Hansen 2003).
Ecology
Habitat
It is found in moist, sunny, low grass-sedge clearings and open pine flatwood and savanna communities.[1]. It is found in dry to wet loamy sands and sand pine scrub environments (Wunderlin and Hansen 2003, FSU Herbarium).
Phenology
It flowers from late September to frost.[1] It has been observed fruiting from October through November (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
It is maintained by fire. [1] flowers in fall only after fire the same year.annjohnson[2]
Pollination
Use by animals
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014. Collectors: Robert K. Godfrey, Ann F. Johnson, Debbie White, Loran C. Anderson, A. F. Clewell, Christopher Campbell, Angus Gholson, Dennis Hardin, and Ann F. Johnson. States and Counties: Florida: Franklin, Liberty, Jackson, Gulf, Bay, Leon, and Calhoun. Georgia: Liberty.
Hall, David Walter. The Grasses of Florida. 1978. University of Florida – Dissertation. 442. Print.
Wunderlin, Richard P. and Bruce F. Hansen. Guide to the Vascular Plants of Florida. Second edition. 2003. University Press of Florida: Gainesville/Tallahassee/Tampa/Boca Raton/Pensacola/Orlando/Miami/Jacksonville/Ft. Myers. 177. Print.