Difference between revisions of "Trichostema dichotomum"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
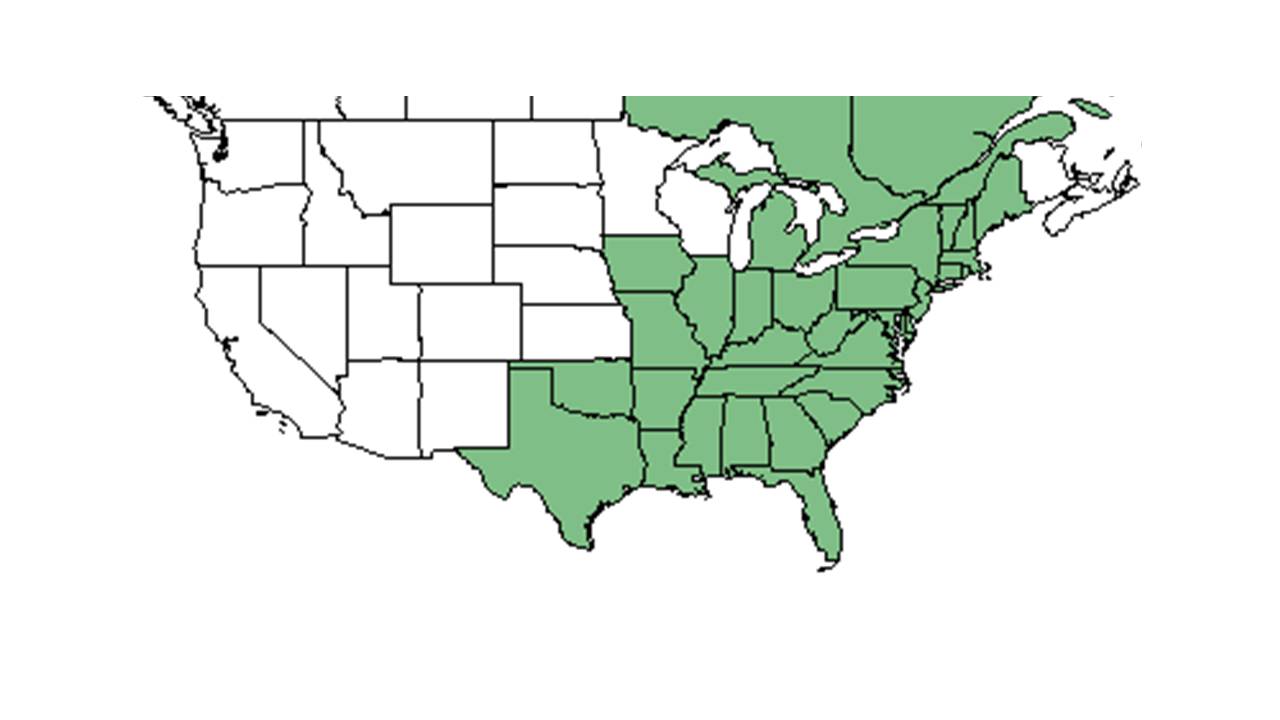
| range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Trichostema dichotomum'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov Plants Database]. | | range_map_caption = Natural range of ''Trichostema dichotomum'' from USDA NRCS [http://www.plants.usda.gov Plants Database]. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Common name: forked bluecurls | ||
==Description== | ==Description== | ||
<!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | <!-- Basic life history facts such as annual/perrenial, monoecious/dioecious, root morphology, seed type, etc. --> | ||
| − | |||
==Distribution== | ==Distribution== | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
| − | + | The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of ''Trichostema dichotomum'' at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015): | |
| − | Halictidae: Lasioglossum placidensis | + | Halictidae: ''Lasioglossum placidensis'' |
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
| Line 44: | Line 45: | ||
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
==References and notes== | ==References and notes== | ||
| − | + | BAZZAZ, F. A. 1979. The physiological ecology of plant succession. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst., 10:351- 371. | |
| − | + | Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA. | |
Deyrup, M. and L. Deyrup (2012). "The diversity of insects visiting flowers of saw palmetto (Arecaceae)." Florida Entomologist 95(3): 711-730. | Deyrup, M. and L. Deyrup (2012). "The diversity of insects visiting flowers of saw palmetto (Arecaceae)." Florida Entomologist 95(3): 711-730. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Kaczor, S. A. and D. C. Hartnett (1990). "Gopher tortoise (gopherus polyphemus) effects on soils and vegetation in a Florida sandhill." American Midland Naturalist 123: 100-111. | ||
Revision as of 15:04, 13 August 2015
| Trichostema dichotomum | |
|---|---|
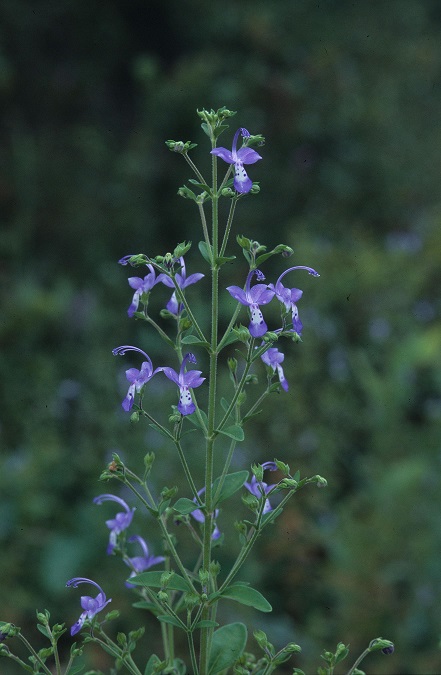

| |
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae ⁄ Labiatae |
| Genus: | Trichostema |
| Species: | T. dichotomum |
| Binomial name | |
| Trichostema dichotomum L. | |
| |
| Natural range of Trichostema dichotomum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: forked bluecurls
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Kaczor and Hartnett found that T. dichotomum had signifcantly lower cover on old tortoise mounds and undisturbed plots (1990). It is found in the longleaf pine patches that surrounded the golf course in Haile Plantation, Gainesville, Florida.
Phenology
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
High light intensities and large diurnal temperature fluctuations as a result of the tortoise mounds are probably favorable for the establishment of T. dichotomum (Bazzaz 1979 cited by Kaczor and Hartnett 1990).
Fire ecology
Pollination
The following Hymenoptera families and species were observed visiting flowers of Trichostema dichotomum at Archbold Biological Station (Deyrup 2015):
Halictidae: Lasioglossum placidensis
Use by animals
It was found to be one of the most common spring recruits on recently abandoned tortoise mounds (Kaczor and Hartnett 1990). Deyrup (2012) observed the bees, Caupolicana electa and Dialictus placidensis, on T. dichotomum.
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
BAZZAZ, F. A. 1979. The physiological ecology of plant succession. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst., 10:351- 371.
Deyrup, M.A. and N.D. 2015. Database of observations of Hymenoptera visitations to flowers of plants on Archbold Biological Station, Florida, USA.
Deyrup, M. and L. Deyrup (2012). "The diversity of insects visiting flowers of saw palmetto (Arecaceae)." Florida Entomologist 95(3): 711-730.
Kaczor, S. A. and D. C. Hartnett (1990). "Gopher tortoise (gopherus polyphemus) effects on soils and vegetation in a Florida sandhill." American Midland Naturalist 123: 100-111.