Difference between revisions of "Crotalaria purshii"
Ruthstetler (talk | contribs) |
Ruthstetler (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
| + | This species is fire tolerant and occurs in burned areas (FSU Herbarium). | ||
| + | |||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Revision as of 18:39, 9 July 2015
| Crotalaria purshii | |
|---|---|
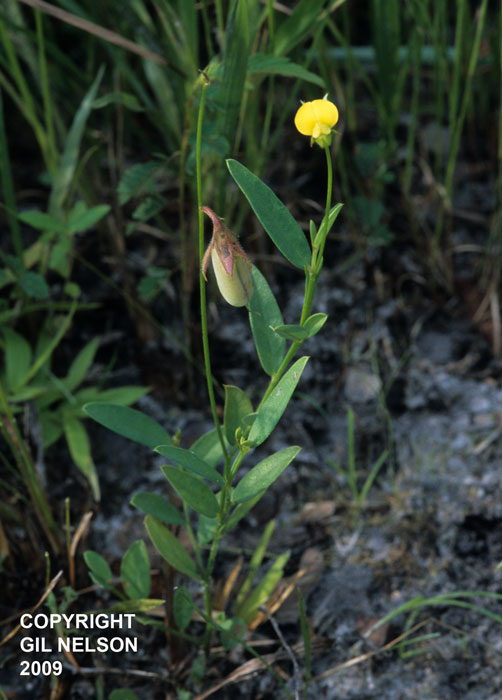

| |
| photo by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Crotalaria |
| Species: | C. purshii |
| Binomial name | |
| Crotalaria purshii DC. | |
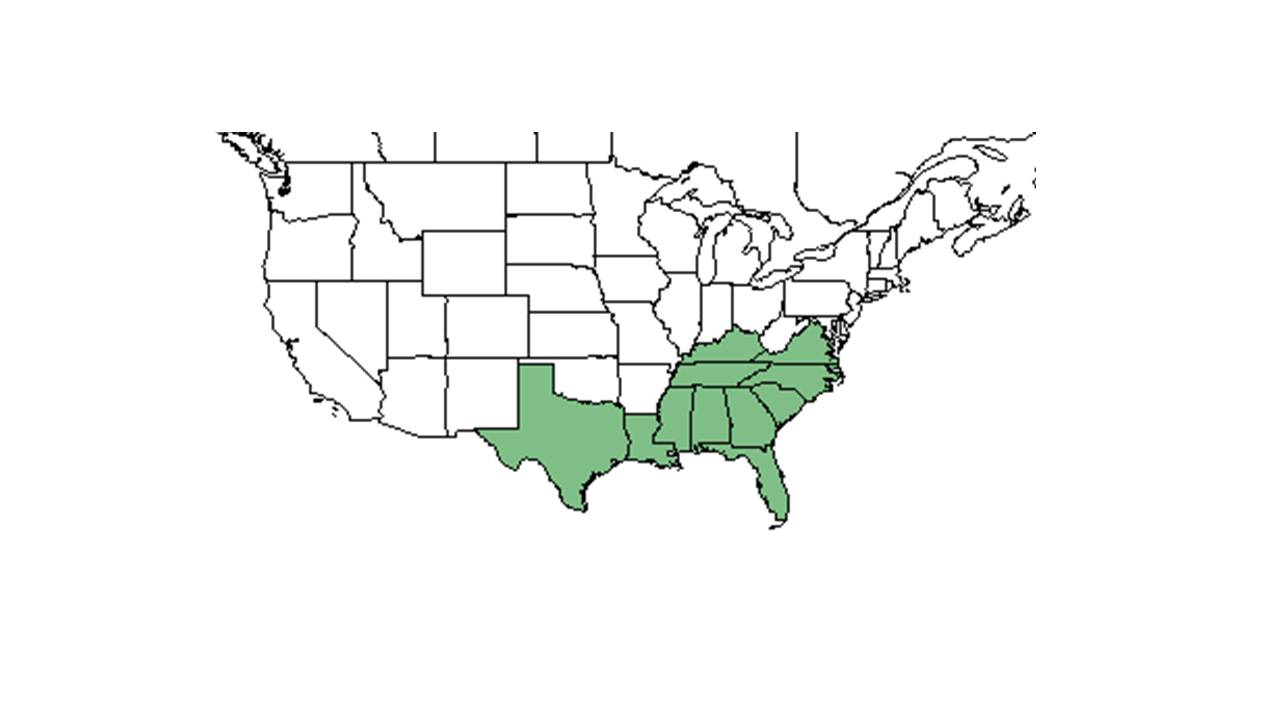
| |
| Natural range of Crotalaria purshii from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Common Name: Pursh's rattlebox
Distribution
Ecology
It is a legume.[1]
Habitat
It can live in temperatures ranging from 10 to 28 degrees Celsius with an average of 115 cm of rain annually.[2] It occurs in grassy pineland communities[1] such as loblolly pine communities.[2]
Phenology
Crotalaria purshii was observed flowering in sandhill and flatwood forests.[3]
Flowering has been observed in April through October, and fruiting has been observed in May through October (FSU Herbarium).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
This species is fire tolerant and occurs in burned areas (FSU Herbarium).
Pollination
Use by animals
It is consumed by bobwhite quail.[1]
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
Florida State University Robert K. Godfrey Herbarium database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2014.
Collectors: Harry E. Ahles, Loran C. Anderson, Grafton Anding, Wilson Baker, M.L. Bomhard, R. S. Campbell, Andre F. Clewell, Richard R. Clinebell II, D. S. Correll, Delzie Demaree, Robert K. Godfrey, J. Haesloop, A. Johnson, Lisa Keppner, Ed Keppner, R. Komarek, R. Kral Paul C Lemon, M. Jenkins, Sidney McDaniel, Thomas E. Miller, John B. Nelson, R. A. Norris, C.K. Pearse, A. B. Pittman, H. R. Reed, Annie Schmidt, Kenneth Lee Tyson, and Jean Wooten.
States and Counties: Alabama: Baldwin, Conecuh, Geneva, and Washington. Florida: Bay, Calhoun, Dixie, Duval, Franklin, Gadsden, Gulf, Lee, Leon, Liberty, Madison, Santa Rosa, Sarasota, Wakulla, Walton, and Washington. Georgia: Berrien, Coffee, Grady, Seminole, Thomas, and Tift. Louisiana: Washington. Mississippi: George, Jackson, and Pearl River. North Carolina: Sampson. South Carolina: Dorchester and Lee.
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Graham, E. H. (1941). Legumes for erosion control and wildlife. Washington, USDA
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Miller, J. H. and K. V. Miller (1999). Forest plants of the southeast, and their wildlife uses Champaign, IL, Southern Weed Science Society.
- ↑ Platt, W. J., Gregory W. Evans, and Mary M. Davis (1988). "Effects of Fires Season on Flowering of Forbs and Shurbs in Longleaf Pine Forests." Oecologia 76(3): 353-363.