Difference between revisions of "Crotalaria rotundifolia"
(→Pollination) |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
Its reproduction is robust to burn treatments and season of burn.<ref name="Hiers et al 2000"/> | Its reproduction is robust to burn treatments and season of burn.<ref name="Hiers et al 2000"/> | ||
| − | ===Pollination=== | + | ===Pollination=== |
| + | Mark Deyrup at Archbold Biological Station observed these Hymenoptera species on ''Crotalaria rotundifolia'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis | ||
| + | |||
===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ===Use by animals=== <!--Herbivory, granivory, insect hosting, etc.--> | ||
Caterpillars are often found consuming C. rotundifolia. Ants, especially Pogonomyrmex badius, help disperse the seeds long distances.<ref name="Stamp and Lucas 1990"/> | Caterpillars are often found consuming C. rotundifolia. Ants, especially Pogonomyrmex badius, help disperse the seeds long distances.<ref name="Stamp and Lucas 1990"/> | ||
Revision as of 17:30, 26 June 2015
| Crotalaria rotundifolia | |
|---|---|
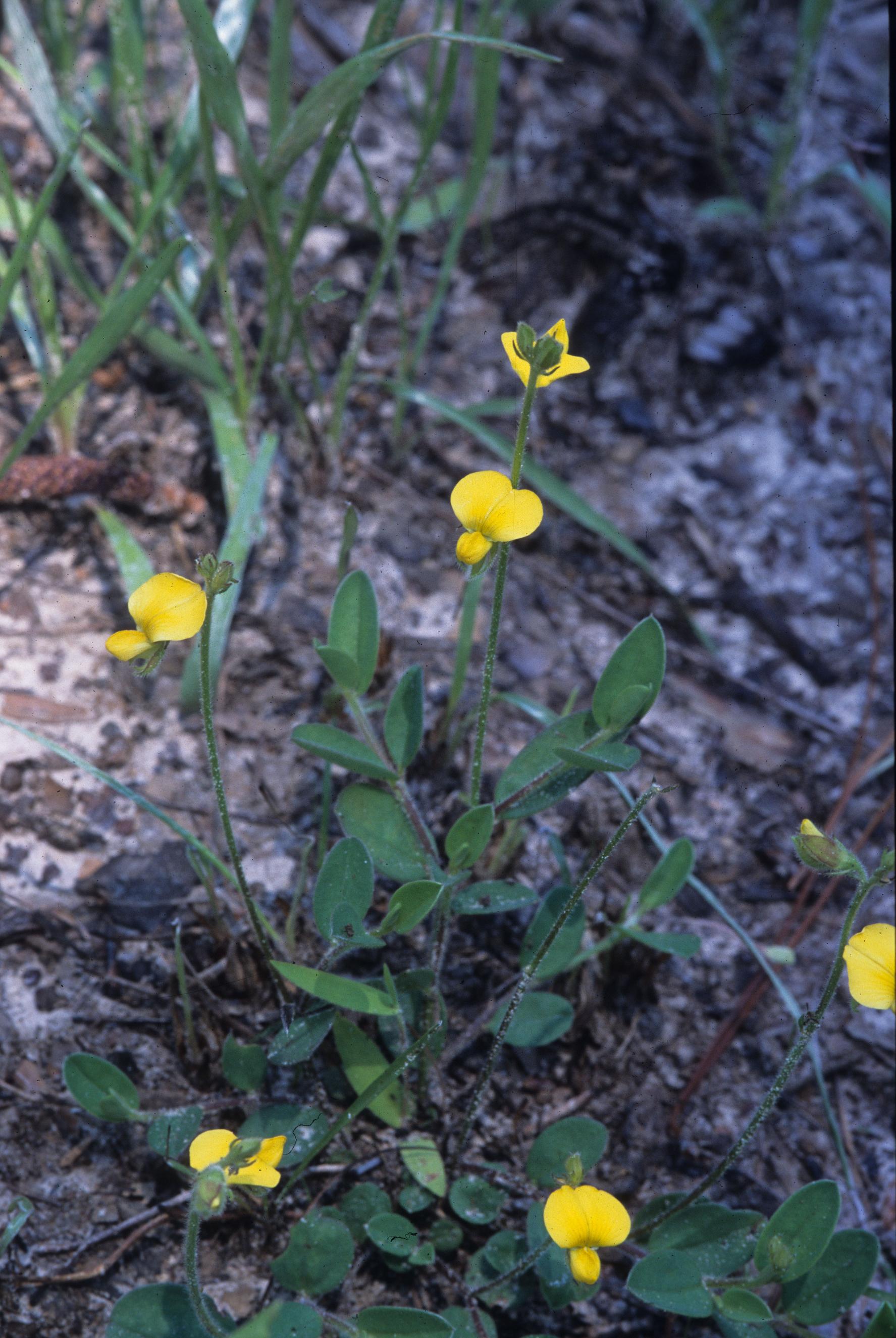

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae ⁄ Leguminosae |
| Genus: | Crotalaria |
| Species: | C. rotundifolia |
| Binomial name | |
| Crotalaria rotundifolia Walter ex J.F. Gmel. | |
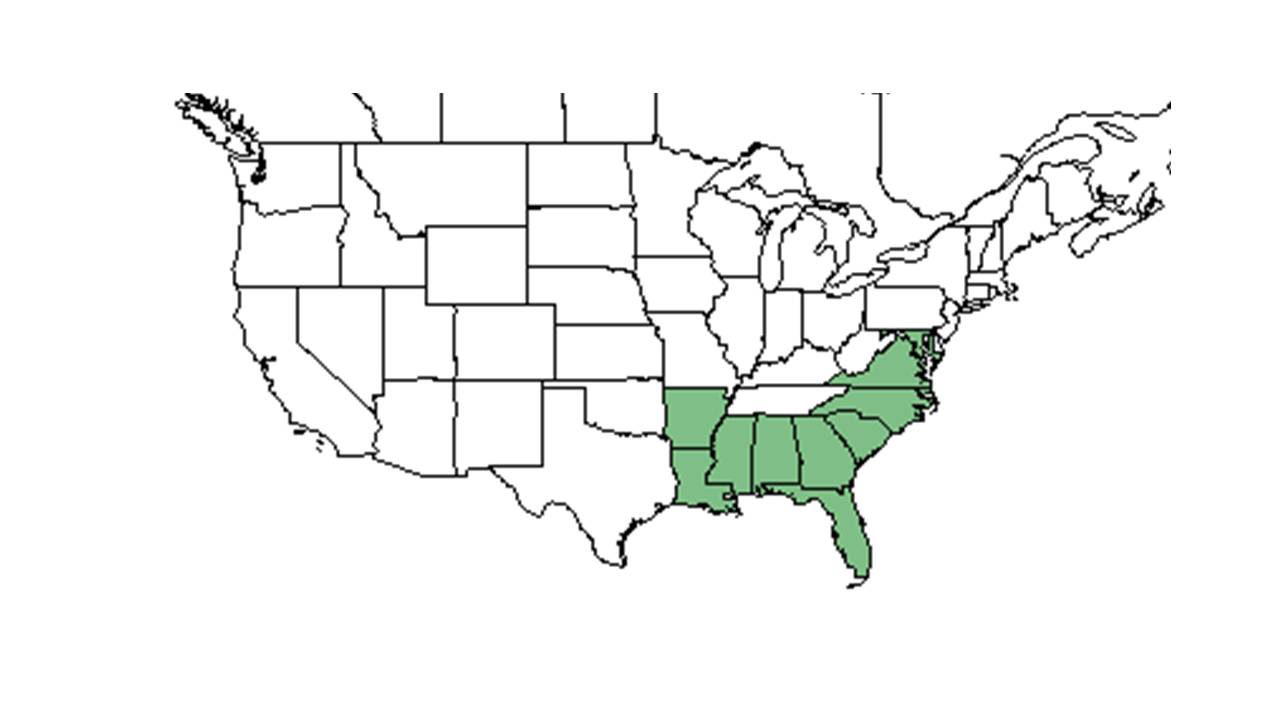
| |
| Natural range of Crotalaria rotundifolia from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
Distribution
Ecology
It is a nitrogen-fixing legume.[1] In a study by Davis, it was discovered that C. rotundifolia had higher mortality and less biomass in high carbon dioxide plots, suggesting that not all species will perform well as global carbon dioxide levels rise.[2]
Habitat
It’s a common associate in longleaf pine savannas.[2] It can also be found in sandhill communities.[3]
Phenology
It has a broad, bimodal flowering phenology with peaks in early April and late fall.[4] Perennial herbaceous legume.[2]
Seed dispersal
Seeds are forcefully expelled after the fruit matures and dries, and ants act as the main dispersal agents. The ballistic dispersal distance was found to be around .94 meters.[3]
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Its reproduction is robust to burn treatments and season of burn.[4]
Pollination
Mark Deyrup at Archbold Biological Station observed these Hymenoptera species on Crotalaria rotundifolia
Megachilidae: Megachile brevis pseudobrevis
Use by animals
Caterpillars are often found consuming C. rotundifolia. Ants, especially Pogonomyrmex badius, help disperse the seeds long distances.[3]
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ Runion, G. B., M. A. Davis, et al. (2006). "Effects of elevated atmospheric carbon dioxide on biomass and carbon accumulation in a model regenerating longleaf pine community." Journal of Environmental Quality 35: 1478-1486.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Davis, M. A., S. G. Pritchard, et al. (2002). "Elevated atmospheric CO2 affects structure of a model regenerating longleaf pine community." Journal of Ecology 90: 130-140.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Stamp, N. E. and J. R. Lucas (1990). "Spatial patterns and dispersal distances of explosively dispersing plants in Florida sandhill vegetation." Journal of Ecology 78: 589-600.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Hiers, J. K., R. Wyatt, et al. (2000). "The effects of fire regime on legume reproduction in longleaf pine savannas: is a season selective?" Oecologia 125: 521-530.