Difference between revisions of "Seymeria cassioides"
(→Seed bank and germination) |
|||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
===Seed dispersal=== | ===Seed dispersal=== | ||
===Seed bank and germination=== | ===Seed bank and germination=== | ||
| + | It requires exposed mineral soil and light on the soil surface to germinate (Stangle 1981). | ||
| + | “Exposed mineral soil and light on the soil surface to germinate and develop.” (Wade 1978). | ||
| + | |||
===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ===Fire ecology=== <!--Fire tolerance, fire dependence, adaptive fire responses--> | ||
===Pollination=== | ===Pollination=== | ||
Revision as of 18:41, 17 June 2015
| Seymeria cassioides | |
|---|---|

| |
| Photo was taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Scrophulariales |
| Family: | Scrophulariaceae |
| Genus: | Seymeria |
| Species: | S. cassioides |
| Binomial name | |
| Seymeria cassioides (J.F. Gmel.) S.F. Blake | |
| |
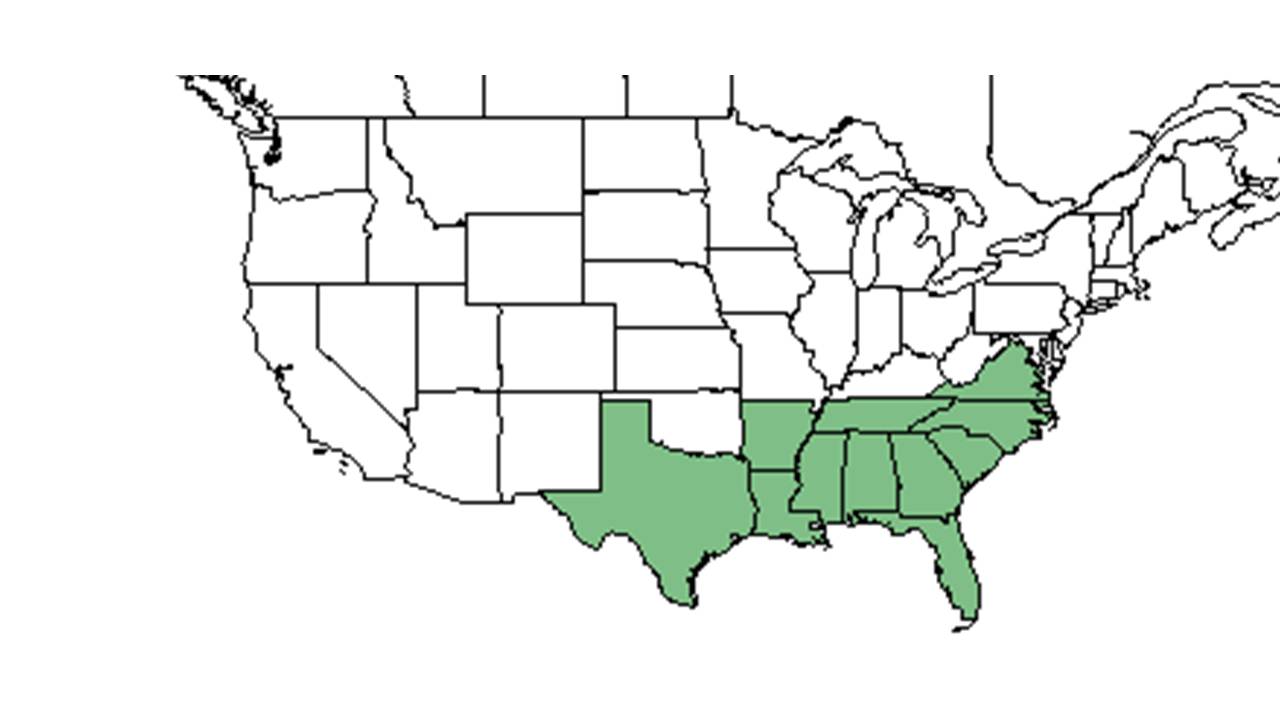
| Natural range of Seymeria cassioides from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
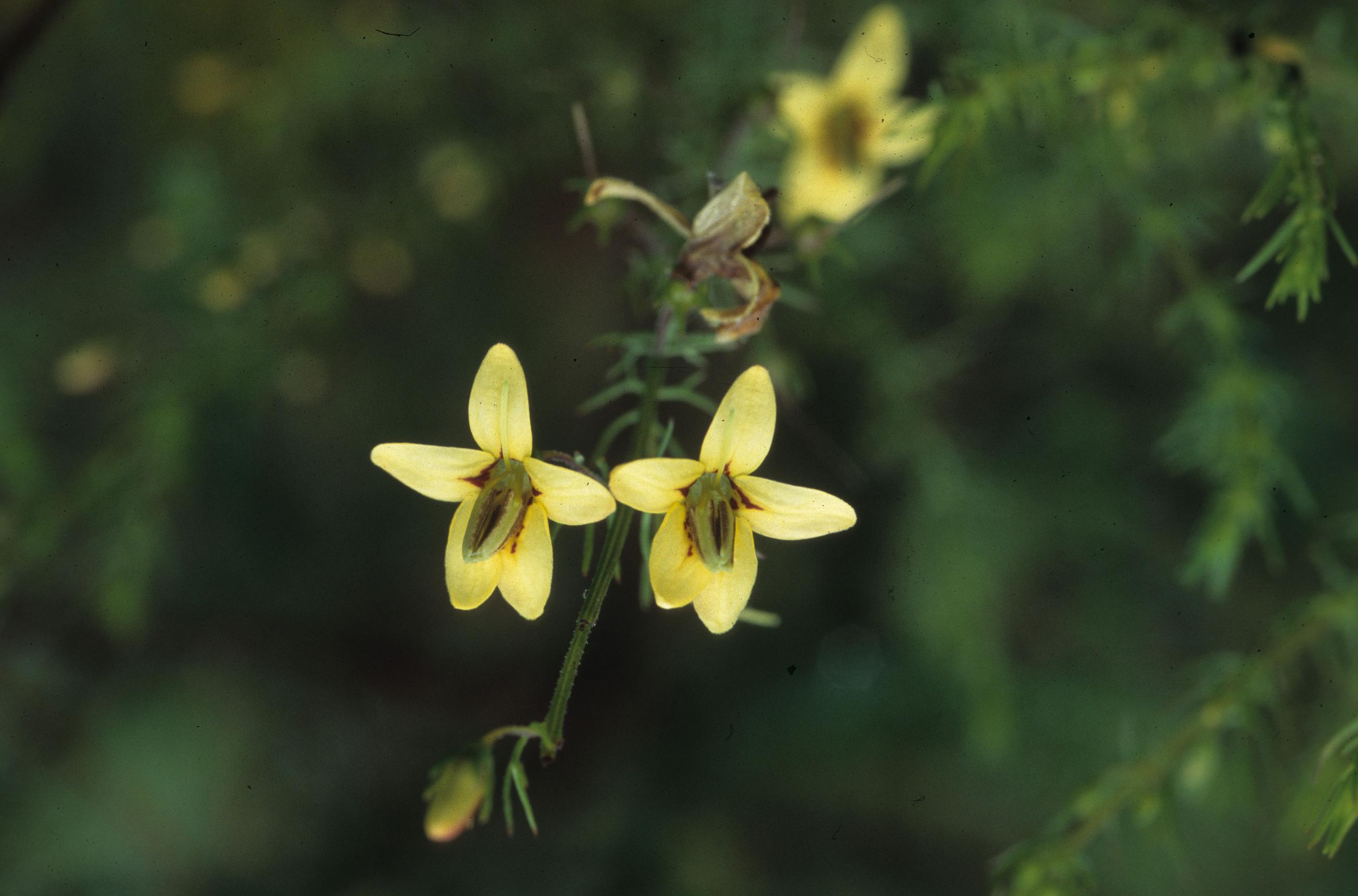
The common names are Yaupon blacksenna or Senna seymeria (Nelson 2005). Is an annual, herbaceous, root parasite on several species of southern pine (Fitzgerald et al 1977). “The stem get up to 1m tall, much branched, entire plant covered with glandular hairs. Leaves are finely divided into linear segments; in the field each segment gives the impression of being an individual leaf. Flowers are 1mm long, bright yellow with brown marks near the ovary, outside of the flower not hairy. Capsules are 5mm long, shiny brown when mature.” – Musselman and Mann 1978. "The flowers of this genus have an unusual type of anther opening, a small pore rather than a long slit.” – Musselman and Mann 1978.
Distribution
Ecology
Habitat
Phenology
Blooms from September to October (Nelson 2005). “Each flower lasts for only one day before falling from the plant."- Musselman and Mann 1978.
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
It requires exposed mineral soil and light on the soil surface to germinate (Stangle 1981). “Exposed mineral soil and light on the soil surface to germinate and develop.” (Wade 1978).