Difference between revisions of "Salvia azurea"
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
==Ecology== | ==Ecology== | ||
===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ===Habitat=== <!--Natural communities, human disturbed habitats, topography, hydrology, soils, light, fire regime requirements for removal of competition, etc.--> | ||
| + | Found in sandhills, flatwoods, and pine-oak-hickory woods (Nelson 2005). | ||
| + | |||
===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ===Phenology=== <!--Timing off flowering, fruiting, seed dispersal, and environmental triggers. Cite PanFlora website if appropriate: http://www.gilnelson.com/PanFlora/ --> | ||
Blooms from September to November (Nelson 2005). | Blooms from September to November (Nelson 2005). | ||
Revision as of 17:42, 17 June 2015
| Salvia azurea | |
|---|---|

| |
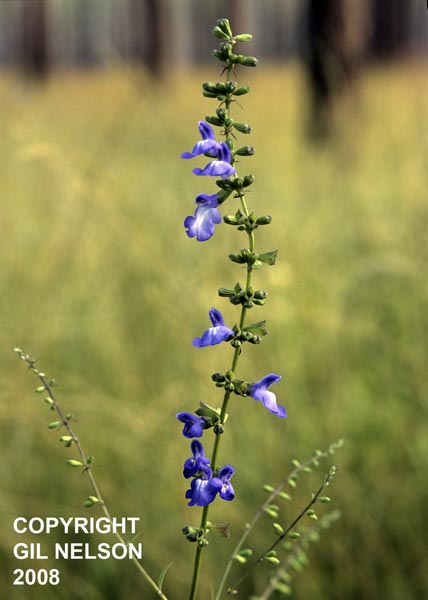
| Photo taken by Gil Nelson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta – Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Lamiales |
| Family: | Lamiaceae ⁄ Labiatae |
| Genus: | Salvia |
| Species: | S. azurea |
| Binomial name | |
| Salvia azurea Michx. ex Lam. | |
| |
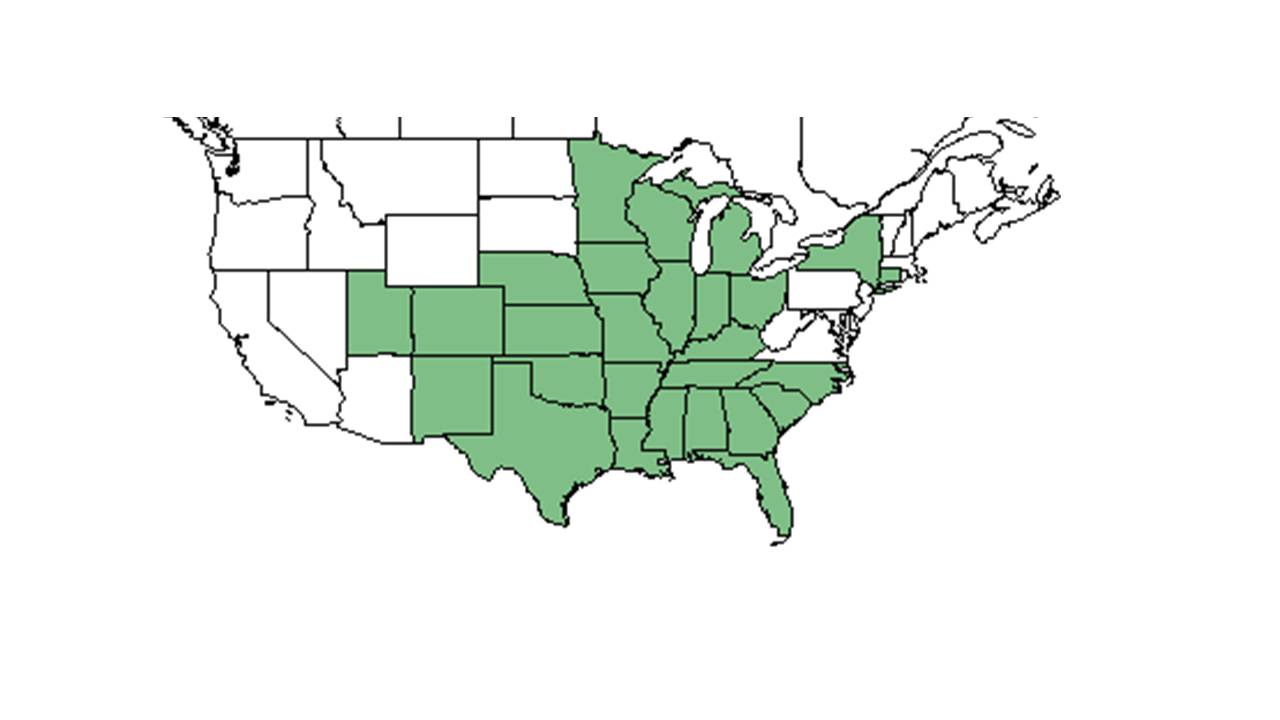
| Natural range of Salvia azurea from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Description
The common name is Azure Blue Sage. Azurea means "sky blue" which is referring to the color of the flower. Although, some individuals or even entire populations may have white colored flowers (Nelson 2005). Corolla is typically white or white with blue tint near the petal tips in northern Florida and southern Georgia (KMR).
Distribution
Is found locally and regionally abundant as a native tallgrass prairie perennial (in Kansas) (Damhoureyeh & Hartnett 1997).
Ecology
Habitat
Found in sandhills, flatwoods, and pine-oak-hickory woods (Nelson 2005).
Phenology
Blooms from September to November (Nelson 2005).
Seed dispersal
Seed bank and germination
Fire ecology
Pollination
Use by animals
Studies conducted with animals
In general (after experimenting the effects of bison and cattle on growth, reproduction, and abundances of Salvia azurea and other perennials), bison resulted in greater plant biomass and height, and lower number of stems per plant relative to plants in ungrazed sites, whereas cattle resulted in lower plant biomass, plant height, and number of stems per plant (Damhoureyeh & Hartnett 1997).
Diseases and parasites
Conservation and Management
Cultivation and restoration
References and notes
- Damhoureyeh, S. A. and D. C. Hartnett. 1997. Effects of bison and cattle on growth, reproduction, and abundances of five tallgrass prairie forbs. American Journal of Botany 84:1719-1728.
- Nelson, Gil. Atlantic Coastal Plain Wildflowers: A Field Guide to the Wildflowers of the Coastal Regions of Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and Northeastern Florida. Guilford, CT: FalconGuide, 2006. 54. Print.