Difference between revisions of "Paspalum floridanum"
(→Taxonomic Notes) |
(→Taxonomic Notes) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==Taxonomic Notes== | ==Taxonomic Notes== | ||
Synonyms: none<ref name=weakley/> | Synonyms: none<ref name=weakley/> | ||
| + | |||
Varieties: ''P. difforme'' Le Conte; ''P. floridanum'' Michaux; ''P. floridanum'' var. ''floridanum''; ''P. floridanum'' var. ''glabratum'' Engelmann ex Vasey; ''P. giganteum'' Baldwin ex Vasey<ref name=weakley/> | Varieties: ''P. difforme'' Le Conte; ''P. floridanum'' Michaux; ''P. floridanum'' var. ''floridanum''; ''P. floridanum'' var. ''glabratum'' Engelmann ex Vasey; ''P. giganteum'' Baldwin ex Vasey<ref name=weakley/> | ||
Revision as of 20:03, 16 June 2023
Common name: Florida paspalum,[1] big paspalum[2]
| Paspalum floridanum | |
|---|---|
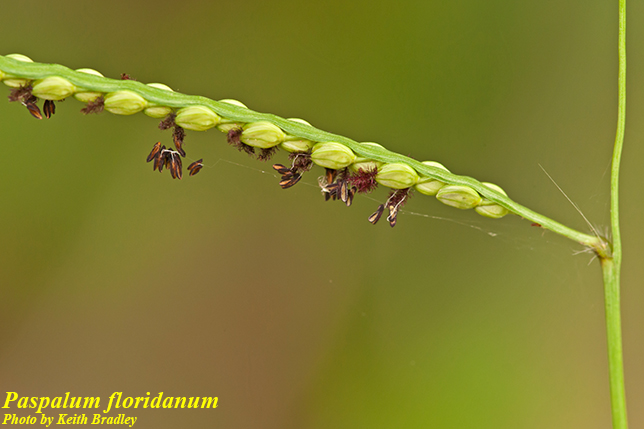

| |
| Photo by Keith Bradley hosted at Atlas of Florida Plants | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Liliopsida - Moncots |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Paspalum |
| Species: | P. floridianum |
| Binomial name | |
| Paspalum floridanum Michx. | |
| |
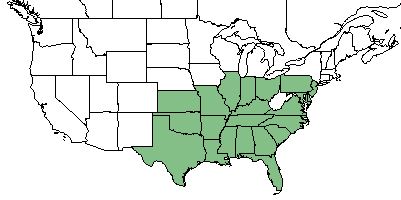
| Natural range of Paspalum floridanum from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Contents
Taxonomic Notes
Synonyms: none[2]
Varieties: P. difforme Le Conte; P. floridanum Michaux; P. floridanum var. floridanum; P. floridanum var. glabratum Engelmann ex Vasey; P. giganteum Baldwin ex Vasey[2]
Description
Paspalum floridanum is a coarse, perennial graminoid of the Poaceae family native to North America.[1] It grows from a stout rhizome. The culms are 5-15 dm tall with glabrous nodes and internodes. The ligules are membranous and 1-2 mm long, while the 2-7 racemes are racemous, ascending, and 3-13 cm long. The spikelets are suborbicular, ellipsoid, 3-4 mm long, and grow in 4 rows.[3]
Paspalum floridanum does not have specialized underground storage units apart from its rhizomes.[4] Diaz-Toribio and Putz (2021) recorded this species to have an non-structural carbohydrate concentration of 246 mg/g (ranking 17 out of 100 species studied).[4]
Distribution
P. floridanum ranges from New Jersey, Illinois, and Kansas, south to Florida and eastern Texas.[2]
Ecology
Habitat
P. floridanum proliferates in wet forests and pine savannas.[5] Specimens have been collected from disturbed roadside in pine-oak woodland, wet pine flatwoods and cypress depression, disturbed sandy field, longleaf pine stand, willow thicket, wiregrass savanna, pond-margin, marsh bank, mesic hammock, hardwood swamp, and sandy loam of hillside seepage.[6]
Phenology
P. floridanum flowers from August through October.[2]
Seed dispersal
P. floridanum is thought to be dispersed by gravity.[7]
Fire ecology
Populations of Paspalum floridanum have been known to persist through repeated annual burning.[8][9]
Herbivory and toxicology
Paspalum floridanum provides moderately palatable forage for cattle in the southeast in the spring and summer, but will decrease in abundance under heavy grazing.[10]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
P. floridanum is listed as extirpated by the Pennsylvania Department of Conservation and Natural Resources.[1]
Cultural use
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 USDA Plant Database https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=PAFL4
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "weakley" defined multiple times with different content Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "weakley" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ Radford, A. E., Ahles, H. E., & Bell, C. R. (1968). Manual of the vascular flora of the Carolinas. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Diaz-Toribio, M.H. and F. E. Putz 2021. Underground carbohydrate stores and storage organs in fire-maintained longleaf pine savannas in Florida, USA. American Journal of Botany 108: 432-442.
- ↑ Weakley, A. S. (2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, University of North Carolina Herbarium.
- ↑ URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2018. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, Cecil Slaughter, R.K. Godfrey, J.R> Burkhalter, D.W. Hall, R.A. Pursell, R.Kral, N.C. Henderson, Paul Redfearn, A.H. Curtiss, William Reese, Jean Wooten, A.F. Clewell, Gary Knight, David Hall, Dan Skean, F.C. Craighead, Ann Johnson, R. Komarek, R.A> Norris, J.S. McCorkle, Wilson Baker, T. MacClendon, Annie Achmidt, William Platt, John Nelson, Wade Biltoft. States and counties: Florida (Wakulla, Nassau, Flagler, Jefferson, Escambia, Leon, Gulf, Dixie, Volusia, Okaloosa, Walton, Jackson, Gadsden, Flageler, Holmes, Duval, Levy, Osceola, Calhoun) Georgia (Thomas, Grady) South Carolina (Berkeley)
- ↑ Kirkman, L. Katherine. Unpublished database of seed dispersal mode of plants found in Coastal Plain longleaf pine-grasslands of the Jones Ecological Research Center, Georgia.
- ↑ Glitzenstein, J. S., D. R. Streng, R. E. Masters, K. M. Robertson and S. M. Hermann 2012. Fire-frequency effects on vegetation in north Florida pinelands: Another look at the long-term Stoddard Fire Research Plots at Tall Timbers Research Station. Forest Ecology and Management 264: 197-209.
- ↑ Platt, W.J., R. Carter, G. Nelson, W. Baker, S. Hermann, J. Kane, L. Anderson, M. Smith, K. Robertson. 2021. Unpublished species list of Wade Tract old-growth longleaf pine savanna, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Byrd, Nathan A. (1980). "Forestland Grazing: A Guide For Service Foresters In The South." U.S. Department of Agriculture.