Difference between revisions of "Mitchella repens"
(→Cultural use) |
|||
| Line 47: | Line 47: | ||
==Cultural use== | ==Cultural use== | ||
| − | Historically, a tea from this plant was used in treating insomnia, water retention, and diarrhea, and it was | + | Historically, a tea from this plant was used in treating insomnia, water retention, and diarrhea, and it was an aid in childbirth.<ref> Korchmal, Arnold & Connie. 1973. A Guide to the Medicinal Plants of the United States. The New York Times Book Company, New York.</ref> |
==Photo Gallery== | ==Photo Gallery== | ||
Latest revision as of 08:32, 16 June 2023
| Mitchella repens | |
|---|---|
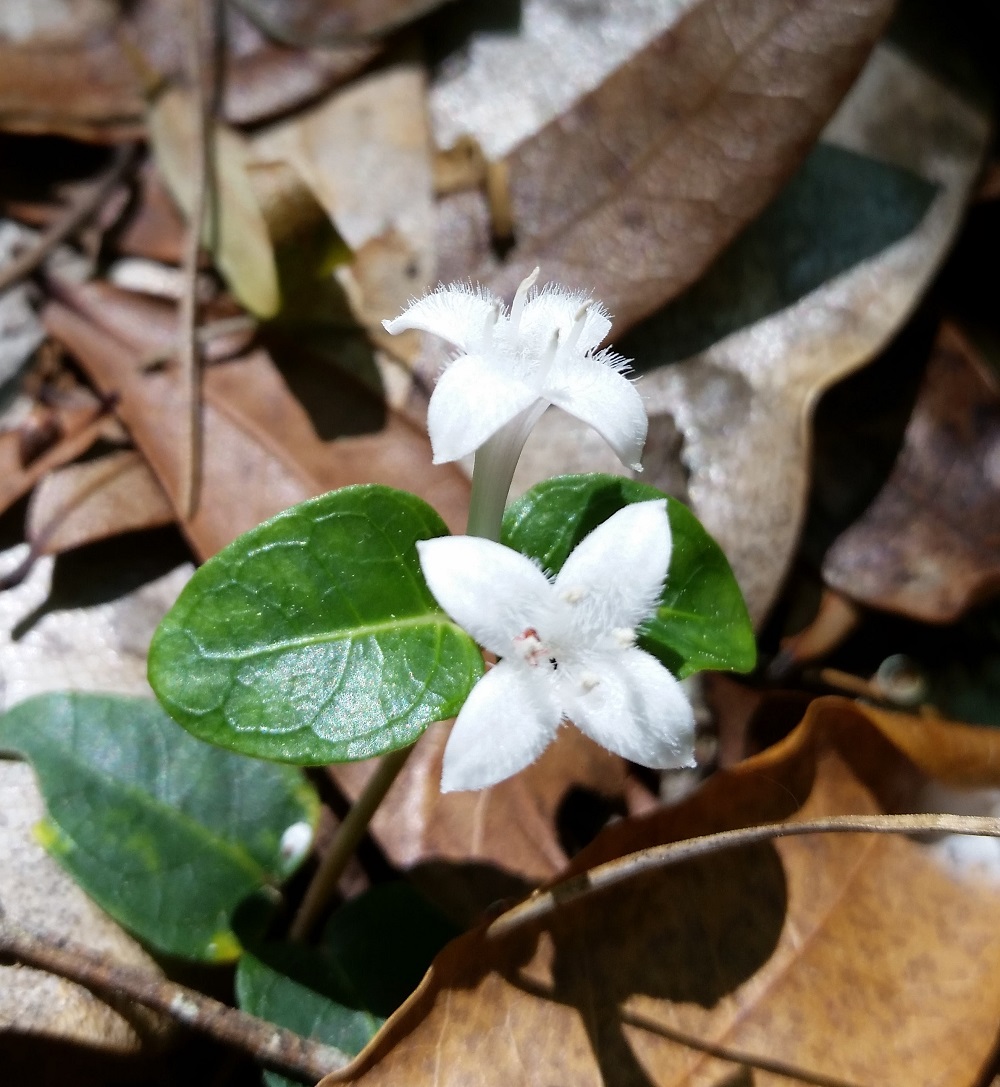

| |
| Photo by Katelin Pearson | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Division: | Magnoliophyta - Flowering plants |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida – Dicotyledons |
| Order: | Rubiales |
| Family: | Rubiaceae |
| Genus: | Mitchella |
| Species: | D. repens |
| Binomial name | |
| Mitchella repens L. | |
| |
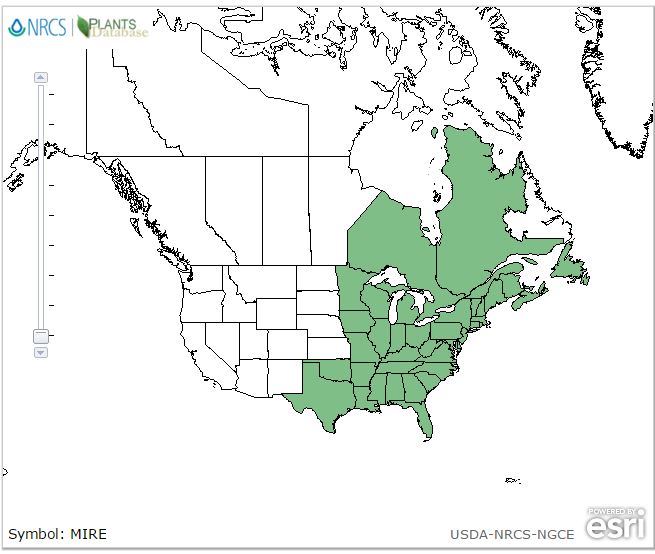
| Natural range of Mitchella repens from USDA NRCS Plants Database. | |
Common name: partridge-berry[1]
Contents
Taxonomic notes
Synonyms: none[1]
Varieties: none[1]
Description
Distribution
M. repens ranges from Novia Scotia, west to Minnesota, and south to central peninsular Florida and Texas. There are disjunct populations in Guatemala.[1]
Ecology
Habitat
M. repens has been found in mesic hardwoods, pinewoods, floodplains, streambanks, Beech-magnolia woods, live oak groves, bogs, and swamps.[2] It is also found in disturbed areas including along fire breaks, railroads, and roadsides.[2] Associated species: Pinus strobus, Acer saccharum, A. rubrum, Betula lenta, Fraxinus americana, Quercus rubra, Fagus grandifolia, Acer pensylvanicum, Caulophyllum thalictroides, Athyrium angustum, Tiarella cordifolia, and Polygonatum biflorum.[3] M. repens is found in deciduous and coniferous forests, streambanks, heath balds, maritime forests, rotten logs and hummocks, and in bottomlands or other wetland habitats. The plants in maritime forests are more robust than others and often have an ascending habit, the stems sometimes 20-30 cm tall.[1]
Phenology
M. repens is an evergreen, but flowers from May through July and flowers from June through July.[1]
Fire ecology
Populations of Mitchella repens have been known to persist through repeated annual burns.[4]
Conservation, cultivation, and restoration
Cultural use
Historically, a tea from this plant was used in treating insomnia, water retention, and diarrhea, and it was an aid in childbirth.[5]
Photo Gallery
References and notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Weakley, A.S. 2020. Flora of the Southeastern United States. Edition of 20 October 2020. University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, North Carolina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Florida State University Herbarium Database. URL: http://herbarium.bio.fsu.edu. Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Loran C. Anderson, K. Craddock Burks, Patricia Elliot, J. P. Gillespie, and R.K. Godfrey. States and counties: Florida: Jefferson, Levy, Leon, Liberty, and Wakulla.
- ↑ Brown University Herbarium accessed using Southeastern Regional Network of Expertise and Collections (SERNEC) data portal. URL: http://sernecportal.org/portal/collections/index.php Last accessed: June 2021. Collectors: Sophie Duncan, Andrew Pisaturo, and Timothy J. S. Whitfeld. States and Counties: Massachusetts: Berkshire.
- ↑ Robertson, K.M. Unpublished data collected from Pebble Hill Fire Plots, Pebble Hill Plantation, Thomasville, Georgia.
- ↑ Korchmal, Arnold & Connie. 1973. A Guide to the Medicinal Plants of the United States. The New York Times Book Company, New York.